Interpersonal Styles - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 14
Title: Interpersonal Styles
1
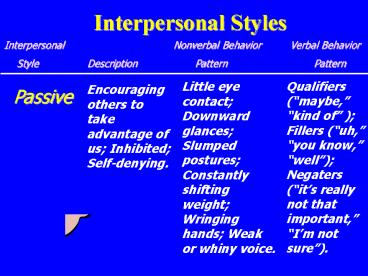
Interpersonal Styles
Interpersonal
Nonverbal Behavior Verbal Behavior
Style Description Pattern
Pattern
Little eye contact Downward glances Slumped
postures Constantly shifting weight Wringing
hands Weak or whiny voice.
Qualifiers (maybe, kind of ) Fillers (uh,
you know, well) Negaters (its really not
that important, Im not sure).
Encouraging others to take advantage of us
Inhibited Self-denying.
Passive
2
Interpersonal Styles (continued)
Interpersonal
Nonverbal Behavior Verbal Behavior
Style Description Pattern
Pattern
Glaring eye contact Moving or leaning too close
Threatening gestures (pointing finger clenched
fist) Loud Voice Frequent interruptions.
Swear words and abusive language Attributions
and evaluations of others behavior Sexist or
racists terms Explicit threats or put-downs.
Taking advantage of others Expressive and
self-enhancing at others expense.
Aggressive
3
Interpersonal Styles (continued)
Interpersonal
Nonverbal Behavior Verbal Behavior
Style Description Pattern
Pattern
Direct and unambiguous language No attributions
or evaluations of others behavior Use of I
statements and cooperative we statements.
Good eye contact Comfortable but firm posture
Strong, steady and audible voice Facial
expressions matched to message Appropriately
serious tone Selective interruptions to ensure
understanding.
Pushing hard without attacking permits others to
influence outcome expressive and self-enhancing
without intruding on others.
Assertive
4
Types of Conflict
- Interpersonal Conflict between individuals.
- Intragroup Conflict occurs within a group or
team. - Intergroup Conflict occurs between 2 or more
teams or groups. - Interorganizational Conflict occurs between
organizations.
5
Team Conflict
- Affective (Relationship) Conflict
- emotional, personal disagreements
- associated with decreased team performance
- Cognitive (Constructive) Conflict
- focuses on problems and issues
- associated with improved team performance
6
Major Causes of Conflict
- Scarce resources
- Jurisdictional ambiguities
- Communication problems
- Personality clashes
- Goal differences
7
Styles to Handle Conflict
Assertive
Competing (Forcing)
Collaborating (Problem Solving)
Assertiveness
Compromising
Avoiding
Accommodating (Yielding)
Unassertive
Uncooperative
Cooperative
Cooperativeness
8
Deciding How to React to Conflict
- Assess importance of the issue
- Consider your ability/power
- Predict other partys likely reaction and
ability/power - Consider long-term effects as well as short-term
9
Manager Responses to Resolve Conflicts Among
Subordinates
- Focus on Super-ordinate goals
- Bargaining/Negotiation
- Mediation
- Team Member Rotation
- Providing well-defined tasks
- Separate opponents
- Change Personnel
10
Interorganizational Relationships FrameworkOrg.
Similarity Org. Relationship
11
Population Ecology
- How Similar (in same industry) Orgs. Compete
- Evolutionary terminology survival of the
fittest - Difficult for existing orgs. to change
- Major environmental changes lead to new forms of
orgs. - Compete by
- Performing well
- Choosing niches
- Hostile takeovers
12
Resource Dependence
- How Dissimilar Orgs. Compete
- e.g., Vendors and Customers (Supply Chain
Relationships) - Struggle to reduce dependence on other
organizations for scarce resources - Try to find ways of influencing these
organizations to make resources available - e.g., Wal-Mart
- e.g., Hostile takeovers
13
Institutionalism
- How Similar Orgs. Cooperate
- Joint Ventures
- Mergers
- Cartels (association of firms that agree to
coordinate activities) - Collusion (secret agreement to share
- information)
14
Collaborative Networks
- How Dissimilar Orgs. Cooperate
- Supply chain relationships
- Joint Ventures
- Holding stock in one another
- Interlocking directorates
- Mergers