Semiconductor Manufacturing - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 31
Title:
Semiconductor Manufacturing
Description:
* * * * * * * * * Photolithographic Process J. Phys. Org. Chem. 2000, 13, 767. Coat Exposure Develop Strip Etch Photoresist Substrate Mask h Positive Negative ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:608
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Semiconductor Manufacturing
1
Semiconductor Manufacturing
2
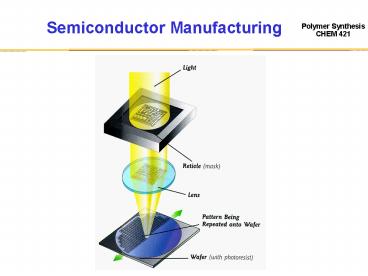
Photolithographic Process
Coat
Mask
h?
Exposure
Negative
Positive
Develop
Etch
Strip
J. Phys. Org. Chem. 2000, 13, 767.
3
Important Properties of a Photoresist
- Resist Thickness (etch resistance)
- Solubility for deposition/development
- Wettability
- Lithographic performance
- Sensitivity, contrast
- Transparency(more important for 193 nm and
beyond)
4
Optics of Imaging
R resolution smallest feature size R ? ? / NA
- ? is the wavelength of light
- NA is the numerical aperture (a function of the
optics)
5
G- and I-line Resists
- Novolac resin
- Base-soluble positive resist (TMAH)
- Variety of structures and MWs
- Diazonapthaquinone (DNQ)
- Photoactive compound (Wolfe Rearrangement)
- Inhibits base-dissolution of novolac
h? -N2
6
Transitions in Optical Lithography
365 nm
248 nm
7
Chemical Amplification
- DUV exposure generates catalytic amount of acid
from a photoacid generator (PAG) - 1-2 min PEB to trigger deprotection
- Catalytic chain length is extremely long
- About 500 - 1000 carbonate cleavages per proton
J. Phys. Org. Chem. 2000, 13, 767. Acc. Chem Res.
1994, 27, 150.
8
Challenges with Chemical Amplification
- What if trace amounts of base (NMP solvent) was
found in the air in a FAB?
- Catalyst susceptible to poisoning by atmospheric
bases
Levinson, Harry J. Principles of Lithography.
SPIE Press, 2001.
9
Model for Constructing a Chemically Amplified
Resist
Backbone
Etch Barrier
Acidic Group
Protecting Group
Levinson, Harry J. Principles of Lithography.
SPIE Press, 2001.
10
Low- and High-Activation Energy Chemically
Amplified Resists
- Copolymer of hydroxy styrene and t-BOC
protected hydroxy styrene - Good hydrophilic/hydrophobic balance
- IBMs Apex Resist
- Low activation energy, very reactive
- PAB below Tg
- IBMs ESCAP Resist
- High activation energy, lower reactivity
- Allows for high T bake
- PAB above Tg
- removes stress
- removes residual solvent
- higher density films
- Low diffusion of PAG
11
Transitions in Optical Lithography
365 nm
248 nm
193 nm
12
Absorption of Resins
1.8 1.5 1.1 0.8 0.5 0.3 0.1
Poly(p-hydroxy styrene)
Absorption Coefficient (micron-1)
190 200 210 220 230 240 250 260
270 280 290 300 310 320 330 340
350
Wavelength (nm)
13
Design Criteria for 193 nm Resists
- Optical transparency
- Hydrophilicity
- High Tg (130-170 C)
- Good etch resistance
- Easily blocked hydroxyl group
14
Photoresists for 193 nm Lithography
- Extremely transparent at 193 nm
- Tunable composition
- Property diversity
- Good hydrophilicity
- High activation energy cleavable group
- Easily synthesized
- But poor etch resistance
15
Photoresists for 193 nm Lithography
16
Photoresists for 193 nm Lithography
ATT / Lucent / Agere
17
Transitions in Optical Lithography
365 nm
248 nm
193 nm
Absorptionat 157 nm??!!
