Red Blood Cells - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 26
Title:
Red Blood Cells
Description:
Red Blood Cells Importance of RBC Shape and Size * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * Blood Functions: Transportation Gases Nutrients and wastes Regulatory ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:2406
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Red Blood Cells
1
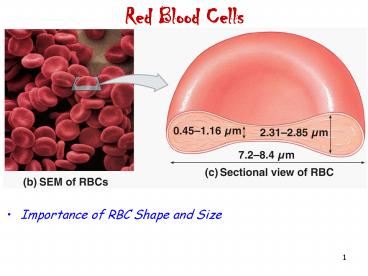
Red Blood Cells
- Importance of RBC Shape and Size
2
Blood
- Functions
- Transportation
- Gases
- Nutrients and wastes
- Regulatory
- Temperature
- pH
- Fluid volume
- Immunity
- antibodies
3
Blood types
- 4 different blood types
- A, B, AB and O
- What determines the blood type?
- Based on the presence or absence of a surface
protein - Surface antigen
- To protect host against foreign blood types each
person has antibodies - Anti-A or anti-B
- Rh blood type presence or absence of Rh antigen
- Rh factor
3
4
Neither antigen A nor B
A and B
B
A
RBCs
Plasma
antibodies
Anti-B antibodies
4
5
Blood type A
Anti-B antibody
Blood type A
Blood from type B Anti-A antibody
agglutinate
5
6
Rh Blood Types
No antigen D
Antigen D
Rh positive
Rh negative
RBCs
Anti-D antibodies (after prior exposure)
Plasma
No anti-D antibodies
6
7
- Rh negative moms and a fetus which is Rh
positive! - Antibodies may cross the placental barrier
- Solution?
- RhoGAM
- blocks mothers immune response
7
8
Composition of blood
Slightly alkaline pH (7.357.45)
Adult male 5 to 6 liters
Adult female 4 to 5 liters
9
So what is in blood?
10
Life span 8-10 days
12 hrs!
120 days
11
Hemopoiesis
- Hemocytoblasts
- Stem cells in myeloid tissue divide to produce
- Myeloid stem cells become RBCs, most WBCs
- Lymphoid stem cells become lymphocytes
- Erythropoiesis
- Only in myeloid tissue (red bone marrow) in
adults - Stem cells mature to become RBCs
12
(No Transcript)
13
Stimulating RBC production
- Erythropoietin (EPO)
- Also called erythropoiesis-stimulating hormone
- From kidneys!
- Secreted when oxygen in peripheral tissues is low
- Hypoxia
- How could this happen?
14
Red Blood Cells
- Red blood cell count
- The number of RBCs in 1 microliter of whole blood
- Male 4.56.3 million
- Female 4.25.5 million
- Fractionation
- Process of separating into plasma and formed
elements - Hematocrit (packed cell volume, PCV)
- Male 4054
- Female 3747
14
15
RBC and Hemoglobin (Hb)
- Normal hemoglobin values
- Adult male 1418 g/dL whole blood
- Adult female 1216 g/dL, whole blood
- Transports respiratory gases
- (oxyhemoglobin)
- (deoxyhemoglobin)
- Binds carbon dioxide and carries it to lungs
- Forms carbaminohemoglobin
16
Quaternary structure of 4 globular protein
subunits
- Each with one molecule of heme
- Each heme contains one iron ion
Each with one molecule of heme Each heme contains
one iron ion
17
Recycling of Red Blood Cell Components
Globin
Ever wonder why urine is yellow?
18
Hemoglobin Conversion and Recycling
- Hemoglobinuria
- Hemoglobin broken down products found in urine
due to excess hemolysis in bloodstream - Alpha and beta chains
- Redish brown urine
- Hematuria -- he ma turia
- Whole red blood cells in urine due to kidney or
tissue damage - Jaundice
- - bilirubin buildup
19
Leukocytes
- Leukocytes possess a nucleus and organelles
- How is this different from RBCs?
- They help initiate an immune response
- attracted to a site of infection by molecules
from damaged cells or invading pathogens - chemotaxis.
- They are 1.5 3 times larger than erythrocytes
- They are capable of leaving the blood vessels and
entering a tissue - Diapedesis
- How is this different from RBCs?
20
Classification of Leukocytes
- The five types of leukocytes
- Divided into two classes - based of the presence
or absence of visible organelles termed granules - Granulocytes
- Agranulocytes
- Some are phagocytic
- Neutrophils, eosinophils, and monocytes
21
(No Transcript)
22
White Blood Cells - Neutrophils
- 5070 of circulating WBCs
- First on the scene of injury
- Cytoplasm granules with
- Lysosomal enzymes
- Bactericides
- Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)
- Prostaglandins / leukotrienes
- Increase capillary permeability
- Call for help
23
White Blood Cells - Eosinophils
- 24 of circulating WBCs
- Attack large parasites
- Parasitic worms and flukes (flat worm)
- Excrete toxic compounds
- Nitric oxide
- Cytotoxic enzymes
- Control inflammation
- Enzymes that counteract inflammatory effects of
neutrophils and mast cells - Allergies
24
White Blood Cells - Basophils
- Are less than 1 of circulating WBCs
- Accumulate in damaged tissue
- Release histamine
- Dilates blood vessels
- Release heparin
- Prevents blood clotting
25
White Blood Cells - Monocytes
- 28 of circulating WBCs
- Are large and spherical
- Enter peripheral tissues and become macrophages
- Engulf large particles and pathogens
- Secrete substances that attract immune system
cells and fibrocytes to injured area
26
WBCs 30 Three Classes of Lymphocytes
- T cells
- Cell-mediated immunity no antibodies
- immune response to viral infected and tumor cells
- B cells
- Humoral immunity use of antibodies
- Differentiate into plasma cells
- Synthesize antibodies
- Natural killer (NK) cells innate immune system
- Detect and destroy abnormal tissue cells (cancers)