VoIP Basics - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
VoIP Basics
Description:
VoIP BASICS VoIP lets you make toll bypass voice and fax calls over existing IP data networks instead of the public switched telephone network (PSTN). – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:87
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: VoIP Basics
1
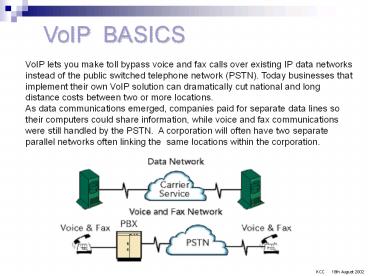
VoIP BASICS
VoIP lets you make toll bypass voice and fax
calls over existing IP data networks instead of
the public switched telephone network (PSTN).
Today businesses that implement their own VoIP
solution can dramatically cut national and long
distance costs between two or more locations. As
data communications emerged, companies paid for
separate data lines so their computers could
share information, while voice and fax
communications were still handled by the PSTN. A
corporation will often have two separate parallel
networks often linking the same locations within
the corporation.
KCC 18th August 2002
2
VoIP BASICS
Today, with the rapid adoption of IP, we now
have a far reaching, low-cost transport mechanism
that can support both voice and data. A VoIP
solution integrates seamlessly into the data
network and operates alongside existing PBXs, or
other phone equipment, to simply extend voice
capabilities to remote locations without the cost
of managing parallel networks.
KCC 18th August 2002
3
VoIP Corporate Example
Central Site
PSTN
Standard Analogue, PBX and IP Phones
and Softphones
IP
Standard PBX Phones
Remote Agents
Branch Agents
PSTN
SoftPhone
IP Phones
Remote dial-up home workers
KCC 18th August 2002
4
Why VoIP ?
- Save on toll bypass voice calls
- Converge and integrate company networks
- - Integrate where and when needed
- - Voice, Video Data over an IP network
- - Reduce the costs of managing parallel networks
- - Reduce the costs of moves and changes
- Centralize or distribute data/voice
architectures - - Add features where they are needed
- Migrate to VoIP as the business grows and updates
- Provide multi-vendor interoperability
- Provide more features and application integration
- Telecommunications Act of 1996 (telco
offerings) - - Deregulation of the Bell networks
- - Open the competitive markets for Service
Providers - i.e. ? More voice/data managed services available
KCC 18th August 2002
5
Questions ?
- What benefits will VoIP provide to this
corporation ? - Can we show a good ROI ?
- Make use of legacy systems
- Migrate to VoIP where it makes sense
- Whats the right architecture ?
- - Partial integration
- Centralized/distributed or both
- How do we ? - Provide better than PSTN
QoS - Provide Admission Control - Secure
the signaling media - Meet all the
regulatory requirements
KCC 18th August 2002