Adipostatic action of Leptin: Leptin signals fat-storage sufficiency
1 / 16
Title:
Adipostatic action of Leptin: Leptin signals fat-storage sufficiency
Description:
Adipostatic action of Leptin: Leptin signals fat-storage sufficiency leptin (Nature 404: 661, 2000) Leptin effect in the arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus: 1 ... –
Number of Views:405
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Adipostatic action of Leptin: Leptin signals fat-storage sufficiency
1
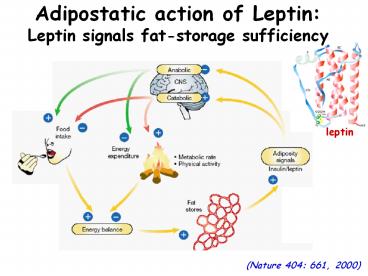
Adipostatic action of LeptinLeptin signals
fat-storage sufficiency
leptin
(Nature 404 661, 2000)
2
Leptin effect in the arcuate nucleus of the
hypothalamus 1. direct effect
(Science 30463-4, 2004)
3
Leptin effect in the arcuate nucleus of the
hypothalamus 2. neuroplasticity
(Science 30463-4, 2004)
4
Leptin effect in the arcuate nucleus of the
hypothalamus 3. Neuronal wiring during a
critical post-natal period body weight set
point?
(Science 30463-4, 2004)
5
Leptin in human obesity
- Circulating leptin levels are regulated by fat
mass, gender, fed-fasted state. - Although loss-of-function mutations in the leptin
or leptin-receptor genes have been described,
this is likely a very rare cause of human
obesity. - Common human obesity is associated with elevated
circulating leptin levels, which are believed to
represent a state of leptin resistance. - ? Leptin therapy trials are largely ineffective
in common human obesity
6
Leptin-induced signal transduction pathways
Overexpression of SOCS3 could be a mechanisms for
leptin resistance (Nat. Med. 10 734, 2004)
(Cell Biol. Int. 28 159, 2004)
7
Adiponectin
- - A complement-related protein secreted
specifically from adipose tissue, reaching high
circulating concentration (0.01 of total plasma
proteins).
Adiponectin trimeric form
- Low circulating adiponectin is found in patients
with - Central adiposity, Insulin resistance, Type 2
diabetes, Hypertriglyceridemiam, Hypertension and
Coronary artery disease. - Low adiponectin is an independent risk factor for
MI Adjusted RR 0.56 (0.32-0.99, plt0.02) for
highest Vs. lowest quintiles of adiponectin - (JAMA 291 1730, 2004)
8
Can low adiponectin be causatively linked to the
metabolic syndrome?
Adiponectin KO mice are insulin resistant...
(J. Biol. Chem. 27725863, 2002)
9
Adiponectin signals readiness for (safe) fat
handling?
Brain
Liver
Adipose tissue
Endothelium
Muscle
10
Resistin a putative insulin resistance factor
- Mediates resistance to insulin Discovered
through a search of genes down-regulated by
Thiazolidindiones. (Nature 409 307, 2001) - Controlling fat mass Shown as a secreted product
(termed ADSF) inhibiting adipogenesis. (JBC 276
11252, 2001) - An inflammation modulator Induced during lung
inflammation (FIZZ1). (EMBO-J 19 4046, 2000)
11
- A genetic loss-of-function approach
Science 203 1195-8, 2004))
Fasting plasma glucose
12
Suggested mechanism for resistin-mediated link
between obesity and diabetes
?
SOCS3
AMPK
(adopted from J. Intern. Med. 255 439-47,
2004 MCB 25 1569-75, 2005)
13
Open questions on the biology of resistin in
human obesity
- Human resistin is only 64 identical in sequence
to the mouse resistin. - It is expressed in low levels in fat tissue, and
highly in circulating and bone-marrow monocytes,
lung, and other tissues. ? is it really a human
adipokine? - Contradictory findings in humans on the
regulation of circulating resistin levels, though
recent studies seem to correlate higher levels
with insulin resistance and the metabolic
syndrome.
14
Fat tissue is a metabolic-endocrine organ. Both
hypo- and hyper-adiposity are pathological.
Metabolic abnormalities? Fat deposition
abnormalities? Endocrine abnormalities? The
combination?
Insulin sensitivity
normal
Fat mass / BMI
obesity
lipodystrophy
15
Does therapy correlate with changes in adipokine
secretion?
Metformin Insulin/SU TZDs Weight loss
? / ? ? (weight loss) ? ? / ? ? Leptin
? ? ? ? / ? Adiponectin
? ? ? / ? Resistin
16
Thank you!
Special thanks to Dr. Hannah Kanety and to Prof.
Nava Bashan for help in preparing this talk