OMICS WORLD - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 45
Title:
OMICS WORLD
Description:
Prof. Jeremy Nicholson, London. A metabolic fingerprint which uniquely defines the ... Jeremy Nicholson. St Thomas's Hospital. Kourosh Ahmadi. Tim Spector ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:173
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: OMICS WORLD
1
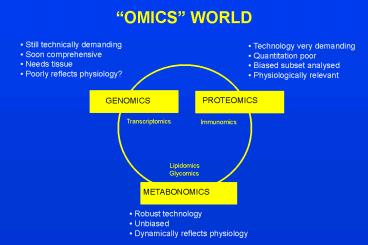
OMICS WORLD
- Still technically demanding
- Soon comprehensive
- Needs tissue
- Poorly reflects physiology?
- Technology very demanding
- Quantitation poor
- Biased subset analysed
- Physiologically relevant
PROTEOMICS
GENOMICS
Transcriptomics
Immunomics
Lipidomics Glycomics
METABONOMICS
- Robust technology
- Unbiased
- Dynamically reflects physiology
2
METABONOMICS
"a systems approach to examining the changes in
hundreds or thousands of low molecular weight
metabolites in an in tact tissue or biofluid
Prof. Jeremy Nicholson, London
A metabolic fingerprint which uniquely defines
the Current physiological status of an individual
3
CLINICAL METABONOMICS
Diagnosis - Identifying new biomarkers - Clinica
l diagnosis where no simple test
exists - Screening subjects for clinical
trials Prognosis Monitoring therapy - Understan
ding basis of drug efficacy - Toxicology - Pharm
acometabonomics - Clinical monitoring Designing
therapy - New insights into physiology and
pathology - Validating animal models of disease
4
INDIVIDUAL
SAMPLE Blood fractions (serum/plasma)
Urine Cells or tissue
SERUM Easy to prepare Readily available
non-invasive
REPRESENTATIVE SPECIMEN
ANALYSIS METHOD NMR spectroscopy LC/MS
NanoSensors
NMR Robust, reproducible Unbiased Low
sensitivity
COMPLEX DATA VECTOR
PROCESSING Digitisation, binning, wavelets
Filters (OSC, variable selection)
BINNING then OSC Practicality Empirical
selection
SIMPLIFIED DATA VECTOR
INTERPRETATION Projection methods (PCA,
PLS) Conventional LDA Genetic computing
PROJECTION Good theoretical basis Readily
validated Empirical selection
MODEL
PREDICTION
5
A 600MHz 1H-NMR spectrum of human serum
Requires 150µl of serum prepared in the same way
as for classical biochemical tests in routine use
in hospital labs
Lipids
Lactate
Arginine
N-acetyl glycoprotein
Lipids
Choline
Sugars
Alanine
Glutamine
The dominant water signal is suppressed by
selective irradiation, and the resulting spectrum
is phased, baseline corrected and referenced
to lactate at 1.33ppm
6
NMR spectroscopy of human serum is very
reproducible
A single serum sample from a healthy
volunteer was split into 14 replicate aliquots
and frozen Eight aliquots were thawed and
spectra generated on day 0 The remaining six
aliquots were thawed and analysed on day
14 The intra-day and inter-day reproducibility
of the NMR spectrum was calculated for 256
integral bins
7
NMR spectroscopy of human serum is very
reproducible
8
NMR spectroscopy of human serum is very
reproducible
Virtually all of the variation is time
independent The mean Cvar across the range
0.6ppm to 4.5ppm is 1.8 Within the range
where most of the information content of the
spectrum resides, the mean Cvar is 1.1 The
NMR spectrum is highly reproducible when compared
to other analytical techniques (eg. ELISA)
9
TO BE USEFUL FOR CLINICAL DIAGNOSIS THE NMR
SPECTRUM MUST CONTAIN INFORMATION WHICH IS UNIQUE
TO THE INDIVIDUAL AND WHICH IS STABLE OVER TIME
10
The NMR spectrum encodes temporally stable
inter-person variation
Serum samples were prepared from 17
volunteers over a period of 3 months Samples
were taken at 0, 7, 16, 37, 67 and 97
days Spectra were prepared for each sample,
allowing variance due to temporal variation
within the same individual to be separated from
variance between individuals
11
The NMR spectrum encodes temporally stable
inter-person variation
Lipids
Sugars
Variance due to analytical imprecision has been
subtracted
12
The NMR spectrum encodes temporally stable
inter-person variation
Lipids
Sugars
Variance due to analytical imprecision and
