inside - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 45
Title:
inside
Description:
inside outside outside inside Model of ATP Synthase complex 3 3 Binding-change model for ATP synthase From Lehninger ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:114
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: inside
1
inside
outside
outside
inside
2
Which way do the electrons flow?
oxidized species ne- ? reduced species or
reduced species ? oxidized species ne-
2H 2e- ? H2 or H2 ? 2H 2e-
From Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
3
Electrochemistry review
- High Eo' indicates a strong tendency to be
reduced - Nernst equation ?Go' -nF?Eo'
- ?Eo' Eo'(acceptor) - Eo'(donor)
- Electrons are donated by the half reaction with
the more negative reduction potential and are
accepted by the reaction with the more positive
reduction potential - ?Eo' positive, ?Go' negative
- If a given reaction is written so the reverse is
true, then the ?Eo' will be a negative number and
?Go' will be positive
4
Why do the electrons flow through the electron
transport chain?
Most oxidizing Most reducing
From Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
5
From Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
6
From Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
7
The sequence of electron transport
8
Electron Transport
9
From Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
10
Complex I NADH to Coenzyme Q Complex II
Succinate to Coenzyme Q Complex IIICoenzyme Q to
Cytochrome c Complex IV Cytochrome c to O2
SDH is on the matrix side of the IMS
From Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
11
NADH dehydrogenase aka NADH-Coenzyme Q reductase
o
NADH 2e- donor FMN
1 or 2 e- donor Fe-S clusters 1 e- donor
- Estimated mass of this complex 850 kD
- Involves more than 30 polypeptide chains
- One molecule of FMN
- As many as 7 Fe-S clusters (2Fe-2S 4Fe-4S)
- Precise mechanism of this complex is unknown
From Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
12
Complex I
o
r
o
r
o
r
o
13
(No Transcript)
14
From Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
15
Complex III structure (half of the functional
dimer)
From Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
16
From Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
17
Electron Transport
From Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
18
Cytochrome c
19
From Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
20
(No Transcript)
21
Core of Complex IV is comprised of 3 subunits
Subunit II
CuA (2 Cu)
Subunit III
CuB
Subunit I
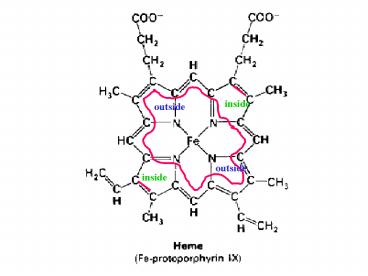
heme a, heme a3, and CuB
From Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
22
(No Transcript)
23
(No Transcript)
24
O2 4 H 4 cyt c (Fe2) ? 2 H2O 4 cyt c
(Fe3)
From Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
25
From Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
26
Determining the sequence of electron carriers
using inhibitors of electron transfer
Those that are reduced are blue.
Those that stay oxidized are pink
From Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
27
(No Transcript)
28
(No Transcript)
29
Coupling of electron transfer and ATP synthesis
in isolated mitochondria
Dinitrophenol causes dissipation of the proton
gradient and thus uncouples.
Inhibits ATP Synthase
30
Determining the sequence of electron carriers
using inhibitors of electron transfer
Those that are reduced are blue.
Those that stay oxidized are pink
From Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
31
(No Transcript)
32
(No Transcript)
33
The proton gradient drives the release of ATP
from the enzyme surface
ATP is stabilized by binding to enzyme. Free
energy required for its release is provided by
proton-motive force.
34
(No Transcript)
35
Model of ATP Synthase complex
????????????? ?3?3???
36
Binding-change model for ATP synthase
37
From Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
38
From Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
39
Regulation of the ATP-producing pathways
From Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
40
(No Transcript)
41
(No Transcript)
42
(No Transcript)
43
Model of ATP Synthase complex
????????????? ?3?3???
44
(No Transcript)
45
Website for animations of ATP Synthase
http//www.biologie.uni-osnabrueck.de/Biophysik/Ju
nge/overheads.html





![[PDF]❤️DOWNLOAD⚡️ Inside UFO 54-40 PowerPoint PPT Presentation](https://s3.amazonaws.com/images.powershow.com/10122535.th0.jpg?_=20240906024)















![❤️[READ]✔️ Surprise-Inside Cakes: Amazing Cakes for Every Occasion--with a Little Something Extr PowerPoint PPT Presentation](https://s3.amazonaws.com/images.powershow.com/10069707.th0.jpg?_=20240702047)
![❤️[READ]✔️ Surprise-Inside Cakes: Amazing Cakes for Every Occasion--with a Little Something Extr PowerPoint PPT Presentation](https://s3.amazonaws.com/images.powershow.com/10068429.th0.jpg?_=20240702092)






![get [PDF] Download Reflections on Critical Museology: Inside and Outside Museums (Museums in Focus) PowerPoint PPT Presentation](https://s3.amazonaws.com/images.powershow.com/10050526.th0.jpg?_=202406071211)
