Supplemental Figure 1: Genomic region targeted in lemurs
Title:
Supplemental Figure 1: Genomic region targeted in lemurs
Description:
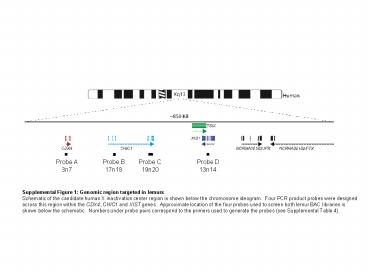
Probe A 3n7 Probe B 17n18 Probe C 19n20 Probe D 13n14 Supplemental Figure 1: Genomic region targeted in lemurs Schematic of the candidate human X inactivation center ... –
Number of Views:81
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Supplemental Figure 1: Genomic region targeted in lemurs
1
Probe A 3n7
Probe B 17n18
Probe C 19n20
Probe D 13n14
Supplemental Figure 1 Genomic region targeted in
lemurs Schematic of the candidate human X
inactivation center region is shown below the
chromosome ideogram. Four PCR product probes
were designed across this region within the CDX4,
CHIC1 and XIST genes. Approximate location of
the four probes used to screen both lemur BAC
libraries is shown below the schematic. Numbers
under probe pairs correspond to the primers used
to generate the probes (see Supplemental Table 4).
2
Human
a)
Black lemur
Human
b)
Ringtailed lemur
Supplemental Figure 2 The human XIC region is
co-linear with both lemur XIC regions A miropeats
analysis (Parsons, J.D., Brenner, S. and Bishop,
M.J. 1992. Clustering cDNA Sequences, Comput.
Applic. Biosci., 8, 461-466) comparing the
repeatmasked human XIC sequence to the
repeatmasked a) black lemur and b) ringtailed
lemur XIC sequences, indicate that these
sequences are co-linear. Black lines connecting
the sequences correspond to regions of sequence
similarity.
3
See attached File SuppFig3.pdf
Supplemental Figure 3 Repeat content and
alignment across the XIC Each page shows a 50kb
window across the XIC region, enlarged from
Figure 2. Colored bars representing sequence for
each species are shown on a separate horizontal
line. The red bars below the sequence indicate
repetitive regions identified by RepeatMasker,
which are color-coded depending on the repeat
identified. Three ancestrally reconstructed
sequences (HCO, CCOR and Primate Ancestor)
are indicated for comparison of which regions
have been gained or lost throughout primate
evolution. Below the aligned sequences are the
exonic regions annotated based on the human and
mouse gene structures.
4
Supplemental Figure 4 Ancestrally reconstructed
XIC confidence plots Confidence level for the a)
structure and b) structure and predicted sequence
for each pair of ancestral sequences. This
representation indicates surface variation in 2D
from one position into another and one ancestor
into another. If the two ancestors have the same
value for an interval, the color surface of that
interval will be homogeneous and will correspond
to the color labeled. If the two have different
values, then a proportion will be computed for
how far the two values are and each ancestor will
have a colored portion. See Diallo, A.B.,
Makarenkov, V., and Blanchette, M. 2010.
Ancestors 1.0 a web server for ancestral
sequence reconstruction. Bioinformatics 26
130-131.
5
Supplemental Figure 5 Ancestrally reconstructed
XIST confidence plot Confidence level for the
structure and predicted sequence for each pair of
ancestral sequences across the XIST locus. This
representation indicates surface variation in 2D
from one position into another and one ancestor
into another. If the two ancestors have the same
value for an interval, the color surface of that
interval will be homogeneous and will correspond
to the color labeled. If the two have different
values, then a proportion will be computed for
how far the two values are and each ancestor will
have a colored portion.