temporal variation has been subtracted
13
The NMR spectrum encodes temporally stable
inter-person variation
There is statistically significant stable
inter-person variation in the NMR spectrum The
inter-person Cvar is 5 across the
information- dense region of the
spectrum There is considerable variation from
bin to bin in the stable inter-person variance
from almost 0 to over 15
14
Our First Example
Coronary artery disease (most commonly due to
atherosclerosis) is one of the major causes of
mortality and morbidity in the UK
1 in 3 will suffer CAD at some time in their
life Over 1,000 deaths per million population
per year attributable to CAD in
2000 Treatment (medical and surgical)
increasingly effective but expensive and
difficult to target
15
Invasive ANGIOGRAPHY is the current gold standard
for diagnosing CAD
An angiography cath lab, like this one, costs
1.5 million to equip, a further 0.4 million per
year to staff. The marginal cost of
each angiography performed is approximately 900.
A X-ray dye is injected into the artery to allow
it to be directly visualised by the X-ray camera
16
Invasive ANGIOGRAPHY is the current gold standard
for diagnosing CAD
A severe blockage is clearly visible
LAD
Cx
An angiography cath lab, like this one, costs
1.5 million to equip, a further 0.4 million per
year to staff. The marginal cost of
each angiography performed is approximately 900.
A X-ray dye is injected into the artery to allow
it to be directly visualised by the X-ray camera
17
Angiography
ADVANTAGES
DISADVANTAGES
Accurate and reproducible Provides
anatomical detail required for PTCA
Well-established
Invasive procedure Associated morbidity
and even mortality Expensive
Consequently, there is demand for a non-invasive
diagnostic procedure (such as a blood test) which
is completely safe and cheaper than
angiography. Such a test would be useful to
identify the 20-30 of patients who currently
undergo angiography only to discover that they
have normal coronary arteries
18
Clinical MetabonomicsA pilot study in CAD
Healthy
Disease
19
Clinical MetabonomicsA pilot study in CAD
Healthy
Disease
20
Projection the principle underlying multivariate
pattern recognition
THE OPTIMAL PROJECTION
A BAD PROJECTION
Reducing the dimensionality through projection
encapsulates the key elements of a large complex
dataset in a just a few numbers
IRTL Reviews (2003) 11-6
21
Unsupervised PCA suggests that there are patterns
associated with CAD
Healthy individuals
Severe heart disease
Plot of the second and third statistically
significant principle components from the PCA
model constructed using spectra from
40 individuals of each class
Brindle et al. (2002) Nature Medicine 81465
22
Impact of Orthogonal Signal Correction (OSC)
Brindle et al. (2002) Nature Medicine 81465
Healthy individuals
PCA prior to OSC
PCA after one OSC filter
Severe heart disease
Application of OSC results in almost complete
separation of the two classes
23
IDENTIFYING NEW BIOMARKERS
Brindle et al. (2002) Nature Medicine 81465
significant
lipids
choline
lipids
Loadings plots underscore the importance of
subtle compositional differences among
lipoproteins in the diagnosis of heart
disease, but also identify serum choline as a
novel biomarker of disease
24
VALIDATION
1. Predicitivity of spectra not used
to construct the model More than 90 at 95
significance level 2. The same NMR bins are
contributing to separation before and after
application of OSC
25
CONCLUSIONS
- Chemometric analysis of 600 MHz 1H-NMR spectra of
human serum samples is able to distinguish
diseased and healthy individuals - Similar techniques can classify on the basis of
disease severity as well as presence or absence - Application of OSC significantly improves
classification - Subtle variations in lipoprotein composition are
the dominant contributors to the model - Multivariate analysis of existing risk factor
data considerably less discriminating
Can such a test find diagnostic utility in a
clinical setting?
