South Asia - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 32
Title: South Asia
1
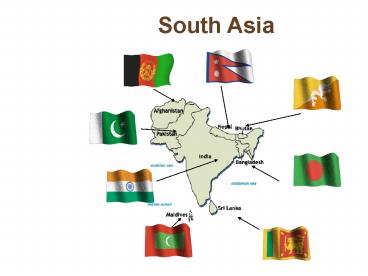
South Asia
2
Vocabulary
- HinduismFaith originated in India based on the
belief that a persons karma (behavior in life)
impacts their reincarnation (rebirth) in their
next life. - BuddhismFaith originating in Nepal, based on the
teachings of Siddhartha Gautama, including belief
that following the Eight-Fold Path and the Four
Noble Truths will lead to Nirvana (absolute
peace)
3
Vocabulary
- Sikhism Monotheistic faith originating in the
Punjab region of India, includes valuing equality - Castehereditary social group ranked by degree of
spiritual purity along with occupation and/or
economic position - Under- represented populationsPeople groups with
limited political and economic power - Outsourcing- to obtain goods or services from an
outside source.
4
South Asia Countries
5
Mt. Everest is the worlds tallest mountain. It
is located in the Himalayan mountain range.
Mt. Everest?
Himalayas
6
Indo-Gangetic plainone of the Worlds most
fertile farming regions. This area contains
3/5ths of Indias population.
Indo-Gangetic Plain
7
Great Indian (Thar) Desert
- The Thar Desert forms a natural boundary between
India and Pakistan. - The ninth largest desert in the world.
lt Right Thar!
8
Thar Desert or Great Indian Desert
Thar Desert
The Great Indian Desert 200 - 1500 feet in
elevation. up to 127ºF in July
9
Rivers of South Asia
Brahmaputra R
Indus R
Ganges R
10
Ganges Delta
- It is the world's largest delta, and empties into
the Bay of Bengal. - It is also one of the most fertile regions in the
world, thus earning the nickname The Green Delta.
11
Indus River
- The Indus River valley civilization began around
2500 BC and was the largest of the worlds first
civilization
12
Mata Ganga (Mother Ganges) Is the sacred river
for Hindus
13
Benefits of the rivers..
- The rivers provide crucial irrigation for
agricultural, cheap transportation, potable water
lands and ..
14
Regions of South Asia- Refer back to our lesson
on Kashmir
Kashmir
Punjab
15
Other important water features
Arabian Sea
Bay ofBengal
Indian Ocean
16
South Asia is about ½ the size of the continental
US with a population of over 1 billion. This
represents 20 of the worlds population.
17
The Indian Subcontinent
- A subcontinent is a large land mass that is
smaller than a continent.
18
FYI How were these mountains formed?
19
Hindu Kush protects South Asia by forming a
barrier between Pakistan and Afghanistan
Hindu Kush
20
Khyber pass Why is this feature important?? This
should be a review!!!
21
The Eastern and Western Ghats prevent moisture
from reaching the Deccan Plateau
Eastern Ghats
Deccan Plateau
Western Ghats
22
Indo-Gangetic plainone of the Worlds most
fertile farming regions. This area contains
3/5ths of Indias population.
Indo-Gangetic Plain
23
Atolls
- Islands that are the low lying tops of submerged
volcanoes, surrounded by coral reefs and shallow
lagoons.
24
Resources of South Asia
25
Why is South Asia not able to capitalize on its
natural resources?
26
Natural Hazards
- Monsoons are seasonal winds. Summer monsoons
bring strong storms from the south and winter
monsoons bring cold air from the north.
27
Cyclones in Bangladesh Look at the map. What
explains why they are so destructive in
Bangladesh?
28
Partition of India
- The partition of India was set forth in
the Indian Independence Act 1947 and resulted in
the dissolution of the British Raj. It resulted
in a struggle between the new states of India and
Pakistan and displaced up to 12.5 million people
in the former British Indian Empire, with
estimates of loss of life varying from several
hundred thousand to a million. The violent nature
of the partition created an atmosphere of mutual
hostility and suspicion between India and
Pakistan that plagues their relationship to this
day.
29
Green Revolution
- The world's worst recorded food disaster happened
in 1943 in British-ruled India. Known as the
Bengal Famine, an estimated four million people
died of hunger that year alone in India. - The term "Green Revolution" is applied to the
period from 1967 to 1978. - Agricultural Scientists introduced new farming
techniques that yielded higher grains. - The green revolution has lead to increased
yields.
30
Climate
31
How does the physical geography help and hurt
Bangladesh and Nepal?
- Mountains provide tourism and protection for
Nepal, but make it difficult for industry and
trade
32
Bangladesh- The Geography helps the country for
industries such as ship dismantling but hurts the
country because of Cyclone destruction.