Reading Condition Codes (Cont.) - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 42
Title:
Reading Condition Codes (Cont.)
Description:
Set single byte based on combinations of condition codes. One ... Example from disassembly. 804854e: e8 3d 06 00 00 call 8048b90 main 8048553: 50 pushl êx ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:21
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Reading Condition Codes (Cont.)
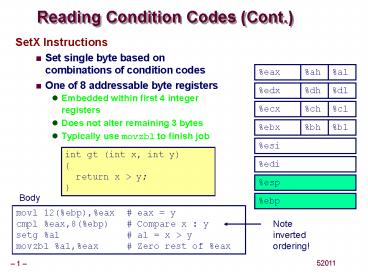
1
Reading Condition Codes (Cont.)
- SetX Instructions
- Set single byte based on combinations of
condition codes - One of 8 addressable byte registers
- Embedded within first 4 integer registers
- Does not alter remaining 3 bytes
- Typically use movzbl to finish job
eax
al
ah
edx
dl
dh
ecx
cl
ch
ebx
bl
bh
esi
int gt (int x, int y) return x gt y
edi
esp
Body
ebp
movl 12(ebp),eax eax y cmpl eax,8(ebp)
Compare x y setg al al x gt y movzbl
al,eax Zero rest of eax
Note inverted ordering!
2
Jumping
- jX Instructions
- Jump to different part of code depending on
condition codes
3
Conditional Branch Example
_max pushl ebp movl esp,ebp movl
8(ebp),edx movl 12(ebp),eax cmpl
eax,edx jle L9 movl edx,eax L9 leave ret
Set Up
int max(int x, int y) if (x gt y) return
x else return y
Body
Finish
4
Conditional Branch Example (Cont.)
int goto_max(int x, int y) int rval y
int ok (x lt y) if (ok) goto done
rval x done return rval
- C allows goto as means of transferring control
- Closer to machine-level programming style
- Generally considered bad coding style
movl 8(ebp),edx edx x movl
12(ebp),eax eax y cmpl eax,edx x
y jle L9 if lt goto L9 movl edx,eax eax
x L9 Done
Skipped when x ? y
5
Do-While Loop Example
C Code
Goto Version
int fact_do (int x) int result 1 do
result x x x-1 while (x gt 1)
return result
int fact_goto(int x) int result 1 loop
result x x x-1 if (x gt 1) goto
loop return result
- Use backward branch to continue looping
- Only take branch when while condition holds
6
Do-While Loop Compilation
Goto Version
Assembly
int fact_goto (int x) int result
1 loop result x x x-1 if (x gt 1)
goto loop return result
_fact_goto pushl ebp Setup movl esp,ebp
Setup movl 1,eax eax 1 movl
8(ebp),edx edx x L11 imull edx,eax
result x decl edx x-- cmpl 1,edx
Compare x 1 jg L11 if gt goto loop movl
ebp,esp Finish popl ebp Finish ret
Finish
- Registers
- edx x
- eax result
7
IA32 Stack
Stack Bottom
- Region of memory managed with stack discipline
- Grows toward lower addresses
- Register esp indicates lowest stack address
- address of top element
Stack Grows Down
Stack Top
8
IA32 Stack Pushing
- Pushing
- pushl Src
- Fetch operand at Src
- Decrement esp by 4
- Write operand at address given by esp
Stack Bottom
Stack Grows Down
-4
Stack Top
9
IA32 Stack Popping
- Popping
- popl Dest
- Read operand at address given by esp
- Increment esp by 4
- Write to Dest
Stack Bottom
Stack Grows Down
4
Stack Top
10
Stack Operation Examples
pushl eax
popl edx
0x110
0x110
0x110
0x10c
0x10c
0x10c
0x108
123
0x108
123
0x108
123
0x104
0x104
213
213
eax
eax
eax
213
213
213
edx
edx
edx
555
555
555
213
esp
esp
esp
0x108
0x108
0x104
0x104
0x108
11
Procedure Control Flow
- Use stack to support procedure call and return
- Procedure call
- call label Push return address on stack Jump to
label - Return address value
- Address of instruction beyond call
- Example from disassembly
- 804854e e8 3d 06 00 00 call 8048b90 ltmaingt
