Electric Field - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 12
Title:
Electric Field
Description:
Electric Field Chapter Objectives know the definition of, and basic uses for, the electric field. be able to sketch electric field lines. know how electrostatic ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:119
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Electric Field
1
Electric Field
2
Chapter Objectives
- know the definition of, and basic uses for, the
electric field. - be able to sketch electric field lines.
- know how electrostatic shielding works.
3
Van der Graff
A Van De Graff Machine is a mechanical-electric
device that produces high voltage at safe levels
of electric current. The parts include -A
hollow metal ball -vertical pipe with rubber
conveyor belt inside -hollow metal box with and
electric motor inside Van De Graaff machines in
the classroom are smaller than the machines in
the laboratory. How does VDG work? -the roller(s)
become charges through contact with the belt. One
roller sucks charge from the metal comb and onto
the belt. The other roller pushes electric charge
from the belt onto the comb. As the belt is
moving charge is sucked in at one end and puts
charge out at the other end.
4
Van Der Graaff
- http//amasci.com/emotor/icepail.html
- http//amasci.com/emotor/belt.html
5
Electrophorus
6
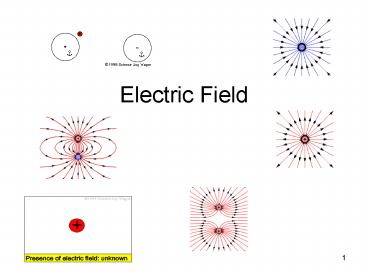
ELECTRIC FIELD
- Michael Faraday developed the concept of
electric field. - TEST CHARGE is used to map out the field
resulting from any collection of charges its
very small in charge and size not being able to
move the source from its location, or affect the
electric field being measured. - A charge creates an electric field around it in
all directions. - If a 2nd charge is placed at some point in the
field, the second charge interacts with the field
at that point. - The ELECTRIC FIELD is a vector quantity that
relates the FORCE exerted on a test charge to the
SIZE of the TEST CHARGE. - The RATIO of FORCE to TEST CHARGE is independent
of the size of the test charge. - The length of the arrow shows the strength of the
field. - The vector quantity of the electric field DOES
NOT DEPEND ON THE TEST CHARGE, but depends only
on the SOURCE CHARGE, and the LOCATION of that
specific point. - DIRECTION of the electric field is the direction
of the force on a positive test charge. - http//www3.ltu.edu/s_schneider/physlets/main/efi
eld.shtml
7
Picturing Electric Field
- Electric Field Lines are the lines to which the
ELECTRIC FIELD VECTORS are TANGENT at any point. - The STRENGTH of the electric field is indicated
by the SPACING between the LINES. - The field is STRONGER where the LINES are CLOSE
together. - It is WEAKER where the lines are SPACED FARTHER
APART. - Electric fields exist in three dimensions.
- The electric field vectors created by a POSITIVE
SOURCE point/extend RADIALLY OUTWARD. - The electric field vectors created by a NEGATIVE
SOURCE point/extend RADIALLY INWARD. - When there are two or more charges, the net field
is the VECTOR SUM of the fields resulting from
THE INDIVIDUAL CHARGES. - For more than one charge, the lines become curved
and they always LEAVE the POSITIVE charge and
ENTER A NEGATIVE charge.
8
Dipole
- Here is the dipole once again, this time with the
electric field lines drawn instead of the field
vectors. If you drag the red test charge to any
point on a field line, you will observe that the
force on the charge is a vector tangent to the
field line. This is because the force is parallel
to the field vector at the location of the
particle, and the field vector is in turn tangent
to the field line. - http//www.phas.ucalgary.ca/physlets/fieldlines.ht
m
9
Links
- http//kingfish.coastal.edu/physics/physlets/EFiel
d/ - Electric field 14 animations
- http//www.edumedia.fr/m195-p1-electric-field.html
- Prof. Selman Hershfield University of Florida
- http//www.phys.ufl.edu/phy3054/elecstat/efield/W
elcome.html
10
Problems
- Two charges, Q1 and Q2, are situated on a
horizontal line at a distance a. The charge on
Q1 is (-5q) and it is at the origin. The charge
on Q2 is (2q) and it is a distance to the right
of Q1. Find the point where the net electric
field is zero. - 2. (Problem 68)
- The electric field at the surface of the
Earth is about 100 N/C and points toward the
center of the Earth. What is the magnitude of the
charge on the Earth? - 3. (Problem 69)
- Calculate the size and direction of the
electric field required if an electron of mass
9.1 x 10-31 kg and electric charge -1.6 x 10 -19
C placed if it is to experience a force that will
exactly cancel its weight at the Earths surface.
11
Problems
- 4. A positively charged oil drop whose mass
is 10-15 kg remains stationary under the
influence of the earths gravitational field and
a uniform electric field of 6.1 x 10 4 N/C. find
the magnitude of the charge on the oil drop. - 5. A proton of mass 1/6 x 10-26kg and
electric charge1/6 x 10-19 C acquires a speed of
12 X 104 m/s when it is accelerated by an
electric field, E. find its magnitude. - 6. A small positively charged object falls
from rest in a uniform downward electric field,
so that the force on the object is given by FqE,
where E is a constant. Write an equation giving
its speed, v, after it has fallen a time t, in
terms of its mass, m, and charge, q. Gravity may
be disregarded.
12
Problems
- A test charge of 1C is placed halfway between a
charge of 5C and a charge of 3C that are 20 m
apart. Find the magnitude and direction of the
force on the test charge. - 8. A proton and an electron are separated
by a distance equal to the radius of a hydrogen
atom (5 x 10 -10 m). If the charge of the
electron is 1.6 x 10 19 C , find the
attractive force between them.