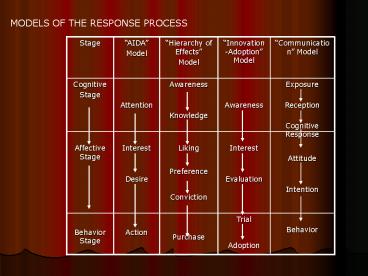
MODELS OF THE RESPONSE PROCESS - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 29
Title:
MODELS OF THE RESPONSE PROCESS
Description:
Public Relations - definitions The PR organization intelligently evaluates public attitudes, ... BreadTalk, Starbucks, Bintang Zero (vs MUI fatwa?) – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:137
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: MODELS OF THE RESPONSE PROCESS
1
MODELS OF THE RESPONSE PROCESS
2
The Differences between Advertising and PR
Advertising is the wind, PR is the
sun Advertising is spatial, PR is
linear Advertising uses the big bang, PR uses
the slow buildup Advertising is visual, PR is
verbal Advertising reaches everybody, PR Reaches
somebody Advertising is self-directed, PR is
other-directed Advertising dies, PR lives
Source The Fall of Advertising and The Rise of
PR, Al Ries Laura Ries
3
(cont.) The Differences between Advertising and PR
Advertising is expensive, PR is
inexpensive Advertising favors line extensions,
PR favors new brands Advertising likes old
names, PR likes new names Advertising is funny,
PR is serious Advertising is uncreative, PR is
creative Advertising is incredible, PR is
credible Advertising is brand maintenance, PR is
brand building
Source The Fall of Advertising and The Rise of
PR, Al Ries Laura Ries
4
Out of Side out of Mind You and PR
- A brief resume
- who you are,
- what did you do,
- why are you here.
- Contacting each others, email.
- Mailing list.
- Your opinion about PR as far as you know,
what do PR practitioner does?
5
Public Relations - definitions
- The PR organization intelligently evaluates
public attitudes, identifies the policies and
procedures of an individual or organization with
the public interest, and plans and executes a
program of action to earn public understanding
and acceptance. - PR is the management function that establishes
and maintains mutually beneficial relationships
between an organization and the publics on whom
its success or failure depends.
Session 1
6
Organizational Aspects of PR An Overview
- Creation of a corporate or executive image
- Support for executive presentations
- Media relations
- Integrated marketing
- Consumer relations in the marketplace
- Issue crisis management
- Reading assignment
- Managing for Reputation, in Running a PR
Department, p.11 - History Place of PR between Western and
Indonesian societies - Development of Public Relations, Fig.1.2 in
Strategic Program Planning for Effective Public
Relations Campaigns, p.4.
Session 1
7
Several Main Sectors
- PR is synonymous with REPUTATION. It is the
result of - what you do,
- what you say and
- what other say about you.
- No universal agreement on terminology and
divisions, but most practitioners look at the
discipline in several main sectors comprising - Financial and Corporate Communication
- Government Affairs
- Marketing Communication
- Internal Communication
- Community Relations
Session 1
8
Outline of Planning Factors
- We dont provide guidance on the planning of PR
programs, but simply to outline some of the
specific characteristics of each main sector
which will impact upon departmental management.
In each case, you need to look at - The PURPOSE of the activity
- The target PUBLICS or AUDIENCES
- Typical Program Content
- The Principal Interface (Working Partnership)
- Skills Needed
Session 1
9
Requirements for Success
- SKILLS
- Effective Writing
- Persuasive Speaking
- KNOWLEDGE
- In-depth knowledge of various media
- Understanding of management process
- Business, financial acumen
- ABILITIES
- Problem solver
- Decision maker
- Deft in handling people, generates confidence
- Assumes responsibility
- QUALITIES
- Stability and Common sense
- Drive and enthusiasm
- Wide-range interest and intellectual curiosity
- Good listener
- Tolerance for frustration
- Style
Session 1
Source Cutlip, Center and Broom, Effective
Public Relations, 8th Ed. .p53
10
Next Activities -- prepare
- Opening Bank Account -- What are the reasons of
your choice? - Creating a short PR campaign for gas company in
NTT (near East Timor). - The Gladiator compare the following, and who
among these characters, is the most successful
PR practitioner, and why? - Commodus
- Maximus
- The Roman Senate
- Lucilla
- Marcus Aurelius
- Senator Falco
- Senator Gracchus
- Proximo
Session 1
11
Adding Value Protecting the Image
- Justifying the Place of PR in Business Today
- How does PR serve Indonesian business,
government, and industry today? - How might it add value, raise the image or
improve the share price of Indonesian businesses?
Session 2
12
Can a Major Corp/Organ Afford to Ignore PR
realities?
- Think of examples of unpopular organizations
that have relied on PR in recent times - Exxon
- ABRI
- Nestle
- Union Carbide
- Ajinomoto
- Compare with BreadTalk, Starbucks, Bintang Zero
- (vs MUI fatwa?)
- What companies can you think of today that would
benefit from better more intelligent PR?
Session 2
13
PR and Crisis Management
- Reading Discussion Problem 9 When
associates disagree in handling an emergency, in
Public Relations Practices, p. 474. - What would be a typical Indonesian public
relations response to this kind of situation,
where a decision making executive is not
available?
Session 2
14
There is no golden rule.
- Management experts recommend plenty of guidelines
but very few rules. - The reason is that management is more about
getting the right results than about applying the
right rules. - What works is what matters.
