Making and Delivering Value - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title: Making and Delivering Value
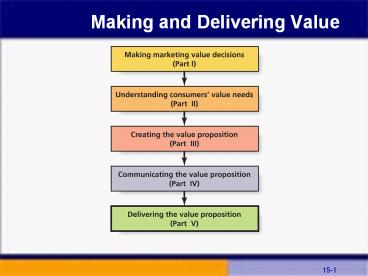
1
Making and Delivering Value
2
Generic Value Chain
3
Supply Chain Management
Software programs help to manage the supply chain
4
Supply Chain Management
- The supply chain includes all the firms that
engage in activities that are necessary to
convert raw materials into a good or service and
put it in the hands of the consumer or business
customer - Supply chain management is the management of
flows among the firms in a supply chain to
maximize total profitability
5
Supply Chain
6
What is a Distribution Channel?
- Series of firms or individuals that facilitate
the movement of a product from the producer to
the final customer - Direct
- Indirect
7
Functions of Distribution Channels
- Time, place, and ownership utilities
- Logistics functions
- Transportation and storage functions
- Efficiency creation
- Facilitating functions
- Repair and maintenance functions
- Risk-taking
- Communications and transaction functions
8
Supermarkets as Channel Members
9
Creating Efficiencies
- Breaking bulk - channel members purchase large
quantities from manufacturers and sell smaller
quantities to many different customers - Creating assortments - channel members provide a
variety of products in one location
10
Reducing Transactions
11
The Internet
- Even small firms with limited resources can enjoy
competitive advantages by making products
available to customers around the globe at a very
low cost - Disintermediation - process by which traditional
intermediaries are eliminated as companies
question the value added by layers in the
distribution channel
12
Types of Wholesaling Intermediaries
- Wholesaling intermediaries are firms that handle
the flow of products from the manufacturer to
retailer or business user - Independent
- Manufacturer owned
13
Independent Intermediaries
- Merchant wholesalers
- Full-service
- Limited-service
- Cash-and-carry wholesalers
- Truck jobbers
- Drop shippers
- Mail-order wholesalers
- Rack jobbers
- Merchandise Agents or Brokers
- Manufacturers agents
- Selling agents
- Commission merchants
- Merchandise brokers
14
Rack Jobbers
15
Wholesalers
16
Manufacturer-Owned Intermediaries
Sales Branches
Sales Offices
Manufacturers Showrooms
17
Independent Intermediaries
18
Types of Distribution Channels
19
Types of Distribution Channels
- Consumer channels
- Direct
- Manufacturer-retailer-consumer
- Manufacturer-wholesaler-retailer-consumer
- Business-to-business channels
- Direct
- Manufacturer-industrial distributor-business
customer
20
Consumer Channels
21
B2B Channels
22
Dual Distribution Systems
- Multiple channel usage
- Example
- pharmaceutical industry sells to hospitals,
clinics, and organizational customers directly
and to consumers indirectly through drug retailers
23
Dual Distribution Systems
24
Steps in Distribution Planning
25
Vertical System
26
Vertical Marketing Systems
Administered
Corporate
Contractual
27
Contractual VMS
Wholesaler-Sponsored
Retailer-Cooperative
Franchise Organizations
28
Distribution Intensity
Decision Factors Company, Customers, Channels,
Constraints, and Competition
Intensive, Exclusive, or Selective Distribution
29
Exclusive Distribution
30
Selective Distribution
31
Selective Distribution
32
Intensive Distribution
33
Managing the Channel
- Selecting channel partners
- Managing the channel of distribution
- Channel leader is the dominant firm that controls
the channel - Channel leaders have some form of power relative
to other members
Economic
Reward
Legitimate
34
Logistics
- Process of designing, managing, and improving the
movement of products through the supply chain - purchasing
- manufacturing
- storage
- transport
35
Logistics and Customer Satisfaction
- Traditionally, logistics was thought of as
physical distribution - order processing, warehousing, materials
handling, transportation, and inventory control - objective to deliver product at lowest cost
- Now, customers goals become the logistics
providers goals
36
Logistics Functions
Order Processing
Warehousing
Materials Handling
Functions
Transportation
Inventory Control
37
Transportation Mode Considerations
Dependability
Cost
Speed of Delivery
Accessibility
Capability
Traceability
38
Modes of Transportation
Water
Internet
Truck
Pipeline
Rail
Air
39
Water Transportation
Water transportation is best for large,
bulky, nonperishable goods