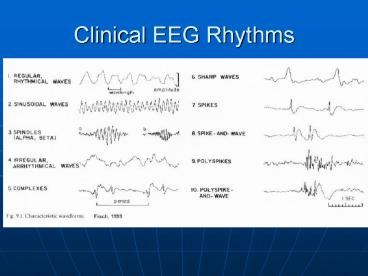
Clinical EEG Rhythms - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 26
Title:
Clinical EEG Rhythms
Description:
Clinical EEG Rhythms Eyes Closed Baseline Eyes Open Baseline Spectral Plot is one way to present frequency and amplitude information start here Brain Maps ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:121
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Clinical EEG Rhythms
1
Clinical EEG Rhythms
2
Eyes Closed Baseline
3
Eyes Open Baseline
4
Spectral Plot is one way to present frequency and
amplitude information start here
5
Brain Maps
6
Topometrics
7
Frontal Slowing during Math Abnormal
8
Numbers for Statistical Analysis
- Quantitative EEG (QEEG)
9
Some of the signal properties that can be
quantified
10
Also between-site differences
- Absolute Magnitude
- Relative Magnitude
- Asymmetry
- Coherence
11
- Attenuation of temporal lobes
- Beta1SMR
- Waveform morphology
- Bipolar
- Non-specific arousal
12
Role of Topography and Timing
13
(No Transcript)
14
Waveform morphology
15
- Power vs Magnitude
- Squared microvolts vs microvolts
16
Cross-spectral analysis
Coherence estimates phase consistency
Comodulation estimates magnitude consistency
between signals at each specified
frequency Coh average normalized
cross-spectrum amplitude2 Comod average
normalized cross-product amplitude Coh
range from 0.0 to 1.0 Comod range from -1.0
to 1.0 Confusing point Tukey called coherency
the square root of coherence
17
- Signals are coherent when phase relationship is
stable
- Signals are comodulated (or hypermodulated) when
magnitude relationship is stable
18
Comodulation
19
Each site compared to all others ( itself) in
each head
20
An individuals data (rho) and his/her
statistical (z) comparison to the database
21
MTBI patient Rage Disorder
22
Hypermodulation
23
Hypomodulation
24
Current EEG Applications
- CLINICAL
- Epilepsy (1930s)
- Sleep (1940s)
- Patient monitoring, anaesthesia
- Head injury assessment
- Neurological assessment (AEP, ERP)
- Neurotherapy
- Psychiatric assessment
25
Current EEG Applications
- SCIENTIFIC
- Attention
- Workload
- Circadian rhythms
- Cognition
- Learning Memory
- Neuroimaging co-registration
26
Future EEG Assessment
- Subtype clinical conditions
- Monitor attentional state
- Lie Detection
- Parole disposition