Plant Cell - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Plant Cell
Description:
... cycads, gnetophytes, and conifers Ginkgo Cycad Welwitschia Gnetum Ephedra Gymnosperms called gnetophytes; only 3 extant species Conifers: top row ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:632
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Plant Cell
1
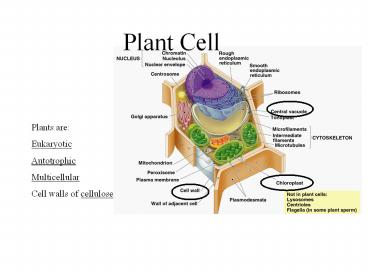
Plant Cell
Plants are Eukaryotic Autotrophic Multicellular C
ell walls of cellulose
2
Vocabulary - vascular refers to an internal
system of tubes or vessels to transport materials
throughout the plant basis or first major
division of plants into bryophytes and
tracheophytes includes - xylem transports
water and minerals up from the roots to the
shoots - phloem transports sugar (food) down
from the leaves to the rest of the plant
3
Xylem brings water up from the roots to the shoots
4
Phloem carries sugar (food) down from leaves
throughout the plant
5
Bryophytes nonvascular plants Examples include
20 mm
Liverworts
Moss
Hornwort
6
Bryophytes nonvascular plants - economically
important Ex) sphagnum moss also called peat or
peat moss Grows in boggy areas called peat bogs
extremely absorbant used in agriculture/horticult
ure
7
Seed dispersal by edible fruit, by wind, as well
as other means. The picture to the right is of a
samara from a maple tree.
Vocabulary Seed adaptation to terrestrial life
composed of a plant embryo, stored food, and a
protective coat
Which is a monocot and which is a dicot? How do
you know?
8
- Tracheophytes vascular plants
- Seedless plants whiskferns, horsetails, and
ferns
Whisk fern horsetail fern
9
Seedless vascular plants Ferns - reproduce with
spores - diagram shows spores growing in
clusters called sori on the back of the frond of
the fern
10
Seedless vascular plants dominated during the
Carboniferous period.
11
Vocabulary Cone reproductive structure of
gymnosperms contains pollen in males and ovules
in females Flower reproductive structure of
angiosperms composed of 4 sets of modified
leaves Fruit mature ovary of a flower that
protects dormant seeds and aids in their
dispersal
12
Ovulate cone from a pinetree (female)
Staminate cone from a pinetree (male)
13
- Tracheophytes vascular plants cont.
- Seed plants
- Gymnosperms have seeds in cones include
ginkgos, cycads, gnetophytes, and conifers
Cycad
Ginkgo
14
Welwitschia Gnetum Ephedra
Gymnosperms called gnetophytes only 3 extant
species
15
Conifers top row Douglas fir, Sequoia,
Cypress bottom row juniper, Australian pine
tree not shown yew, spruce, other pines
16
- Tracheophytes vascular plants cont
- Seed plants
- Angiosperms flowering plants - have flowers,
fruits, and seeds
17
Grasses are flowering plants, too. So are trees.
Grass flowers
18
Flower
(male)
(female)
pistil
19
Ovaries with ovules become fruits with seeds
after the ovule (egg) is fertilized by sperm from
the pollen
20
Pollen grains contain sperm. They are produced
in the anthers of the flowers in angiosperms.
21
Pollination - by many vectors,
including Wind Water Animals
22
Fruit or Veggie
Humans eat lots of different plant parts. A
fruit is the ripened ovary and contains seeds.
Therefore, tomatoes, peppers, squash, olives, and
cucumbers are fruits, not vegetables.
23
- Vegetables the vegetative parts of the plants
that we eat. Includes - Roots carrots, turnips,radishes
- Stems celery, bok choi, rhubarb, garlic,
- broccoli, onions, potatoes
- Leaves lettuce, cabbage, parsley
- Other plant parts that we eat
- Seeds pinto beans, peas, sunflower seeds,
- corn, pepper corns, rice, pecans, coconut
- Flowers anise flowers (licorice), basil
http//homecooking.about.com/library/weekly/blflow
ers.htm - Good rule of thumb if you didnt get it at the
store, DONT EAT IT!
24
We dont just eat plants, we also wear them,
build with them, and use them for medicines!
25
(No Transcript)
26
Plant Structure Function
27
Each plant part - root, stem, leaf - has a
specific role in keeping the plant alive through
photosynthesis
28
Monocots Dicots
29
Cotyledons nonphotosynthetic leaves of an
immature plant provide source of nutrients until
plant can produce its own food
30
Leaves - site of photosynthesis - cross
section - epidermis adaptation for
terrestrial life - waxy cuticle - stomata -
transpiration
31
Leaf
32
Leaf structure supports its function as the
primary organ for photosynthesis
33
Leaves - composed of blade, veins, petiole -
simple or compound (see identifying leaves ppt)
- pinnately or palmately compound - alternate
or opposite if compound - pinnate or palmate
venation
34
Overview of movement of photosynthesis reactants
and products through a plant
35
Stems Support and transport Contains xylem and
phloem Modified
Strawberry runners
onion
potatoes
36
Stems
Define plant type herbaceous, shrub, vine, tree
Herbaceous plant shrub vine
37
Stems cross sections through a dicot and a
monocot
38
Roots Function absorption, storage,
anchorage Root hairs extensions of the
epidermis that increase absorption by increasing
surface area see photo Fibrous roots see
monocot information Tap roots see dicot
information
39
Root Structure
40
Nitrogen fixation occurs in the roots and in
the soil around the roots of plants performed by
bacteria
41
Plants that live in nitrogen poor soils trap and
break down insects with enzymes to obtain nitrogen
Venus fly trap Pitcher plant
42
Vocabulary Primary growth increase in length
stems get longer, roots grow deeper Meristem
tissue that is growing Apical meristem tissue
found at the tips of roots and stems that is
actively dividing/growing
43
Plant Responses
Plant responses are called tropisms. Tropisms
can be positive or negative. They include
phototropism, gravitropism, and
thigmotropism. Most plant responses involve the
action of hormones, including gibberellins,
auxins, and ethylene.
44
Plant Responses
Effect of gibberellens on Thompsons seedless
grapes and on growth in a dwarf plant
45
Auxins make plants bushier by making more
branches at nodes when the apical meristem is cut
off (the tips of the existing branches)
46
Positive Phototropism
47
Effect of ethylene on the ripening of an apple.
48
NEGATIVE Gravitropism in Stems
http//plantsinmotion.bio.indiana.edu/plantmotion/
movements/tropism/gravitropism/gravi1/gravitrop.ht
ml
49
Vines Illustrate Positive Thigmotropism