- 8048553 50 pushl eax
- Return address 0x8048553
- Procedure return
- ret Pop address from stack Jump to address
12
Procedure Call Example
804854e e8 3d 06 00 00 call 8048b90
ltmaingt 8048553 50 pushl eax
call 8048b90
0x110
0x110
0x10c
0x10c
0x108
123
0x108
123
0x104
0x8048553
esp
esp
0x108
0x108
0x104
eip
eip
0x804854e
0x804854e
0x8048b90
eip is program counter
13
Procedure Return Example
8048591 c3 ret
ret
0x110
0x110
0x10c
0x10c
0x108
123
0x108
123
0x104
0x8048553
0x8048553
esp
esp
0x104
0x104
0x108
eip
eip
0x8048591
0x8048591
0x8048553
eip is program counter
14
Call Chain Example
- Code Structure
Call Chain
yoo() who()
yoo
who() amI() amI()
who
amI
amI
amI() amI()
amI
amI
- Procedure amI recursive
15
Stack Frames
- Contents
- Local variables
- Return information
- Temporary space
- Management
- Space allocated when enter procedure
- Set-up code
- Deallocated when return
- Finish code
- Pointers
- Stack pointer esp indicates stack top
- Frame pointer ebp indicates start of current
frame
yoo
who
amI
proc
Stack Top
16
Stack Operation
yoo
Call Chain
yoo() who()
yoo
17
Stack Operation
yoo
Call Chain
who() amI() amI()
yoo
who
who
18
Stack Operation
yoo
Call Chain
amI() amI()
yoo
who
who
amI
amI
19
Stack Operation
yoo
Call Chain
amI() amI()
yoo
who
who
amI
amI
amI
amI
20
Stack Operation
yoo
Call Chain
amI() amI()
yoo
who
who
amI
amI
amI
amI
amI
amI
21
Stack Operation
yoo
Call Chain
amI() amI()
yoo
who
who
amI
amI
amI
amI
amI
22
Stack Operation
yoo
Call Chain
amI() amI()
yoo
who
who
amI
amI
amI
amI
23
Stack Operation
yoo
Call Chain
who() amI() amI()
yoo
who
who
amI
amI
amI
24
Stack Operation
yoo
Call Chain
amI()
yoo
who
who
amI
amI
amI
amI
amI
25
Stack Operation
yoo
Call Chain
who() amI() amI()
yoo
who
who
amI
amI
amI
amI
26
Stack Operation
yoo
Call Chain
yoo() who()
yoo
who
amI
amI
amI
amI
27
IA32/Linux Stack Frame
- Current Stack Frame (Top to Bottom)
- Parameters for function about to call
- Argument build
- Local variables
- If cant keep in registers
- Saved register context
- Old frame pointer
- Caller Stack Frame
- Return address
- Pushed by call instruction
- Arguments for this call
Caller Frame
Arguments
Frame Pointer (ebp)
Return Addr
Old ebp
Saved Registers Local Variables
Argument Build
Stack Pointer (esp)
28
Revisiting swap
Calling swap from call_swap
int zip1 4 int zip2 5 void main()
swap(zip1, zip2)
call_swap pushl zip2 Global
Var pushl zip1 Global Var call swap
Resulting Stack
void swap(int xp, int yp) int t0 xp
int t1 yp xp t1 yp t0
zip2
zip1
Rtn adr
esp
29
Revisiting swap
swap pushl ebp movl esp,ebp subl 16,
esp movl 8(ebp),edx movl (edx),eax
mov1 eax,-8(ebp) movl 12(ebp),ecx movl
(ecx),eax movl eax,-4(ebp) movl
-8(ebp),eax movl eax,(edx) movl
-4(ebp),eax movl eax,(ecx) leave ret
Set Up
void swap(int xp, int yp) int t0 xp
int t1 yp xp t1 yp t0
Body
Finish
30
swap Setup 1
Resulting Stack
Entering Stack
ebp
zip2
zip1
Rtn adr
esp
swap pushl ebp movl esp,ebp
31
swap Setup 2
Resulting Stack
Entering Stack
ebp
yp
zip2
xp
zip1
Rtn adr
Rtn adr
esp
ebp
Old ebp
esp
swap pushl ebp movl esp,ebp
32
swap Setup 3
Resulting Stack
Entering Stack
ebp
yp
zip2
xp
zip1
Rtn adr
Rtn adr
esp
ebp
Old ebp
t1
swap pushl ebp movl esp,ebp subl 16, esp
t0
esp
33
Effect of swap Setup
Entering Stack
Resulting Stack
ebp
Offset (relative to ebp)
yp
12
zip2
xp
8
zip1
Rtn adr
4
Rtn adr
esp
ebp
Old ebp
0
t1
t0
movl 8(ebp),eax get xp . . .