157 nm
18
Polymeric Materials Outlook for 157 nm Resist
Design
Polymer Absorbtion Coefficient (157 nm) Thickness (nm) (OD 0.4)
Poly(hydrosilsesquioxane) 0.06 6667
Poly(tetrafluoroethylene) 0.70 571
Poly(tetrafluoroethylene-co-ethylene) (30 TFE) 1.34 298
Poly(dimethylsiloxane) 1.61 248
Poly(vinyl alcohol) 4.16 96
Poly(methyl methacrylate) 5.69 70
Poly(norbornene) 6.10 66
Polystyrene 6.20 64
Poly(p-hydroxystyrene) 6.25 64
Poly(p-chlorostyrene) 10.15 39
R. R. Kunz et.al. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B 17(6),
Nov/Dec 1999
19
Emerging 157 nm Resist Platforms
H. Ito, G. Walraff, et. al. IBM
20
Poly(TFE-co-NB-co-EVE)
EVE is Ester Vinyl Ether
21
Poly(TFE-co-NB-co-EVE)
TFE(mol ) NB(mol ) FG(mol ) Tg(C) Mn /MWD Liq. CO2Sol. Abs._at_ 157 nm
50 38 50 59 0 3 125 126 ?? 3300 /1.47 Insol. Insol. 1.4 1.38
40 55 5 115 3600 /1.32 Insol. 1.29
41 52 7 92 3500 /1.42 Insol. To be determined
22
157/193 nm PhotoresistsTeflon AF as Backbone
Material
- Due to its amorphous structure and rigid
backbone, Teflon AF has unique properties that
are desirable in a photoresist backbone
Tetrafluoroethylene(TFE)
2,2-Bis(trifluoromethyl)-4,5-difluoro-1,3-dioxole
(PDD)
Teflon AF
Advantages Challenges
very low absorbance cost of PDD monomer
rigid structure (good etch resistance) need functional monomer without significantly increasing absorbance
forms smooth films
broad range of Tgs available
23
157/193 nm PhotoresistsAbsorbance at 157 nm and
193 nm
Absorbance a10(mm-1)
Sample 157.6 (nm) 193 (nm)
Teflon AF 0.154 0.004
CO2 Synthesized Copolymer 0.153 0.019
- Values for Teflon AF and the CO2 synthesized
copolymer are very close and well below 1 mm-1 at
157 nm - Values at 193 nm are slightly different but both
extremely low
24
157/193 nm PhotoresistsTeflon AF as Backbone
Material
- In order for a Teflon AF derivative to serve as
a photoresist, a functionalized monomer that can
be cleaved by an acid must be incorporated into
the backbone - After cleaving with a photo acid generator (PAG)
the functional monomer will exhibit different
solubility properties from unexposed regions
Protected Functional Monomer
PAG
Acidic Group
25
157/193 nm Photoresists EVE/PDD/TFE
Plackett-Burman Experiment Scheme
- Chose to explore Ester Vinyl Ether (EVE) as a
prototype for potential EVE derived functional
monomers - Conducted a Plackett-Burman experimental scheme
varying five parameters (composition, initiator
concentration, temperature, pressure and reaction
time) to study the reaction of EVE with PDD and
TFE
poly(TFE-co-PDD-co-EVE)
Exp. EVE/PDD/TFE (mol ) Initiator (mol ) Temp (oC) Pressure (psi) Rxn Time (hr)
1 7/73/20 1 15 3500 4
2 25/55/20 0.2 35 3500 4
3 25/55/20 0.2 15 3500 0.5
4 25/55/20 1 15 1500 4
5 7/73/20 1 35 3500 0.5
6 7/73/20 0.2 35 1500 4
7 25/55/20 1 35 1500 0.5
8 7/73/20 0.2 15 1500 0.5
26
157/193 nm Photoresists EVE/TFE/PDD - Absorbance
VASE Absorbance a10(mm-1) Measurements
Sample Composition(mol ) 157.6(nm) 193(nm)
REH-004 7/73/20 EVE/PDD/TFE (Charged) 0.128 0.013
REH-013 12/59/29EVE/PDD/TFE 0.252 0.011
REH-005 18/54/28EVE/PDD/TFE 0.574 0.017
- Absorbance values at 157 nm increase with
increasing EVE content but still remain well
below 1 (mm-1) - Values at 193 nm are very low and vary only
slightly
27
Bilayer Resist Processes
Levinson, Harry J. Principles of Lithography.
SPIE Press, 2001.
28
Top-Surface Imaging
Levinson, Harry J. Principles of Lithography.
SPIE Press, 2001.
29
Comparisons
Single LayerResist
Top-SurfaceImaged Resist
Bi-LayerResist
Spin coating
Spin coating
1st Spin coating
2nd Spin coating
NegativeExposure
Expose
Expose
Silylate
Develop
Develop
O2-RIE
O2-RIE
30
Transitions in Optical Lithography
365 nm
248 nm
?
193 nm
E-beam
EUV
157 nm
X-ray
31
More Reading Materials
Advances in Patterning Materials for 193 nm
Immersion Lithography Chem. Rev. 2010, 110,
321360 Organic imaging materials a view of
the future J. Phys. Org. Chem. 2000, 13, 767