Surface anatomy of the eye - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Surface anatomy of the eye
Description:
Surface anatomy of the eye Over the iris the transparent layer is the cornea Pupil Sclera Iris Conjunctiva Different color of iris in human eye Blue eyes in Europe ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:132
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Surface anatomy of the eye
1
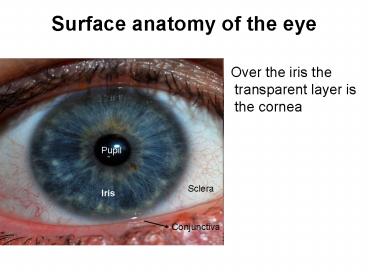
Surface anatomy of the eye
Over the iris the transparent layer is the
cornea
Pupil
Sclera
Iris
Conjunctiva
2
Different color of iris in human eye
Green in Asia
Amber in Asia
Blue eyes in Europe
Albino In Europe
Brown eyes in Asia, Africa, and Scandinavia
Grayish eyes in Russia, Finland, North Africa
3
IRIS PLANT
Iris is a genus of 260 species of flowering
plants. It takes its name from the Greek word for
a rainbow, referring to the wide variety of
flower colors found among the many species.
Iris latifolia
4
About Tapetum Lucidum
- The tapetum lucidum is a layer of tissue in the
eye of many vertebrates animals, that lies
immediately behind or sometimes within the
retina. - It reflects visible light back through the
retina, increasing the light available to the
photoreceptors. This improves vision in low-light
conditions. - The tapetum lucidum contributes to the superior
night vision of some animals. Many of these
animals are nocturnal, especially carnivores that
hunt their prey at night, while others are deep
see animals.
5
Tapetum Lucidum
1. Tapetum lucidum reflect lights and when the
eyes examined it appears as a metallic green,
blue, orange gold, brown. 2. The tapetum in
horse, ruminants, man and few others animals is
fibrous and can not reflect light. 3. The
tapetum lucidum which reflects light consists of
10 15 layers of flat, irregular, pentagonal
cells.
Tapetum Lucidum
Tapetum
Lens
Retina
Tapetum
6
Different eye shines due to tapatum
White eye shine in walleye fish
Yellowish-green eye shine in cat and dog
Yellow eye shine in raccoons
Red eye shine in opossum, rodents and birds.
7
Brightness of human and dog eye
MZI Khan
Human eye can not shine because the tapetum is
fibrous.
Yellowish-green eye shine in dog due to tapetum
lucidum
8
CATS EYE
Carnivores can see in night due to (1) Wide
vertical pupil which permits more amount of light
to enter in to the eye. (2) Presence of metallic
green tapetum in between retina and choroids.
9
Vision in night
snakes "see" their prey in green night-heat
vision
10
Color blindness
- Rod cell are
- responsible
- for photosensation
- Cones for the color
11
Vision of Shark
Sharks do not possess the same variety of
photorec- eptors as humans. They have few
retinal cones, and as a result, most have no
color vision. They have much larger rod
receptors (which pick up light), so their vision
is much less acute than ours.
12
Color Blindness
Human eye vision (color vision okay)
Horse vision (color blindness for red and green)