Machines
1 / 8
Title: Machines
1
Machines
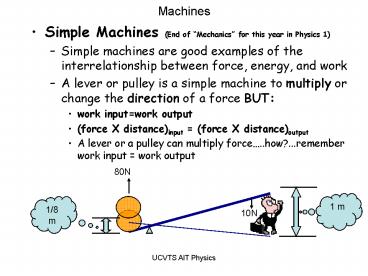
- Simple Machines (End of Mechanics for this year
in Physics 1) - Simple machines are good examples of the
interrelationship between force, energy, and work - A lever or pulley is a simple machine to multiply
or change the direction of a force BUT - work inputwork output
- (force X distance)input (force X
distance)output - A lever or a pulley can multiply
force..how?...remember work input work output
80N
1 m
1/8 m
10N
2
Machines
- Simple Machines
- Pulleys
- A kind of lever that can
- Can change the direction of a force
- Multiply force
- When combined with another pulley
- Change direction and multiply the force
- Other examples of Simple Machines???
3
Machines
- Simple Machines
- Harry the painter swings year after year from his
bosun's chair. His weight is 500N and the rope,
unknown to him, has a breaking point of 400N. - Why doesn't the rope break when he is supported
as shown to the left on the above picture? - One day Harry is painting near a flagpole, and,
for a change he ties the free end of the rope to
the flagpole instead of to his chair as shown to
the right. - Why did Harry end up taking his vacation early?
(Not really funny! Too bad!)
4
Machines
- Simple Machines
- Actual Mechanical Advantage (AMA)
- Ratio of output force to input force
- AMA for a pulley number of strands of
cable/rope that actually support the load - Pulley examples on board
5
Machines
- Simple Machines
- Efficiency
- Any real machine is not 100 efficient
- There are always losses of energy
- Therefore efficiency is always less than 1
- Automotive example
- Fuel energy in (100) cooling water losses
(35)-Engine output (30)-exhaust heat (35) - Other examples?
6
Torque
- Torque
- A torque is a force exerted at a distance from an
axis of rotation the easiest way to think of
torque is to consider a door. When you open a
door, where do you push? If you exert a force at
the hinge, the door will not move the easiest
way to open a door is to exert a force on the
side of the door opposite the hinge, and to push
or pull with a force perpendicular to the door.
This maximizes the torque you exert. - We can state the equation for torque as
7
Torque
- Torque
- In a given situation, there are usually three
ways to determine the torque arising from a
particular force. Consider the example of the
torque exerted by a rope tied to the end of a
hinged rod, as shown in the diagram. - The first thing to notice is that the torque is a
counter-clockwise torque, as it tends to make the
rod spin in a counter-clockwise direction. The
rod does not spin because the rope's torque is
balanced by a clockwise torque coming from the
weight of the rod itself. - There are three equivalent ways to determine this
torque, as shown in the diagram below. - Method 1 - In method one, simply measure r from
the hinge along the rod to where the force is
applied, multiply by the force, and then multiply
by the sine of the angle between the rod (the
line you measure r along) and the force. - Method 2 - For method two, set up a right-angled
triangle, so that there is a 90 angle between
the line you measure the distance along and the
line of the force. This is the way the textbook
does it done in this way, the line you measure
distance along is called the lever arm. If we
give the lever arm the symbol l, from the
right-angled triangle it is clear that
8
Torque
- Center of Gravity
- Center of gravity
- The center of gravity of an object is the point
you can suspend the object from without there
being any rotation because of the force of
gravity, no matter how the object is oriented. If
you suspend an object from any point, let it go
and allow it to come to rest, the center of
gravity will lie along a vertical line that
passes through the point of suspension. Unless
you've been exceedingly careful in balancing the
object, the center of gravity will generally lie
below the suspension point. - The center of gravity is an important point to
know, because when you're solving problems
involving large objects, or unusually-shaped
objects, the weight can be considered to act at
the center of gravity. In other words, for many
purposes you can assume that object is a point
with all its weight concentrated at one point,
the center of gravity. - For any object, the x-position of the center of
gravity can be found by considering the weights
and x-positions of all the pieces making up the
object - COG
- A similar equation would allow you to find the y
position of the center of gravity. - The center of mass of an object is generally the
same as its center of gravity. Very large
objects, large enough that the acceleration due
to gravity varies in different parts of the
object, are the only ones where the center of
mass and center of gravity are in different
places. - Neat facts about the center of gravity
- Fact 1 - An object thrown through the air may
spin and rotate, but its center of gravity will
follow a smooth parabolic path, just like a ball.
- Fact 2 - If you tilt an object, it will fall over
only when the center of gravity lies outside the
supporting base of the object. - Fact 3 - If you suspend an object so that its
center of gravity lies below the point of
suspension, it will be stable. It may oscillate,
but it won't fall over.