Synthesis of 2 - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title: Synthesis of 2
1
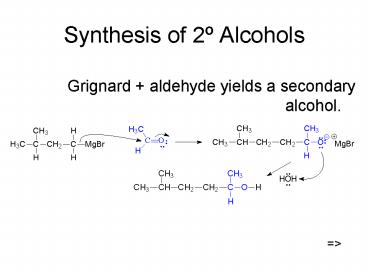
Synthesis of 2º Alcohols
- Grignard aldehyde yields a secondary alcohol.
2
Synthesis of 3º Alcohols
- Grignard ketone yields a tertiary alcohol.
3
How would you synthesize
4
Grignard Reactions with Acid Chlorides and
Esters
- Use two moles of Grignard reagent.
- The product is a tertiary alcohol with two
identical alkyl groups. - Reaction with one mole of Grignard reagent
produces a ketone intermediate, which reacts with
the second mole of Grignard reagent.
gt
5
Grignard Acid Chloride (1)
- Grignard attacks the carbonyl.
- Chloride ion leaves.
Ketone intermediate gt
6
Grignard and Ester (1)
- Grignard attacks the carbonyl.
- Alkoxide ion leaves! ? !
Ketone intermediate gt
7
Second step of reaction
- Second mole of Grignard reacts with the ketone
intermediate to form an alkoxide ion. - Alkoxide ion is protonated with dilute acid.
8
How would you synthesize...
- Using an acid chloride or ester.
9
Grignard Reagent Ethylene Oxide
- Epoxides are unusually reactive ethers.
- Product is a 1º alcohol with 2 additional carbons.
10
Limitations of Grignard
- No water or other acidic protons like O-H, N-H,
S-H, or -CC-H. Grignard reagent is destroyed,
becomes an alkane. - No other electrophilic multiple bonds, like CN,
CN, SO, or NO.
gt
11
Reduction of Carbonyl
- Reduction of aldehyde yields 1º alcohol.
- Reduction of ketone yields 2º alcohol.
- Reagents
- Sodium borohydride, NaBH4
- Lithium aluminum hydride, LiAlH4
- Raney nickel
gt
12
Sodium Borohydride
- Hydride ion, H-, attacks the carbonyl carbon,
forming an alkoxide ion. - Then the alkoxide ion is protonated by dilute
acid. - Only reacts with carbonyl of aldehyde or ketone,
not with carbonyls of esters or carboxylic acids.
13
Lithium Aluminum Hydride
- Stronger reducing agent than sodium borohydride,
but dangerous to work with. - Converts esters and acids to 1º alcohols.
14
Comparison of Reducing Agents
- LiAlH4 is stronger.
- LiAlH4 reduces more stable compounds which are
resistant to reduction.
gt
15
Catalytic Hydrogenation
- Add H2 with Raney nickel catalyst.
- Also reduces any CC bonds.
16
Thiols (Mercaptans)
- Sulfur analogues of alcohols, -SH.
- Named by adding -thiol to alkane name.
- The -SH group is called mercapto.
- Complex with heavy metals Hg, As, Au.
- More acidic than alcohols, react with NaOH to
form thiolate ion. - Stinks!
gt
17
Thiol Synthesis
- Use a large excess of sodium hydrosulfide with
unhindered alkyl halide to prevent dialkylation
to R-S-R.
18
Thiol Oxidation
- Easily oxidized to disulfides, an important
feature of protein structure.
- Vigorous oxidation with KMnO4, HNO3, or NaOCl,
produces sulfonic acids.