- Management is not an all-purpose solutions and
foolproof formula (rigid, inflexible, immensely
strong under some situations but most brittle
under other situations). - Some guidelines work frequently under various
situations and for so many people that they are
known as golden guidelines. - There are not such things as golden rules.
15
Objectives do we have to solve this problem?
- The road to successful PR management is littered
with unnecessary data that justify considerations
for solution. - Subsequently, the PR question in most cases is
not can we solve this problem but rather Do we
have to solve this problem?
16
The guidelines
- There are no rules for management, however, there
are systematic approach, and some are known as
guidelines. - These guidelines are
- The Pareto Principle (may be modified)
- The systematic approach involving 8 stages
17
PARETO PRINCIPLE
- Vilfredo Pareto (Italian sociologist, economist
and engineer) provides a respectable academic
basis for the study of unequal distribution of
incomes. - Society is made up of an elite minority and a
large mass. - A small minority hold most of the power and own
an overwhelming percentage of the wealth.
18
PARETO PRINCIPLE
- The value of the Pareto Principle to a manager is
that it focuses attention on separating the
vital few from the trivial many. - One company finds that a small number of
establishments accounts for a high proportion of
total purchase. - Another observes that the majority of sales
derives from a minority of customers. - Identifying these vital few and concentrating
effort upon them is seen as the key to success.
19
PARETO PRINCIPLE
- These unequal patterns are traditionally
described as the 20/80 distribution rule. - Depending on the situations
- It may vary to 10/90, or 5/95.
- Thomas Alva Edison asserted that genius is 1
inspiration and 99 perspiration (1/99).
20
PARETO PRINCIPLE
- U.K. a more characteristic relationship 1/3 or
thereabouts. - Stone ) 25/75 ratio
- 25 of the customers place 75 of the orders.
- A writer 75 of the script is structure and 25
is words. - A PR team 25 of the staff thought up 75 of the
ideas. - 25 of what business did was responsible for 75
of the earnings. - Conversely in many firms, 75 of what the
business costs accounts for 25 of what it earns. - ) Norman Stone, How to Manage Public Relations
practical guidelines for effective PR
management.
21
PENTING
- It must not be understood, however, that once the
vital 25 is identified then we can totally
forget about the rest. - What is true is that the more managements work
can be done in the triangular area of the 25/75
golden guideline, the more effective it will be.
22
ANALYSIS and AUDIT
- A communications audit is A broad scale, loosely
structured research exercise, which examines the
effectiveness of communications within
organizations and between organizations and
groups outside. - A survey approach determines how well
communication being implemented with its members - Do members understand the objectives?
- Do they understand their role to achieve the
objectives? - How could communication be improved?
- A new manager may prompt the need of an audit to
learn how well the organization is communicating
with its members and to evaluate problems, such
as high turnover of staff or high rates of
absenteeism.
23
ANALYSIS and AUDIT
- Understanding an audit is not without risk.
Questions on how improvement in communication can
be made will cause expectation for improvement.
Failure to act on findings that need changes will
damage credibility of management. - An audit may also be necessary when existing
communication programs newsletters, etc. need
to be checked.
24
ANALYSIS and AUDIT
- It is essential.
- It is a professional opinion, based on judgment
applied to information (or evidential matter as
the accountants call it). - The judgment is not only on how this evidential
matter is to be interpreted, but what information
should be amazed. - More useful when a new managing director runs the
company, during an acquisition or merger.
25
ANALYSIS and AUDIT3 stages process
- Information gathering identifying and collecting
data and information on attitudes and trends, by
means of internal and external interviews against
a common topic menu. - Strategic analysis weighing all options and
choosing the most appropriate alternative
strategies to be articulated in a preferred
strategy matrix. - Communications program putting the chosen
option(s) into effect after spelling out a
communication strategy, program, action plan and
timetable. - ? See PR Toolkit!!
26
ANALYSIS and AUDIT
- This structured approach makes effective use of a
classic management technique known as SWOT
analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities,
Threats). - Other variant ADOPTS.
- ADOPTS taken to imply the idea of choice, of
picking up or taking over something that already
exists, and making it ones own.
27
AUDIT ADOPTS
- Advantages
- Disadvantages
- Opportunities
- Problems
- Time Factor
- Stakeholders
- 1,2 inward looking.
- 3,4 outward looking.
- 5 applies no matter which way you are looking.
- 6 is the reason for the other five.
28
STAKEHOLDERS
- Whatever other purposes an organization may have,
it must also have the purpose of serving the
interest of all its stakeholders that is, all
the people affecting the organization and
affected by it. Stakeholders are not necessarily
all of equal importance. Before an ADOPTS
analysis, it is first of all necessary to
identify and rank the stakeholders. - Who and where they are will depend on who and
where you are. There can be no standard list,
although some stakeholders e.g. customers are
bound to occur on pretty well every list. Only
you can decide who your stakeholders are, but
mote that your organization cannot choose its own
competitors. - ADOPTS analysis is not about program targeting or
getting coverage. It is about meeting the needs
of stakeholders.
29
STAKEHOLDERS
- Academics
- Agents
- Analysts
- Consumers
- Distributors
- Finance provider
- Government (central)
- Government (local)
- INVESTOR
- LOOBYISTS
- MANAGEMENT
- NEIGHBORING COMMUNITY
- CUSTOMERS
- POLICY COMMUNITY
- PRESSURE GROUPS
- SHARE HOLDERS
- SHOPFLOOR WORKERS
- SUPPLIERS