6
Consensus
Human
Chimpanzee
Orangutan
Macaque
Marmoset
Ringtailed Lemur
Black Lemur
Ancestral Primate
Mouse
Dog
Cow
Consensus
Human
Chimpanzee
Orangutan
Macaque
Marmoset
Ringtailed Lemur
Black Lemur
Ancestral Primate
Mouse
Dog
Cow
Consensus
Human
Chimpanzee
Orangutan
Macaque
Marmoset
Ringtailed Lemur
Black Lemur
Ancestral Primate
Mouse
Dog
Cow
Supplemental Figure 6 Alignment of XIST/Xist A
repeat The human sequence corresponding to the A
repeat (hg19) chrX73071816-73072238 was
submitted to the program Tandem Repeats Finder
V4.03 to identify A repeat monomers. Annotations
using blue blocks were made in Geneious V5.3.4
(Biomatters Ltd) based on the human tandem repeat
monomers identified within the larger XIST/Xist
alignment. The orthologous regions in all other
species are shown below.
7
Consensus
Human
Chimpanzee
Orangutan
Macaque
Marmoset
Ringtailed Lemur
Black Lemur
Ancestral Primate
Mouse
Dog
Cow
Consensus
Human
Chimpanzee
Orangutan
Macaque
Marmoset
Ringtailed Lemur
Black Lemur
Ancestral Primate
Mouse
Dog
Cow
Consensus
Human
Chimpanzee
Orangutan
Macaque
Marmoset
Ringtailed Lemur
Black Lemur
Ancestral Primate
Mouse
Dog
Cow
Supplemental Figure 7 Primate XIST D Repeat
Alignment The human sequence corresponding to
(hg19) chrX73063470-73066838 was submitted to
the program Tandem Repeats Finder to identify D
repeat monomers. Annotations of purple blocks
were made in Geneious V5.3.4 (Biomatters, Ltd)
based on the human tandem repeat monomers
identified within the larger XIST/Xist alignment.
The orthologous regions in all other species are
shown below. The mouse, dog and cow D repeat
regions have little sequence orthology to the
primate D repeat regions and are therefore not
shown in this short alignment window.
8
Black Lemur Genomic, PR00254
Ringtailed Genomic, AG7100
Ringtailed Lemur BAC LB223D18
Black Lemur Genomic, PR00254
Human BAC R11-216E22
Black Lemur BAC CH16H20
Black Lemur BACCH16H20
Bioline Hyperladder I
Bioline Hyperladder II
Human Genomic
Human Genomic
Negative control
10kb
6kb
3kb
2kb
2kb
1kb
1kb
0.8kb
0.2kb
Supplemental Figure 8 The XIST D repeat is
absent from the black lemur genome. Primers
were designed flanking the D repeat in XIST exon
1. To the left of the Hyperladders, a PCR assay
was set up using primers JH617 and JH619 designed
to regions flanking the human D repeat sequence
in XIST exon 1. The human product was expected
to be 3.3kb. The human XIST containing BAC
(216E22) amplifies a robust product at just over
3kb with a slight ladder of products below, while
the black lemur XIST BAC (16H20) amplifies a
product around 200bp. To the right of the
Hyperladders, a PCR assay was set up using
primers designed to conserved sequences in both
lemurs (JH616 and JH619). The ringtailed lemur
XIST BAC (223D18) produces a ladder while the
black lemur genomic and black lemur BAC both
produce a 200bp product indicating the absence of
the intervening D repeat sequence in the black
lemur.
9
Supplemental Figure 9 Black and ringtailed
lemurs have an inactive X chromosome a) Male
black lemur image above b) DAPI stained metaphase
chromosomes hybridized with an X
chromosome-specific black lemur BAC (CH273-16H20)
and c) immunostained with an antibody specific to
H3K4me2. d) Female black lemur image above e)
DAPI stained metaphase chromosomes hybridized
with an X chromosome-specific black lemur BAC
(CH273-16H20) and f) immunostained with an
antibody specific to H3K4me2. g) Male ringtailed
lemur image above h) DAPI stained metaphase
chromosomes hybridized with an X
chromosome-specific ringtailed lemur BAC
(LB2-223D18) and i) immunostained with an
antibody specific to H3K4me2. j) Female
ringtailed lemur image above k) DAPI stained
metaphase chromosomes hybridized with an X
chromosome-specific ringtailed lemur BAC
(LB2-223D18) and l) immunostained with an
antibody specific to H3K4me2. These experiments
indicate that female black and ringtailed lemurs
have one X chromosome devoid of H3K4me2 staining,
suggestive of an inactive X chromosome.
