DCI 2.1 - Stoichiometry - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
DCI 2.1 - Stoichiometry
Description:
DCI 2.1 - Stoichiometry An atom of R weighs 1 mass unit (mu), G weighs 3 mass units (mu) and B weighs 2 mass units (mu). i) the mass of BG would be: ____mu – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:48
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: DCI 2.1 - Stoichiometry
1
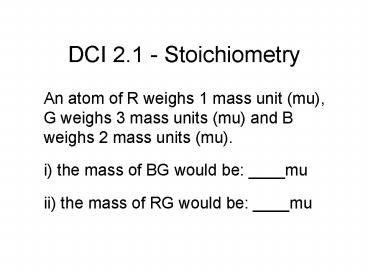
DCI 2.1 - Stoichiometry
- An atom of R weighs 1 mass unit (mu), G weighs 3
mass units (mu) and B weighs 2 mass units (mu). - i) the mass of BG would be ____mu
- ii) the mass of RG would be ____mu
2
(No Transcript)
3
(No Transcript)
4
(No Transcript)
5
(No Transcript)
6
(No Transcript)
7
Compare the results of Tables II and III.
- What is the relationship between the amounts of
substances in each of the two tables? - How is the set of numbers for the initial
amounts related to the balanced chemical
equation?
8
Compare the results of Tables II and III.
- How is the set of numbers for the final amounts
related to the balanced chemical equation? - How is the set of numbers for the change
amounts related to the balanced chemical
equation? - Do the DCI on page 25 in the activities manual.
9
1. Consider the following chemical equation
describing the reaction between sulfur dioxide
and oxygen. 2SO2 (g) O2(g) ?
2SO3(g)
- Given the following container as representing the
final condition - Which of the containers (--gt) best represents the
initial conditions?
10
1. Consider the following chemical equation
describing the reaction between sulfur dioxide
and oxygen. 2SO2 (g) O2(g) ?
2SO3(g)
- Given the following container as representing the
final condition - Which of the containers (--gt) best represents the
initial conditions?
11
2. Which of the following changes can be
described by the balanced chemical
equation, A2(g) 3B2(g) ? 2AB3(g)
- A) I only
- B) II only
- C) I and III
- D) II and III
- E) I, II and III
12
3. Consider the following chemical equation
describing the reaction between sulfur dioxide
and oxygen. 2SO2 (g) O2(g) ?
2SO3(g)
- Given the following container as representing the
final condition - Which of the containers (--gt) best represents the
initial conditions?
13
3. Which of the chemical equations best
describes the reaction represented by the
containers below? Consider the container label
initial condition as the reactants before any
reaction has occurred, and the container labeled
final condition as the same container after the
reaction has reached completion.
- A) 4A2(g) 7B2(g) ? 4AB3(g)
- B) 4A2(g) 7B2(g) ? 4AB3(g) 1B2(g) 2A2(g)
- C) A2(g) 3B2(g) ? 2AB3(g)
- D) 4A2(g) 6B2(g) ? 4AB3(g)
- E) A2(g) B2(g) ? AB3(g)
14
4. Consider the hypothetical reaction2G R --gt
G2RIf G has a mass 3 mu and R 2 muWhat is
in excess and what is the limiting reagent if 6
mu of R and 6 mu of G are mixed?
- A. R is the excess reagent and G is the limiting
reagent - B. G is the excess reagent and R is the limiting
reagent - C. both R and G are excess reagents
- D. both R and G are limiting reagents