Spectroscopy for Analysis of Automobile Emissions - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Spectroscopy for Analysis of Automobile Emissions
... for Analysis of Automobile Emissions. Stedman, Univ. of ... Molecules put into excited state by a lamp or electric discharge. Laser light is coherent, ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Title: Spectroscopy for Analysis of Automobile Emissions
1
Spectroscopy for Analysis of Automobile Emissions
Stedman, Univ. of Denver
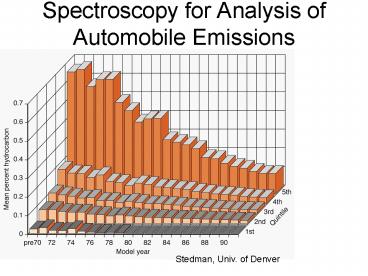
2
Stedmans Work
3
Double-Beam Spectrometer
Light is alternated through a reference and
sample cell so you do not have to swap out the
blank and the analyte.
4
Insides of a DB Spectrophotometer
Deuterium arc lamp
Halogen lamp
5
Lamp Sources
- Tungsten lamp (320-2500 nm)
- Deuterium arc lamp (200-400 nm)
- Hg vapor arc lamp (225 -800)
- Xe gas arc lamp (200-1000 nm)
- Globar (SiC) (1-40 mm)
6
Emission Wavelentghs of D2 and W
7
How does a Laser Work?
When a photon from E2 hits another E2 it causes
another photon
Molecules put into excited state by a lamp or
electric discharge
Fast Processes
(Greater population of excited state than ground
state)
Laser light is coherent, meaning that all
waves are in phase
8
Laser Sources
- Lasers can be operated as constant output
(continuous wave-CW) or pulsed output - Solid-state
- NdYAG (1064, 532, 266 nm)
- Ruby laser (694.3 nm)
- Gas lasers
- HeNe (3390, 1150, 633 nm)
- Ar (488.8, 514.6 nm)
- CO2 (10600 nm)
- Dye lasers (virtually any wavelength)
Most reliable lasers
Most powerful lasers
9
Monochromators
- A monochromator disperses light into component
wavelengths and picks a narrow band to pass on to
sample cell or detector - The most common is a diffraction grating, which
is an optical component with a series of lines
that reflect light - As light hits the lines, each of the lines
behaves as an individual light source
10
Grating Diagram
Collimates (makes parallel) the light
Focuses the light
?s diffract at different angles
Only 1 ? at a time can make it through the slit
PowerShow.com is a leading presentation sharing website. It has millions of presentations already uploaded and available with 1,000s more being uploaded by its users every day. Whatever your area of interest, here you’ll be able to find and view presentations you’ll love and possibly download. And, best of all, it is completely free and easy to use.
You might even have a presentation you’d like to share with others. If so, just upload it to PowerShow.com. We’ll convert it to an HTML5 slideshow that includes all the media types you’ve already added: audio, video, music, pictures, animations and transition effects. Then you can share it with your target audience as well as PowerShow.com’s millions of monthly visitors. And, again, it’s all free.
About the Developers
PowerShow.com is brought to you by CrystalGraphics, the award-winning developer and market-leading publisher of rich-media enhancement products for presentations. Our product offerings include millions of PowerPoint templates, diagrams, animated 3D characters and more.