Darwin - 5 Points
1 / 41
Title: Darwin - 5 Points
1
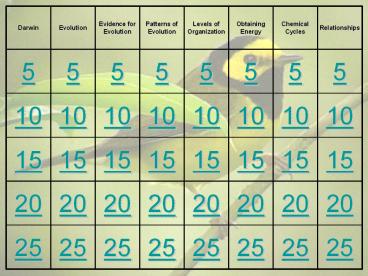
Darwin Evolution Evidence for Evolution Patterns of Evolution Levels of Organization Obtaining Energy Chemical Cycles Relationships
5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5
10 10 10 10 10 10 10 10
15 15 15 15 15 15 15 15
20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20
25 25 25 25 25 25 25 25
2
Darwin - 5 Points
- The individual who published On the Origin of
Species in 1859, the father of natural selection - Who is Charles Darwin?
Menu
3
Darwin - 10 Points
- The sailing ship on which Darwin traveled for
five years - What is The Beagle?
Menu
4
Darwin - 15 Points
- The location off the coast of South America where
Darwin collected finches - What is the Galapagos Islands?
Menu
5
Darwin - 20 Points
- The theory stating that organisms change over
time - What is evolution?
Menu
6
Darwin - 25 Points
- The scientist who hypothesized that acquired
characteristics can be passed on to offspring - Who is Jean-Baptiste LaMarck?
Menu
7
Evolution - 5 Points
- A method used by humans to choose and breed
individuals of a species with the most desirable
traits - What is selective breeding (artificial selection)?
Menu
8
Evolution - 10 Points
- The ability of an organism to survive and
reproduce in an environment and thereby pass on
their genes to their offspring - What is fitness?
Menu
9
Evolution - 15 Points
- An inherited trait that increases an organisms
chance of survival in a particular environment - What is an adaptation?
Menu
10
Evolution - 20 Points
- The process by which individuals with variations
that make them best-suited to their environment
reproduce more than individuals without those
variations - What is natural selection or survival of the
fittest?
Menu
11
Evolution - 25 Points
- Individuals do not evolve, but these do
- What are species?
Menu
12
Evidence for Evolution 5 Points
- The preserved remnant or trace of an organism
from a past ecological age - What is a fossil?
Menu
13
Evidence for Evolution 10 Points
- The study of development of fertilized eggs that
shows similar patterns across species - What is embryology?
Menu
14
Evidence for Evolution 15 Points
- Structures that have similar structures but
different functions, such as a whale fin and a
bat wing - What are homologous structures?
Menu
15
Evidence for Evolution 20 Points
- Structures that have different structures but
similar functions, like bird wings and bee wings - What are analogous structures?
Menu
16
Evidence for Evolution 25 Points
- Structures that served a purpose in an ancestral
organism but do not have a useful function in the
modern organism, like the appendix in humans - What are vestigial structures?
Menu
17
Patterns of Evolution - 5 Points
- The process by which many organisms become
extinct at the same time - What is mass extinction?
Menu
18
Patterns of Evolution - 10 Points
- A pattern of evolution in which two species
interact closely and change in response to each
other over time - What is coevolution?
Menu
19
Patterns of Evolution - 15 Points
- A pattern of evolution in which one species
evolves into several different species - What is divergent evolution?
Menu
20
Patterns of Evolution - 20 Points
- A pattern of evolution in which different species
evolve to have similar structures as a result of
living in similar environments - What is convergent evolution?
Menu
21
Patterns of Evolution - 25 Points
- The formation of a new species
- What is speciation?
Menu
22
Levels of Organization - 5 Points
- An individual of a species
- What is an organism?
Menu
23
Levels of Organization 10 Points
- A group of individuals of the same species living
in the same area at the same time - What is a population?
Menu
24
Levels of Organization 15 Points
- Different populations interacting and living in
the same area - What is a community?
Menu
25
Levels of Organization 20 Points
- All of the living species in an area interacting
with the nonliving environment - What is an ecosystem?
Menu
26
Levels of Organization 25 Points
- The broadest level of organization that extends
from Earths atmosphere to below the ocean floor - What is a biosphere?
Menu
27
Obtaining Energy 5 Points
- An organism that uses sunlight or chemicals to
make organic compounds - What is a producer or autotroph?
Menu
28
Obtaining Energy 10 Points
- An organism that must consume other plants or
animals to obtain energy - What is a heterotroph or consumer?
Menu
29
Obtaining Energy 15 Points
- An organism that gains energy by eating only
plants - What is a herbivore or primary consumer?
Menu
30
Obtaining Energy 20 Points
- An organism that gains energy by eating only
animals - What is a carnivore or secondary consumer?
Menu
31
Obtaining Energy 25 Points
- An organism that gains energy by breaking down
dead plants and animals - What is a decomposer?
Menu
32
Chemical Cycles - 5 Points
- The chemical cycle that involves evaporation,
transpiration, condensation, and precipitation - What is the water cycle?
Menu
33
Chemical Cycles - 10 Points
- The chemical cycle that involves photosynthesis,
respiration, decomposition, and combustion - What is the carbon cycle?
Menu
34
Chemical Cycles - 15 Points
- The chemical cycle that involves nitrogen
fixation, nitrification, and denitrification - What is the nitrogen cycle?
Menu
35
Chemical Cycles - 20 Points
- The chemical cycle that involves a chemical
released gradually from rocks and is needed to
make DNA and RNA - What is the phosphorus cycle?
Menu
36
Chemical Cycles - 25 Points
- The process by which chemicals, elements, and
matter are cycled between organisms and parts of
the biosphere - What is biogeochemical cycling?
Menu
37
Relationships - 5 Points
- The biological and physical role of an organism
in its environment - What is a niche?
Menu
38
Relationships - 10 Points
- Interaction in which one animal kills and
consumes another organism - What is predation or predator-prey?
Menu
39
Relationships - 15 Points
- A relationship in which two organisms live
together and both benefit - What is mutualism?
Menu
40
Relationships - 20 Points
- A relationship in which one organism lives in or
on another organism and harms it by taking
nutrient from it - What is parasitism?
Menu
41
Relationships - 25 Points
- A relationship in which one organism benefits
from another organism and that organism is
neither harmed nor helped - What is commensalism?
Menu







![Reading Quiz [10 points]](https://s3.amazonaws.com/images.powershow.com/P1252428283tCThs.th0.jpg?_=20151021093)






