26
Metabonomic and Genomic Investigation of
Coronary Artery Disease
THE MaGiCAD STUDY http//www.magicad.org.uk
AIMS To evaluate clinical metabonomics for
diagnosing CAD in a clinical environment To
compare metabonomics and genomics with
existing methods of diagnosing CAD To
investigate risk-factors for CAD in the East
Anglian population
27
Metabonomic and Genomic Investigation of
Coronary Artery Disease
THE MaGiCAD STUDY http//www.magicad.org.uk
Collect serum, plasma, urine, DNA and RNA from
more than 1,650 patients attending for coronary
angiography More than 850 have been collected
to date
28
Metabonomic and Genomic Investigation of
Coronary Artery Disease
THE MaGiCAD STUDY http//www.magicad.org.uk
Collect serum, plasma, urine, DNA and RNA from
more than 1,650 patients attending for coronary
angiography More than 850 have been collected
to date Obtain metabolic, proteomic and
genetic profiles
29
Metabonomic and Genomic Investigation of
Coronary Artery Disease
THE MaGiCAD STUDY http//www.magicad.org.uk
Collect serum, plasma, urine, DNA and RNA from
more than 1,650 patients attending for coronary
angiography More than 850 have been collected
to date Obtain metabolic, proteomic and
genetic profiles Accurately assess the
phenotype of the patient
30
Metabonomic and Genomic Investigation of
Coronary Artery Disease
THE MaGiCAD STUDY http//www.magicad.org.uk
Collect serum, plasma, urine, DNA and RNA from
more than 1,650 patients attending for coronary
angiography More than 850 have been collected
to date Obtain metabolic, proteomic and
genetic profiles Accurately assess the
phenotype of the patient Compare the various
diagnostic approaches
31
Metabonomic and Genomic Investigation of
Coronary Artery Disease
THE MaGiCAD STUDY http//www.magicad.org.uk
Collect serum, plasma, urine, DNA and RNA from
more than 1,650 patients attending for coronary
angiography More than 850 have been collected
to date Obtain metabolic, proteomic and
genetic profiles Accurately assess the
phenotype of the patient Compare the various
diagnostic approaches
RECRUITMENT COMPLETE End 2004
ANALYSIS COMPLETE Mid 2005
32
Here is a summary of the results for a pilot
study with approximately 100 patients Of those
with severe heart disease 6 were rejected by
the expert system 6 were diagnosed as
unclassified 88 were correctly diagnosed as
Diseased 0 were incorrectly diagnosed as
Normal Of those with normal coronary
arteries 0 were rejected by the expert
system 4 were diagnosed as unclassified 92
were correctly diagnosed as Normal 4 were
incorrectly diagnosed as Diseased
Metabolic profiling out-performs
existing diagnosis methods based on blood samples
33
Using Clinical Metabonomics to Select Subjects
for Clinical Trials in Heart Disease
The Solution Individuals scored as positive for
CHD by Clinical Metabonomics have an estimated
absolute risk of almost 15 per annum. A trial
with 80 chance of detecting a 30 reduction in
risk with 95 power, now requires only 1,000
individuals per group followed for three
years. This represents a saving of as much as
10 million, and yields results sooner. Clinical
metabonomic screening will soon be available, but
what is the impact on the applicability of the
trial?
The Problem For primary prevention trials,
selecting subjects on the basis of lipid
measurements and other risk factors rarely
identifies a group at more than 5 per annum
absolute risk. For a trial with 80 chance of
detecting a 30 reduction in risk with 95 power,
this requires approx 2,000 individuals per group
followed for four years. A monitored trial with
this design costs 10 - 30 million.
