Types of knowledge - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 13
Title:
Types of knowledge
Description:
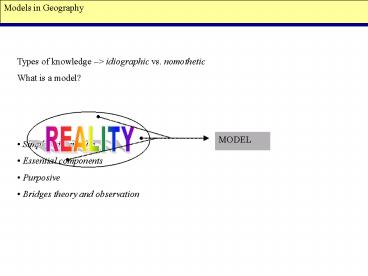
Models in Geography Types of knowledge idiographic vs. nomothetic What is a model? Simplified structure Essential components Purposive Bridges theory and observation – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:998
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Types of knowledge
1
- Types of knowledge gt idiographic vs. nomothetic
- What is a model?
- Simplified structure
- Essential components
- Purposive
- Bridges theory and observation
REALITY
MODEL
2
- Characteristics of models
- selective
- structured
- suggestive
- approximates reality
- reapplication (replication) to real world
conditions.
3
- Types of models
- Descriptive versus Normative
- Descriptive
- static (equilibrium)
- dynamic (historical)
- classificatory (taxonomic)
- theoretical, symbolic, conceptual, or mental
- mathematical deterministic v. stochastic
4
- Overview of geographic models
- locational relativity
- geometrical form
- 0th order points
- 1st order lines, networks
- 2nd order areas, states
- 3rd order surfaces, terrain.
- 4th order space-time
5
Three-Stage Model for the Analysis of Regional
Systems (Chorely and Haggett, 1967)
I. Identification
III. Integration
II. Form Differentiation
Stage
Static Static Dynamic
0,2 0
1 3 4
0-4
Dimension
Geographical Form
Analytical Techniques
Spatial Model
Heritage of Spatial Model
6
- Terminology
- dependent independent variables
- causality
- deterministic versus stochastic
- parameters, variables, parameter estimates
- macro-, micro-models
7
The big picture.
REALITY
MODEL
8
STAGE I
System Identification 0,2
City (polar axis) City region (boundaries)
Geographical Form
Numerical Taxonomy, Local residuals, Regional
analogues
Analytical Techniques
Regional hierarchies Formal, functional regions
Spatial Model
Decision theory (Psychology), Taxonomy (Biology),
Discriminant analysis (Statistics)
Heritage of Spatial Model
9
STAGE I
System Identification, 0
Cities, Settlements, Urban hierarchies
Geographical Form
Rank-size analysis, Nearest-neighbor analysis,
Quadrat analysis
Analytical Techniques
Central-place theory, Gravity models, Weberian
models, Economic base models
Spatial Model
Point set theory (Mathematics), Organization
models (Management), Packing theory (Mathematics)
Heritage of Spatial Model
10
STAGE II
Form Differentiation, 1 (Static)
Cities, Settlements, Urban hierarchies
Geographical Form
Rank-size analysis, Nearest-neighbor analysis,
Quadrat analysis
Analytical Techniques
Central-place theory, Gravity models, Weberian
models, Economic base models
Spatial Model
Point set theory (Mathematics), Organization
models (Management), Packing theory (Mathematics)
Heritage of Spatial Model
11
STAGE II
Form Differentiation, 3 (Static)
Urban fields, Density gradients, Land-use
intensity
Geographical Form
Trend-surface analysis, Harmonic analysis,
Fourier analysis
Analytical Techniques
Gravity models, Absorption models,
Intervening-opportunity models, Von Thunen
models, Potential models
Spatial Model
Least-effort models (Sociology), Minimum-energy
Potential models (Phys.), Game theory (Psych.)
Heritage of Spatial Model
12
STAGE II
Form Differentiation, 4 (Dynamic)
Innovation waves, Frontier movements, Sequent
occupance, Colonization
Geographical Form
Physical simulation, Monte Carlo models,
Markov-chain models, Cellular automata,
Agent-based simulation
Analytical Techniques
Diffusion models, Migration models, Colonization
models.
Spatial Model
Epidemic theory (Med.), Diffusion theory (Fluid
dynamics), Colonization succession models (Bot.)
Heritage of Spatial Model
13
STAGE III
System Integration, 0-4
Regional systems, Internal feedback,
Interregional systems, External feedbacks
Geographical Form
Matrix analysis, factor analysis, input-output
analysis, Interregional linear programming
Analytical Techniques
Regional climax models, Regional multipliers,
Growth poles
Spatial Model
General systems theory, Ecosystems (Biology),
Interregional trade theory multipliers (Econ.)
Heritage of Spatial Model