Body
esp
34
swap Finish
ebp
swaps Stack
swaps Stack
Offset
Offset
yp
12
yp
12
xp
8
xp
8
Rtn adr
4
Rtn adr
4
esp
Old ebp
0
ebp
esp
leave ret
35
swap Finish
ebp
ebp
swaps Stack
Exiting Stack
Offset
zip2
yp
12
zip1
esp
xp
8
Rtn adr
4
esp
leave ret
36
Register Saving Conventions
- When procedure yoo calls who
- yoo is the caller, who is the callee
- Can Register be Used for Temporary Storage?
- Contents of register edx overwritten by who
yoo movl 15213, edx call who addl edx,
eax ret
who movl 8(ebp), edx addl 91125,
edx ret
37
Register Saving Conventions
- When procedure yoo calls who
- yoo is the caller, who is the callee
- Can Register be Used for Temporary Storage?
- Conventions
- Caller Save
- Caller saves temporary in its frame before
calling - Callee Save
- Callee saves temporary in its frame before using
38
IA32/Linux Register Usage
- Integer Registers
- Two have special uses
- ebp, esp
- Three managed as callee-save
- ebx, esi, edi
- Old values saved on stack prior to using
- Three managed as caller-save
- eax, edx, ecx
- Do what you please, but expect any callee to do
so, as well - Register eax also stores returned value
eax
Caller-Save Temporaries
edx
ecx
ebx
Callee-Save Temporaries
esi
edi
esp
Special
ebp
39
Pointer Code
Recursive Procedure
Top-Level Call
void s_helper (int x, int accum) if (x lt
1) return else int z accum x
accum z s_helper (x-1,accum)
int sfact(int x) int val 1 s_helper(x,
val) return val
- Pass pointer to update location
40
Creating Initializing Pointer
Initial part of sfact
_sfact pushl ebp Save ebp movl esp,ebp
Set ebp subl 16,esp Add 16 bytes movl
8(ebp),edx edx x movl 1,-4(ebp) val 1
_sfact pushl ebp Save ebp movl esp,ebp
Set ebp subl 16,esp Add 16 bytes movl
8(ebp),edx edx x movl 1,-4(ebp) val 1
_sfact pushl ebp Save ebp movl esp,ebp
Set ebp subl 16,esp Add 16 bytes movl
8(ebp),edx edx x movl 1,-4(ebp) val 1
_sfact pushl ebp Save ebp movl esp,ebp
Set ebp subl 16,esp Add 16 bytes movl
8(ebp),edx edx x movl 1,-4(ebp) val 1
x
8
Rtn adr
4
Old ebp
0
-4
-8
- Using Stack for Local Variable
- Variable val must be stored on stack
- Need to create pointer to it
- Compute pointer as -4(ebp)
- Push on stack as second argument
-12
-16
int sfact(int x) int val 1 s_helper(x,
val) return val
41
Passing Pointer
Calling s_helper from sfact
Stack at time of call
x
8
leal -4(ebp),eax Compute val pushl eax
Push on stack pushl edx Push x call
s_helper call movl -4(ebp),eax Return
val Finish
leal -4(ebp),eax Compute val pushl eax
Push on stack pushl edx Push x call
s_helper call movl -4(ebp),eax Return
val Finish
leal -4(ebp),eax Compute val pushl eax
Push on stack pushl edx Push x call
s_helper call movl -4(ebp),eax Return
val Finish
Rtn adr
4
ebp
Old ebp
0
val 1
-4
val x!
Unused
-8
-12
int sfact(int x) int val 1 s_helper(x,
val) return val
-16
42
Using Pointer
void s_helper (int x, int accum)
int z accum x accum z
accumx
accumx
x
ecx
movl ecx,eax z x imull
(edx),eax z accum movl eax,(edx)
accum z
- Register ecx holds x
- Register edx holds pointer to accum
- Use access (edx) to reference memory