How does an - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 21
Title:
How does an
Description:
Book equation is not too ecology friendly. Text eq: net = solar in solar out ... The Ogallala Aquifer. 250,000 km2. Capacity of est. 2 billion acre-feet ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:122
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: How does an
1
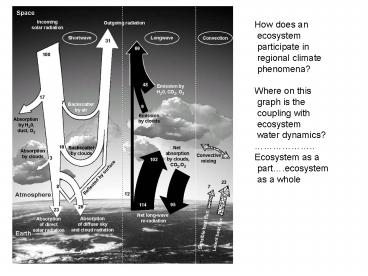
How does an ecosystem participate in regional
climate phenomena? Where on this graph is the
coupling with ecosystem water
dynamics? .. Ecosystem as a
part.ecosystem as a whole
2
Net radiation
- Energy input to ecosystem
- Balance between
- Input (long- and short-wave radiation)
- Output (long- and short-wave radiation)
- Book equation is not too ecology friendly.
3
Text eq net solar in solar out longwave
in longwave out
4
Text eq net solar in solar out longwave
in longwave out
Whats Rnet composed of?
5
Energy Partitioning
text
- Rnet H LE G ?S
- Rnet net radiation
- H sensible heat flux
- LE evapotranspiration
- G ground heat flux
- Chemical or heat storage in mass
- (usually ignored)
6
(not normal response!...forest was stressed?!
7
Energy, Water, and Carbon are strongly coupled
8
In our part of the world, wet surfaces are
fewthe only way ecosystems have high LE values
is due to root uptake of stored soil
water. Without the plants, our world would
largely be H!
9
Energy partitioning
- Ecosystems differ substantially in
- Albedo (reviewed earlier)
- Bowen ratio (H/LE)
- The ratio of sensible heat (H) to Latent
- Heat (which is also evapotranspiration)
- is an ecosystem characteristic and CAN
- relate to productivity (local bias)
10
Use thermal imagery to look at temperatures of
various canopies
11
A wheat field next to a fallow field. What
would the Components of the Net Radiation budget
look for this in terms of H, LE, and G? Why do
farmers in Colorado practice fallow field
rotation?
12
Subsidized ET???
- The Ogallala Aquifer
- 250,000 km2
- Capacity of est. 2 billion acre-feet
- Primary source of irrigation H2O in Great Plains
- Withdrawals have tripled since 1950 to gt 2
million acre-feet/yr - Projected to be pumped out by 2010 (estimates
vary)
13
Soil volume exploited differs among ecosystems
(roots in search of a good time)
14
In terms of life forms, grassesgttreesgtshrubs in
terms of of shallow-rooted roots.
Quantity of water available depends on soil
volume exploited Shrubs are more deeply
rooted Use more soil
15
The zone of soil affected by roots is called
the rhizosphere. Water within the zone of the
rhizosphere will be reduced to permanent
wilting. Water moves from high to low
concentration gradients (Osmosis). Plants use
ONLY solar energy for water uptake (but use
fixed energy to make the roots!)
16
One more trick to get more water.
Hydraulic Lift (plants move water in soils)
17
Hydraulic Lift
water
(no nutrients)
18
Hydraulic Lift
moon
water
(no nutrients)
19
Hydraulic Lift
During day plant slurps up both deep water
and water exuded during night
water
(no nutrients)
20
Hydraulic lift.... Instructor comment Plant
physiologists fail to recognize that these roots
are getting ripped to shreds by herbivores. ( The
poor things bleed) Uptake of these losses
may simply minimize the damage Either way,
the mechanism occurs. We will revisit it when we
talk about nutrient uptake.
21
Exam Monday Material on web Jan 12-Feb 6
Study questions sets 1-3
Chpt 1 overview. Definitions of subject
area Chpt 2 climate, energy Chpt. 3
soils Chpt 4 soils, water, interactions