The Amazing World of Bacteria - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 36
Title:
The Amazing World of Bacteria
Description:
Sulfurous hot springs, very salty lakes, and in ANAEROBIC environments, such as ... Rod (bacillus) Spiral. The shape may determine the GENUS/GROUP name ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:117
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: The Amazing World of Bacteria
1
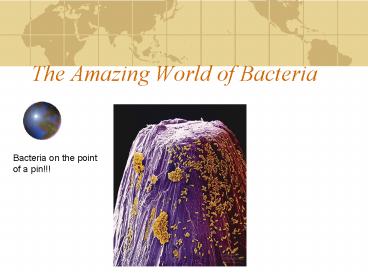
The Amazing World of Bacteria
Bacteria on the point of a pin!!!
2
Differences Between Bacteria and Viruses
- Bacteria are classified as living
- Bacteria are prokaryotic cells
- No Nucleus
- Bacteria can perform metabolic functions
- Replication
- Protein Synthesis
- Use and obtain own energy in various ways
- Move on their own
Viruses are not affected by antibiotics
3
KINGDOMS 1 2The Prokaryotes
- Eubacteria Archaebacteria
- 1st life forms
- Ubiquitous
- What does this mean?
- Most are helpful, some are harmful
- Can you give an example of each?
4
KINGDOMS 1 2The Prokaryotes
- Prokaryotic
- Single celled
- No nucleus
- No membrane-bound organelles
- Bacteria are grown in the lab colonies
5
(No Transcript)
6
Kingdom 1
- Archaebacteria
- archae Greek "ANCIENT
- Modern archaebacteria MAY BE directly descended
from (and are very similar to) the first
organisms on Earth - Biochemical genetic properties differ from ALL
other kinds of life - UNICELLULAR PROKARYOTES
- Cell wall made of pseudopeptidoglycan
- No distinct nucleus with membrane around it
- Most are heterotrophic, a few are autotrophic
- Live in harsh environments
- Sulfurous hot springs, very salty lakes, and in
ANAEROBIC environments, such as the intestines of
mammals - 3 phyla
- Methanogens
- Halophiles
- Thermoacidophiles
7
Kingdoms 2
- Eubacteria
- EU "TRUE
- UNICELLULAR PROKARYOTES
- No distinct nucleus with membrane around it
- Cell wall made from peptidoglycan
- Some are heterotrophic, some are autotrophic,
some are chemotrophic - Examples
- Most of the Bacteria (Germs) that affect your
life - Includes the disease-causing bacteria such as
tooth decay or food poisoning - E. coli, Salmonella, Streptococcus
8
Typical Prokaryotic Structure
Can move using Flagella Slime Capsule Brownian
Movement
9
Bacterial Structure
- Some other important structures
- Plasmids
- Small, circular pieces of DNA
- Separate from the chromosome
- Pillus (pilli)
- Long, rigid, projection used in attachment or DNA
exchange
10
Bacteria Shapes Names
- Bacteria come in several shapes
- 3 main shapes are
- Sphere
- Rod (bacillus)
- Spiral
- The shape may determine the GENUS/GROUP name
- Whats the name of the spherical bacteria?
11
3 shapes of bacteria
Cocci
Bacillus
Spirillum
12
Shape names...plural vs. singular
- Round
- Coccus (cocci)
- Rod
- Bacillus (bacilli)
- Spiral
- Spirillum (spirilla
- or spirillia)
13
Bacterial Arrangement Naming
Pairs Diplo-
Chains Strepto-
Clusters Staphylo-
14
What kinds of Bacteria are these?
A
B
C
15
Kingdom Eubacteria
- Very strong cell walls
- Made of peptioglycan
- Less complex genetic make-up than ancient
bacteria - A. Coccoid single cells.
- B. Rod or bacillus.
- C. Spirilla or spirilloid.
- D. Coccoid filamentous streptococcus.
- E. Coccoid colonial staphylococcus. F.
Flagellate spirilloid procaryote. - G-I Examples of Cyanobacteria or "blue-green
algae"
16
What about these?
