VTA dopamine - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 1
Title:
VTA dopamine
Description:
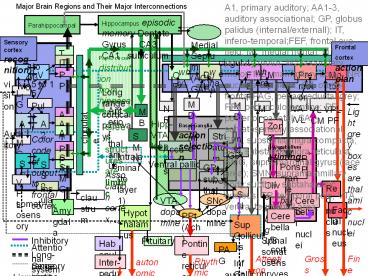
A1, primary auditory; AA1-3, auditory associational; GP, globus palidus (internal/externall); IT, infero-temporal;FEF, frontal eye field; Mf, medial frontal, M1 ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:63
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: VTA dopamine
1
A1, primary auditory AA1-3, auditory
associational GP, globus palidus
(internal/externall) IT, infero-temporalFEF,
frontal eye field Mf, medial frontal, M1,
primary motor, M2 secondary motor MB, mammilary
body NR, nucleus reuinions OF,
orbito-frontalPAG, periaqueductal grey PPt,
pedunculo-pontine PP, posterior parietal SA,
somatosensory associational SNc, substantia
nigra compacta SNr, substantia nigra reticulata
SMG, supra-marginal gyrus (face area) SMN,
supramammillary bodysubthal, subtahalamic
nucleus TP, temporal pole VTA, ventral
tegmental area
Major Brain Regions and Their Major
Interconnections
Hippocampus episodic memory Dentate Gyrus CA3
CA1 subiculum
Parahippocampal
Medial Septum (ACh/GABA
Sensory cortex recognition
Frontal cortex action plan
TP
Papez circuit distribution from hippocampus
cingulate
IT
3 to 4/3
where
what
why
Motor
V1
V2
DL
FEF
OF
Premotor
MF
PP
vision
5 to 1
6
Long range cortical pathways
LGN
5
MDm mid
Pulvinar
MDi mid
VA/VL
MDl
NR
VL VPL CM PF
Anterior thalamus
MB
Light grey boxes are thalamic nuclei
AA1
A1
AA2
A2
Basal Ganglia action selection
Hipp-VTA loop
Zona incerta
Green structures are limbic
cingulate
AA3
Audiitory
Striatum Matr/Stri
SMN
Color code of output to frontal cortex
MG
Cerebellum timing
PP
Accumbens
GPi
Intralaminar (to layer 1)
SA
PP
SS1
SS2
Pons granule parallel CS
Ventral pallidum
SMG
GPe
Association cortex,
subthal
VPL
Olive climbing US
Red nuclus
Insula
SNr
claustrum
VTA dopamine
Cerebellar nuclei
SNc dopamine
somatosensory
Facial nucleus
Amygdala
Hypothalamus Chiasmatic N
PPt (Ach)
Cerebellar cortex
Sup Colliculus Inf Colliculus
Inhibitory
Spinal somatosensoryvestibular
Pontine reticular formation
Habenula/ pineal
Pituitary
Attentional system
PAG
Long-range cortico-cortico tracts
Gross motor postural
Fine motor
Attention orienting movement
Rhythmic movement
autonomic
Inter-peduncular
Sensory input
auditory
Lisman,2005