GLYCOLYSIS - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 30
Title:
GLYCOLYSIS
Description:
Figure 9.9 A closer look at glycolysis: energy investment phase (Layer 2) ... glycolysis if there is a shortage. of oxygen in the cells. Pyruvate does not ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:240
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: GLYCOLYSIS
1
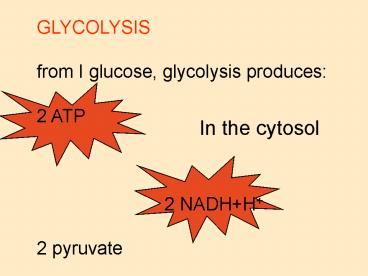
GLYCOLYSIS from I glucose, glycolysis
produces 2 ATP 2
NADHH 2 pyruvate
In the cytosol
2
Figure 9.9 A closer look at glycolysis energy
investment phase (Layer 2)
3
Figure 9.9 A closer look at glycolysis energy
payoff phase (Layer 3)
4
Figure 9.9 A closer look at glycolysis energy
payoff phase (Layer 4)
PEP
5
Conversion of pyruvate to acetyl CoA, the
junction between glycolysis and the Krebs cycle
Linking reaction
6
Figure 9.11 A closer look at the Krebs cycle
(Layer 4)
x2
7
Can make 12 amino acids
Can oxidize amino acids
Krebs Cycle is a metabolic hub
Can oxidize fatty acids as molecules of acetyl CoA
8
A summary of the Krebs cycle
8 NADHH 2 FADH2 2 ATP
1x22
1x22
3x26
1x22
9
Each molecule of glucose yields many ATP
molecules during cellular respiration
10
Figure 9.15 Chemiosmosis couples the electron
transport chain to ATP synthesis
11
(No Transcript)
12
Muscle cells
Lactic acid forms at the end of glycolysis if
there is a shortage of oxygen in the cells
Pyruvate does not become acteylCoA
13
Free-energy change during electron transport
14
Energy from the transferred electrons is used to
transport H ions into the intermembranous space
of the mitochondrion
15
Figure 9.14 ATP synthase, a molecular mill
16
Figure 9.15 Chemiosmosis couples the electron
transport chain to ATP synthesis
17
The energy input and output of glycolysis
18
Fermentation similar to glycolysis
- An anerobic , inefficient pathway making
- 2ATP and alcohol, lactic acid or
- acetic acid
- Occurs in bacteria and yeast
- Much energy still remains in the organic end
products
19
Figure 9.17a Fermentation
20
Figure 9.17a Fermentation
NAD is restored as Acetyaldehyde is changed to
alcohol
21
Yeast a unicellular fungus makes alcohol
C2H5OH
22
Anaerobic conditions in muscle
Pyruvate builds up causing muscle fatigue
and cramps occur when there is an oxygen debt
in the cells
23
Acids are made from sugar when bacteria do
anaerobic fermentation. Soured milk products
contain lactic acid
In muscle when it is anaerobic
24
Figure 9.18 Pyruvate as a key juncture in
catabolism
25
Figure 9.19 The catabolism of various food
molecules
Metabolic Hub Products of carbohydrate. protein
and lipid Catabolism enter here
Needed amino acids
26
Figure 9.11 A closer look at the Krebs cycle
(Layer 4)
x2
27
(No Transcript)
28
(No Transcript)
29
Figure 9.17b Fermentation
NAD is restored as pyruvate Is converted to
lactic acid
30
- What products are made through fermentation by
yeast or bacteria?