A
B
17
Identifying Bacteria
- 1st level of identification
- GRAM STAIN gram positive purple peptidoglycan
Easily TREATABLE!!! - A staining technique that will stain bacteria in
2 different ways - Gram () stain purple
- Gram (-) stain pink
18
Mix of Gram() and (-) Bacteria
19
Bacterial Growth conditions
- Moist
- Warm
- Nutrient Rich
- Some like O2, some hate it
- Obligate aerobe
- Obligate anaerobe
20
Bacterial Survival
- When conditions are unfavorable, many bacteria
can form endospores - Tough outer coating to resist extreme conditions
- They can survive boiling
- To kill them items must sterilized in an
autoclave - Uses pressure heat to kill bacteria spores!
- Ex Clostridium botulinum forms into spores
(which give off toxins) and is a major concern to
the canned food industry
21
Figure 27.10x Endospores
22
Bacteria Reproduction
- ASEXUAL
- Binary Fission
- New organism from one parent
- Not much variety in offspring
23
Bacteria Reproduction
- SEXUAL
- CONJUGATION
- Transfer of genes from one bacterial cell to
another - Occurs through a pilus
conjugation
24
Bacterial Modes of Nutrition Very Diverse
- Nutrition of prokaryotes how org obtains energy
and a carbon source to build org molecules - Are 4 categories
- 1. photoautotrophs use light to make food
- 2. chemoautotrophs need CO2 as carbon source,
and get chemical energy from inorganic substances - 3. photoheterotrophs use light to make
energy, but need a carbon source to start with - 4. chemoheterotrophs must eat other
organisms to get food in chemical form (most
bacteria are this type saprobes and parasites)
25
Ecological Impact of Prokaryotes
- Recycling of nutrients (decomposers)
- Symbiotic relationships interact with other
orgs and form food webs - Bioremediation use or orgs to remove pollutants
from water, air, and soil - Ex. Sewage treatment plants anaerobic prok
- Ex. Decompose petroleum compounds at oil spills
-- pseudomonads - Act as metabolic factories for human use
- -produce acetone, butanol
- -make vitamins, antibiotics
- -food flavorings (yogurt, cheese)
- -DNA technology produce hormones like insulin
26
Nitrogen Fixation
- All organisms need nitrogen (DNA, RNA, ATP, etc)
- Most organisms cant use N2 from the air it
needs to be in a usable form Nitrogen Fixation - Some bacteria convert N2 from the air/soil waste
into a usable form for plants
27
Bacteria are often used to fight other organisms
28
What are other bacterial uses?
29
Pathogenic Bacteria
- Pathogenic Causes disease
- Only 1 of the bacteria we know are pathogenic
- Your body will respond by making antibodies
- Antibiotics can be given to help kill them too!
- They USUALLY target bacterial cell walls break
them down or disrupt metabolism
30
Kochs Postulates 19th Century
- 1. A specific organism must be always be observed
in association with the disease. - 2. The organism must be isolated from an infected
host and grown in pure culture in the laboratory.
- 3. When organisms from the pure culture are
inoculated into a susceptible host organism, it
must cause the disease. - 4. The infectious organism must be re-isolated
from the diseased organism and grown in pure
culture.
31
(No Transcript)
32
Bacterial Infection Symptoms
- Physical damage by product of bacteria
digesting your tissue Streptococcus pyogenes - Endotoxins Listeria monocytogenes
- Exotoxins Clostridium botulinum antibodies
may work but may be overpowered - Immune reaction to foreign invaders
33
Bacterial Diseases Modes of Transmission
34
Preventing bacterial infection
- Sterilization of surfaces (with antiseptics,
heat, or steam) - Cooling, freezing food
- Dehydrating food (salt curing)
- Use chemical preservatives (food or water
chlorine) - Radiation
- Pasteurization (heating liquids)
- Canning
- Washing hands!!!
- Antibiotics are used only AFTER have infection
present
35
Antibodies vs. Antibiotics vs. Antiseptics
- Antibodies produced by white blood cells in the
body (internal line of defense) - Antibiotics kill bacteria using chemicals that
are produced OUTSIDE of the body by other sources
then - introduced IN TO body as injection or ON TO
site of infection as surface medication
36
- Antiseptics Kill bacteria on OUTSIDE of body or
on membranes that line areas leading to inside
(ex. Mouth) - Ex. Alcohol
- Listerine
- Iodine
- Hydrogen Peroxide
- Disinfectants act as surface antiseptics for
non-living surfaces before bacteria even get to
body - Ex. Chlorox
- Lysol
- Ammonia