4. Built-In Self Test (BIST): Periodical Off-Line Test on the Field
1 / 19
Title:
4. Built-In Self Test (BIST): Periodical Off-Line Test on the Field
Description:
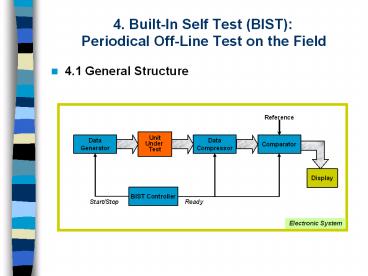
4. Built-In Self Test (BIST): Periodical Off-Line Test on the Field 4.1 General Structure Reference Unit Under Test Data Compressor Data Generator Comparator –
Number of Views:331
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: 4. Built-In Self Test (BIST): Periodical Off-Line Test on the Field
1
4. Built-In Self Test (BIST)Periodical
Off-Line Test on the Field
- 4.1 General Structure
2
4. Built-In Self Test (BIST)Periodical
Off-Line Test on the Field
- 4.2 Pattern Generator
General Structure of an n-1 Stage Linear
Feedback Shift Register (LFSR).
3
4. Built-In Self Test (BIST)Periodical
Off-Line Test on the Field
- 4.2 Pattern Generator
Example of a 4-Bit LFSR as a Pattern Generator.
Pseudorandom States Generated by the LFSR.
4
4. Built-In Self Test (BIST)Periodical
Off-Line Test on the Field
- 4.3 Signature Generator
Serial
r-Bit (Internal XOR) Signature Generator. The
content of the LFSR is the remainder of the
division operation.
5
4. Built-In Self Test (BIST)Periodical
Off-Line Test on the Field
- 4.3 Signature Generator
Serial
r-Bit (External XOR) Signature Generator. The
content of the LFSR is not the remainder of the
division operation.
6
4. Built-In Self Test (BIST)Periodical
Off-Line Test on the Field
- 4.3 Signature Generator
Serial
Example of a 4-Bit (External) Signature
Generator.
7
4. Built-In Self Test (BIST)Periodical
Off-Line Test on the Field
- 4.3 Signature Generator
Parallel
r-Bit (Internal XOR) Parallel Signature
Generator. The content of the LFSR is not the
remainder of the division operation.
r-Bit (External XOR) Parallel Signature
Generator. The content of the LFSR is the
remainder of the division operation.
8
4. Built-In Self Test (BIST)Periodical
Off-Line Test on the Field
- 4.3 Signature Generator
Problem When compacting results, there is a
probability of fault masking ! Probability of
failing to detect an error in the response
sequence
9
4. Built-In Self Test (BIST)Periodical
Off-Line Test on the Field
- 4.4 Example 8-bit-Length Datapath
10
4. Built-In Self Test (BIST)Periodical
Off-Line Test on the Field
- 4.4 Example 8-bit-Length Datapath
11
4. Built-In Self Test (BIST)Periodical
Off-Line Test on the Field
- 4.4 Example 8-bit-Length Datapath
Signature Generator (External XOR). Parallel
Pattern Generator (External XOR) all inputs Zs
equal to 0.
12
4. Built-In Self Test (BIST)Periodical
Off-Line Test on the Field
- 4.5 Built-In Logic Block Observer (BILBO)
Example of a BILBO structure.
13
4. Built-In Self Test (BIST)Periodical
Off-Line Test on the Field
- 4.5 Built-In Logic Block Observer (BILBO)
Modular Bus-Oriented Design with BILBO.
14
4. Built-In Self Test (BIST)Periodical
Off-Line Test on the Field
- 4.6 Transparent BIST for Memory Test
Transparent Built-In Self Test is a test
algorithm that is periodically executed on the
field in order to verify the integrity of large
amounts of critical data stored on mass memory
systems
15
4. Built-In Self Test (BIST)Periodical
Off-Line Test on the Field
- 4.6 Transparent BIST for Memory Test
- Main characteristics
- a) Minimum area overhead this approach is one of
the best choices found in the literature in terms
of area overhead and types of faults detected in
memory structures. E.g., authors claim an area
overhead of 1.2 due to the inclusion of
Transparent BIST in a 128Kbytes X 8bytes SRAM
(this value decreases as the RAM size increases).
16
4. Built-In Self Test (BIST)Periodical
Off-Line Test on the Field
- 4.6 Transparent BIST for Memory Test
- Main characteristics
- b) High capability of fault detection by
indicating the occurrence of stuck-at faults,
transition faults, coupling faults, decoder
faults and read/write logic faults.
17
4. Built-In Self Test (BIST)Periodical
Off-Line Test on the Field
- 4.6 Transparent BIST for Memory Test
- Main characteristics
- c) Short down times that are periodically
required to check the functionality of mass
memory systems used in real-time applications.
The Transparent BIST approach presents the
incomparable advantage of preserving the contents
of the RAM memory after testing. Thus, this
approach is very suitable for periodic testing
since we do not need to save the memory contents
before the test session and to restore them at
the end of this session.
18
4. Built-In Self Test (BIST)Periodical
Off-Line Test on the Field
- 4.6 Transparent BIST for Memory Test
19
4. Built-In Self Test (BIST)Periodical
Off-Line Test on the Field
- 4.6 Transparent BIST for Memory Test
- Note that the data read during the execution of
sequences S1 through S4 of the signature
prediction algorithm (Table 2) are sometimes
inverted in order to match the data read during
the execution of sequences S1 through S4 of the
Transparent BIST (Table 1).