10
Supplemental Table 1 XIST/Xist A Repeat Region Comparisons Supplemental Table 1 XIST/Xist A Repeat Region Comparisons Supplemental Table 1 XIST/Xist A Repeat Region Comparisons
Species Compared to Human Size ID to Human (423bp)
Chimpanzee 425bp 99.3
Orangutan 421bp 97.4
Rhesus Macaque 422bp 96.2
Common Marmoset 420bp 93.5
Ringtailed Lemur 429bp 82.6
Black Lemur 429bp 82.6
Ancestral Primate 443bp 90.7
Mouse 421bp 57.1
Dog 431bp 52.4
Cow 469bp 62.6
Alignments were compared using Geneious V5.3.4
11
Supplemental Table 2 Comparison of XIST D Repeat Monomer Consensus Sequences Supplemental Table 2 Comparison of XIST D Repeat Monomer Consensus Sequences Supplemental Table 2 Comparison of XIST D Repeat Monomer Consensus Sequences Supplemental Table 2 Comparison of XIST D Repeat Monomer Consensus Sequences
Species compared to Human Size (bp) ID to Human (290bp) Blast2 prog used
Chimpanzee 293 94.8 blastn
Orangutan 288 94.5 blastn
Rhesus Macaque 289 97.2 blastn
Marmoset 290 98.3 blastn
Ringtailed Lemur 284 87.6 blastn
Black Lemur absent n/a n/a
Ancestral Primate 185 94.6 blastn
Consensus Sequences Generated by Tandem Repeats Finder (TRF) v 4.03 Consensus Sequences Generated by Tandem Repeats Finder (TRF) v 4.03 Consensus Sequences Generated by Tandem Repeats Finder (TRF) v 4.03 Consensus Sequences Generated by Tandem Repeats Finder (TRF) v 4.03
12
Supplemental Table 3 Lemur Cell Line Information Supplemental Table 3 Lemur Cell Line Information Supplemental Table 3 Lemur Cell Line Information
Common Name Species Source Catalog Number Sex
Black lemur Eulemur macaco macaco IPBIR PR00254 Female
Black lemur Eulemur macaco macaco IPBIR PR00266 Male
Ringtailed lemur Lemur catta Coriell AG07100 Female
Ringtailed lemur Lemur catta IPBIR PR00119 Male
Coquerel's Sifaka Propithecus vereauxi coquereli IPBIR PR00227 Female
Coquerel's Sifaka Propithecus verreauxi coquereli IPBIR PR00302 Male
Gray Mouse lemur Microcebus murinus IPBIR PR00275 Female
Aye-aye Daubentonia madagascariensis IPBIR PR1134 Female
Aye-aye Daubentonia madagascariensis IPBIR PR1017 Male
Coriell Cell Repositories (http//locus.umdnj.edu/) Coriell Cell Repositories (http//locus.umdnj.edu/) Coriell Cell Repositories (http//locus.umdnj.edu/)
IPBIR is the Integrated Primate Biomaterials and Information Resource (http//ccr.coriell.org/Sections/Collections/IPBIR/?SsId18) IPBIR is the Integrated Primate Biomaterials and Information Resource (http//ccr.coriell.org/Sections/Collections/IPBIR/?SsId18) IPBIR is the Integrated Primate Biomaterials and Information Resource (http//ccr.coriell.org/Sections/Collections/IPBIR/?SsId18) IPBIR is the Integrated Primate Biomaterials and Information Resource (http//ccr.coriell.org/Sections/Collections/IPBIR/?SsId18) IPBIR is the Integrated Primate Biomaterials and Information Resource (http//ccr.coriell.org/Sections/Collections/IPBIR/?SsId18) IPBIR is the Integrated Primate Biomaterials and Information Resource (http//ccr.coriell.org/Sections/Collections/IPBIR/?SsId18) IPBIR is the Integrated Primate Biomaterials and Information Resource (http//ccr.coriell.org/Sections/Collections/IPBIR/?SsId18)
13
(No Transcript)