Tablets - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 23
Title:
Tablets
Description:
... Khon Kaen University Direct compression Tablets are compressed directly from powder blends of the active ingredient and suitable excipients No pretreatment of ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:1097
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Tablets
1
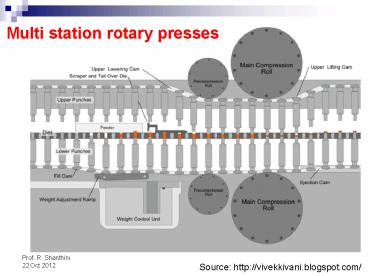
Multi station rotary presses
Source http//vivekkivani.blogspot.com/
2
(No Transcript)
3
- Although tablet compressing machinery has
undergone numerous mechanical modifications over
the years, the compaction of materials between a
pair of moving punches within a stationary die
has remained unchanged - The principle modification from earlier equipment
has been an increase in production rate which is
regulated by - Number of tooling sets
- Number of compression stations
- Rotational speed of the press
Source Assoc. Prof. Dr. Jomjai Peerapattana,
Faculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Khon Kaen
University
4
- Special adaptations of tablet machines allow for
the compression of layered tablets and coated
tablets - A device that chills the compression components
to allow for the compression of low-melting point
substances such as waxes i.e. suppositories
Source Assoc. Prof. Dr. Jomjai Peerapattana,
Faculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Khon Kaen
University
5
Compression
- The ultimate test of a tablet formulation and
granulation process is whether the granulation
can be compressed on a high-speed tablet press. - During compression, the tablet press performs the
following functions - Filling of empty die cavity with granulation.
- Precompression of granulation (optional).
- Compression of granules.
- Ejection of the tablet from the die cavity and
take-off of compressed tablet.
6
- When evaluating the compression characteristics
of a particular formulation, prolonged trial runs
at press speeds equal to that to be used in
normal production should be tried. - Only then are potential problems such as sticking
to the punch surface, tablet hardness, capping,
and weight variation detected. - High-speed tablet compression depends on the
ability of the press to interact with granulation.
7
- Following are the parameters to be considered
while choosing speed of press. - Granulation feed rate.
- Delivery system should not change the particle
size distribution. - System should not cause segregation of coarse and
fine particles, nor it should induce static
charges.
8
- The die feed system must be able to fill the die
cavities adequately in the short period of time
that the die is passing under the feed frame. - The smaller the tablet , the more difficult it is
to get a uniform fill a high press speeds. - For high-speed machines, induced die feed systems
is necessary. - These are available with a variety of feed
paddles and with variable speed capabilities. - So that optimum feed for every granulation can
be obtained.
9
- After the die cavities are filled ,the excess is
removed by the feed frame to the center of the
die table. - Compression of the granulation usually occurs as
a single event as the heads of the punches pass
over the lower and under the upper pressure
rollers. - This cause the punches to the penetrate the die
to a preset depth, compacting the granulation to
the thickness of the gap set between the punches.
10
- The rapidity and dwell time in between this press
event occurs is determined by the speed at which
the press is rotating and by the size of
compression rollers. - Larger the compressions roller, the more
gradually compression force is applied and
released.
11
- Slowing down the press speed or using larger
compression rollers can often reduce capping in a
formulation. - The final event is ejection of compressed tablets
from die cavity. - During compression, the granulation is compacted
to form tablet, bonds within compressible
material must be formed which results in sticking.
12
- High level of lubricant or over blending can
result in a soft tablet, decrease in wettability
of the powder and an extension of the dissolution
time. - Binding to die walls can also be overcome by
designing the die to be 0.001 to 0.005 inch wider
at the upper portion than at the center in order
to relieve pressure during ejection.
13
DIFFERENT PUNCHES DIES
14
Tableting methods (already seen)
- Dry methods
- Direct compression
- Dry granulation
- Wet methods
- Wet granulation
Source Assoc. Prof. Dr. Jomjai Peerapattana,
Faculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Khon Kaen
University
15
WET GRANULATION DRY GRANULATION DIRECT COMPRESSION
1. Milling and mixing of drugs and excipients 1. Milling and mixing of drugs and excipients 1. Milling and mixing of drugs and excipients
2. Preparation of binder solution 2. Compression into slugs or roll compaction 2. Compression of tablet
3. Wet massing by addition of binder solution or granulating solvent 3. Milling and screening of slugs and compacted powder
4. Screening of wet mass 4. Mixing with lubricant and disintegrant
5. Drying of the wet granules 5. Compression of tablet
6. Screening of dry granules
7. Blending with lubricant and disintegrant to produce running powder
8. Compression of tablet
16
Direct compression
- Tablets are compressed directly from powder
blends of the active ingredient and suitable
excipients - No pretreatment of the powder blends by wet or
dry granulation procedures is necessary
Source Assoc. Prof. Dr. Jomjai Peerapattana,
Faculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Khon Kaen
University
17
Advantages
- Economy
- Machine fewer manufacturing steps and pieces of
equipment - Labor reduce labor costs
- Less process validation
- Lower consumption of power
Source Assoc. Prof. Dr. Jomjai Peerapattana,
Faculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Khon Kaen
University
18
Advantages (contd.)
- Elimination of granulation process
- Heat (wet granulation)
- Moisture (wet granulation)
- High pressure (dry granulation)
- Processing without the need for moisture and heat
which is inherent in most wet granulation
procedures - Avoidance of high compaction pressures involves
in producing tablets by slugging or roll
compaction
Source Assoc. Prof. Dr. Jomjai Peerapattana,
Faculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Khon Kaen
University
19
Advantages (contd.)
- Elimination of variabilities in wet granulation
processing - Viscosity of the granulating solution (depend on
its temperature), - How long it has been prepared,
- Rate of binder addition and kneading can affect
the properties of the granules formed - The granulating solution, the type and length of
mixing and the method and rate of wet and dry
screening can change the density and particle
size of the granules, which can have a major
effect on fill weight and compaction qualities
Source Assoc. Prof. Dr. Jomjai Peerapattana,
Faculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Khon Kaen
University
20
Advantages (contd.)
- Type and rate of drying
- can lead to unblending as soluble active
ingredients migrate to the surfaces of the drying
granules - Less unit processes incorporated in production
means less chances of batch-to-batch variation
are compounded
Source Assoc. Prof. Dr. Jomjai Peerapattana,
Faculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Khon Kaen
University
21
Direct compression fillers
- Common materials that have been modified in the
chemical manufacturing process to improve
fluidity and compressibility
Source Assoc. Prof. Dr. Jomjai Peerapattana,
Faculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Khon Kaen
University
22
Soluble fillers
- Spray dried lactose (good flowability less
compressibility) - Fast-Flo lactose (much more compressible and
highly fluid) - Tabletose aggromerate form of lactose (More
compressible than spray dried but less
compressible than Fast Flo lactose) - Di-Pac cocrystallization of 97 sucrose and 3
modified dextrin - Sorbitol
- Maltodextrin (Highly compressible completely
soluble ) - And more.
Source Assoc. Prof. Dr. Jomjai Peerapattana,
Faculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Khon Kaen
University
23
Insoluble fillers
- Starch 1500 intact starch grains and ruptured
starch grains that have been partially hydrolyzed
and subsequently agglomerated - Era-Tab spray-dried rice starch (good fluidity
compressibility depends on moisture) - Avicel microcrystalline cellulose (the most
important tablet excipient developed in modern
times most compressible) - Dicalcium phosphate (Emcompress or DiTab)
Source Assoc. Prof. Dr. Jomjai Peerapattana,
Faculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Khon Kaen
University