Elementary Particles - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 3
Title:
Elementary Particles
Description:
Higgs Boson (not quite yet). Forces: 1. strong (hadronic) nuclear interaction (carried by exchange bosons called gluons). 2. electromagnetic interaction (carried by ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:48
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Elementary Particles
1
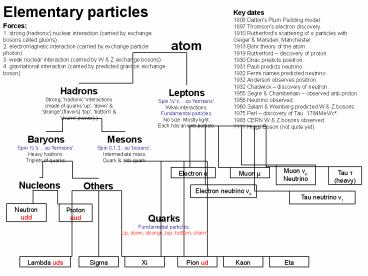
Elementary particles
Key dates 1808 Dalton's Plum Pudding model. 1897
Thomson's electron discovery. 1910 Rutherford's
scattering of a particles with Geiger Marsden,
Manchester. 1913 Bohr theory of the atom. 1919
Rutherford discovery of proton. 1930 Dirac
predicts positron. 1931 Pauli predicts
neutrino. 1932 Fermi names predicted
neutrino. 1932 Anderson observes positron. 1932
Chadwick discovery of neutron. 1955 Segre
Chamberlain observed anti-proton. 1956 Neutrino
observed. 1960 Salam Weinberg predicted W Z
bosons. 1975 Perl discovery of Tau
1784MeV/c². 1983 CERN W Z bosons observed. ????
Higgs Boson (not quite yet).
Forces 1. strong (hadronic) nuclear interaction
(carried by exchange bosons called gluons). 2.
electromagnetic interaction (carried by exchange
particle photon). 3. weak nuclear interaction
(carried by W Z exchange bosons). 4.
gravitational interaction (carried by predicted
graviton exchange boson).
atom
Hadrons Strong, 'hadronic' interactions (made of
quarks 'up', 'down' 'strange' (flavors) 'top',
'bottom' 'charm' (newer).)
Leptons Spin ½ 's so 'fermions'. Weak
interactions. Fundamental particles. No size.
Mostly light. Each has an anti-particle.
Baryons Spin ½ 's so 'fermions'. Heavy
hadrons. Triplets of quarks.
Mesons Spin 0,1,2,..so 'bosons'.. Intermediate
mass. Quark anti-quark.
Muon ?µ Neutrino
Tau t (heavy)
Electron e
Muon µ
Nucleons
Others
Electron neutrino ?e
Tau neutrino ?t
Proton uud
Neutron udd
Quarks Fundamental particles. Up, down, strange,
top, bottom, charm
Lambda uds
Sigma
Xi
Pion ud
Kaon
Eta
2
Conservation laws
Apparatus Cloud chambers Bubble chambers
Charge Electrostatic charge
Properties conserved during reactions and decays
of elementary particles Charge Energy Angular
momentum Linear momentum Lepton number Baryon
number Strangeness (not Universal)
Fermions? Pauli exclusion?
Strangeness discovered Gellman Nishijima (1952).
3
Field particles
Quantum dynamics Virtual photons (quantum
electrodynamics) Graviton (gravitational
interaction) Vector boson (weak
interactions) Gluon (strong interactions between
quarks)
The Standard Model
Including Quark model Electroweak
theory Quantum chromodynamics
Feynman Diagrams