34
Our Second Example
Osteoporosis (usually defined by low bone mineral
density on a DEXA scan) affects one in three
women over the age of 70
Non-traumatic fracture (often of hip or spine)
is the major cause of morbidity associated with
the disease Recent data tells us that fracture
risk is poorly predicted by bone mineral density
scans Osteoporosis follows menopause, but the
molecular physiology of the disease remains
poorly understood
35
Clinical Metabonomics Identifies Individualswith
Low Bone Mineral Density
Controls
Osteoporosis (Z-score lt -1.5)
PCA model after one OSC filter, applied to
600MHz NMR spectra of serum from
40 Post-menopausal women with low bone Density,
compared with 40 age-matched Women with normal
bone density. Spectra Were collected under
identical conditions to The CHD study, and were
binned into 207 Integral bins (with the water
region set to 0) Prior to application of centred
scaling, OSC And PCA. Submitted to Nature
Medicine (2004)
36
Clinical Metabonomics Readily Distinguishes Osteop
orosis from other Bone Disorders such as
Osteoarthritis
Controls
Osteoarthritis
Osteoporosis (Z-score lt -1.5)
37
Clinical Metabonomics Readily Distinguishes Osteop
orosis from other Bone Disorders such as
Osteoarthritis
metabolic trajectory
Controls
Osteoarthritis
Osteoporosis (Z-score lt -1.5)
38
The Osteoporosis Diagnostic Model Is Readily
Validated using Samples Of Unknown Status
Of those with osteoporosis 5/5 were correctly
identified at 95 confidence Of those with
normal BMD 5/5 were correctly identified at 95
confidence
39
SIGNIFICANT
proline
lipids
Loadings plots identify the metabolites which
were responsible for the separation between the
groups. Lipid compositional differences are
important. More surprising, however, was the
association between low serum proline and the
presence of osteoporosis.
choline
40
A Biochemical Assay confirms the Findings from
Clinical Metabonomics
- Colorimetric assay for free proline based on the
isatin assay of Bocter (1971) Anal. Biochem.
4366-70 - Sensitive (31 11µM) and reproducible (CV 4.8)
microtitre plate format assay - Negligible cross-reactivity with hydroxyprolines
- Mean proline concentration in serum 258 55µM,
with no difference between sexes, with age or
renal function
P lt 0.01 (n79)
MEAN S.D.
OP
Serum proline 25 lower In women with osteoporosis
Grainger Aitken (2004) Clin Chim Acta In the
press
41
Proline Balance
Proline is a major constituent of collagen (27
by weight) and gt90 of daily collagen synthesis
is performed by osteoblasts
Uniquely, proline is poorly salvaged from
degraded collagen because about half of it has
been converted into hydroxyproline, which is
excreted in urine
Probably as a result of this, proline and glycine
are the only amino acids actively salvaged from
the nephron
To maintain the normal rate of collagen
synthesis requires the de novo synthesis or
dietary acquisition of up to 100 grams of proline
per day
42
Proline Balance
MeAIB
2
SAT2
Plasma
3
1. Glutamate pathway Dominant in other cell
types 2. Arginine pathways Minor contributor 3,
Proline uptake Inhibited by hydroxy- proline in
osteoblasts
1
43
DOES PROLINE DEFICIENCY CAUSE OSTEOPOROSIS?
Perform a proline supplementation study to
normalise plasma proline levels and monitor
effects on bone mineral density
IS IT DIET, GENES OR OTHER ENVIRONMENTAL FACTORS
THAT DETERMINE PROLINE BALANCE?
Investigate the relative contribution of the
three pathways to collagenic proline requirements
in osteoblasts, and also the factors that
determine the rates of the independent pathways
44
CLINICAL METABONOMICS
Diagnosis - Identifying new biomarkers - Clinica
l diagnosis where no simple test
exists - Screening subjects for clinical
trials Prognosis Monitoring therapy - Understan
ding basis of drug efficacy - Toxicology - Pharm
acometabonomics - Clinical monitoring Designing
therapy - New insights into physiology and
pathology - Validating animal models of disease
45
Cambridge University David Grainger David
Mosedale Jim Metcalfe Nick Wareham Robert
Luben Papworth Hospital Sarah Hayns Claire
Nugent Caryl Barnard Hester Goddard Duncan
McNab Sarah Clarke Hugh Bethell Andrew
Grace Peter Schofield
Imperial College Joanne Brindle Elaine
Holmes Marc Dumas George Tranter Henrik
Antti Jeremy Nicholson St Thomass
Hospital Kourosh Ahmadi Tim Spector GlaxoSmithkl
ine Elaine McKilligin
www.graingerlab.org