Framework of Statistical Information
Title:
Framework of Statistical Information
Description:
Examples of online indexes to print resources: ... of online catalogues that include print resources: ... If Statistics, is the information in print or online? ... –
Number of Views:15
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Framework of Statistical Information
1
Framework of Statistical Information
2
Framework of Statistical Information
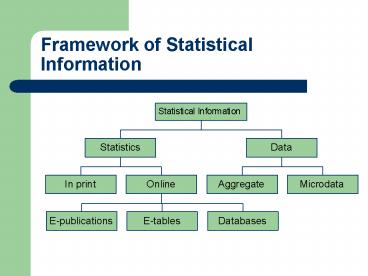
This is a typology of the categories or classes
of statistical information. Remember the
relationship between statistics and data,
however, is causal. Statistics are created from
data.
3
Framework of Statistical Information
An overlap occurs in this chart between
Statistics Databases and Data Aggregate, which
will be discussed below.
4
Framework of Statistical Information
5
Framework of Statistical Information
In print
6
In Print
- Rely on yearbooks, statistical abstracts,
catalogues, and indexes to locate statistics in
print. - Examples of online indexes to print resources
- Statistical Universe (U.S., international,
government and private) - Tablebase
- Example of online catalogues that include print
resources - U.S. Census Bureau Sales Catalog
- Statistics Canadas Online Catalogue
7
(No Transcript)
8
Framework of Statistical Information
Online
9
Online Statistics
- Example of e-publications
- Statistical Abstract of the United States
- Statistics Canada Downloadable Publications (DSP)
- Example of e-tables
- Tables and publications containing U.S.
Consumer Price Indexes - Canadian Statistics (STC Website)
- Example of statistical databases
- American Fact Finder and Data Ferrett
- CANSIM II (STC Website, E-STAT, CHASS)
10
E-Publications
- Tend to be available in PDF format
- Can use the Select Text Tool in the Adobe
Reader and copy columns to another application
11
(No Transcript)
12
Statistical Information
13
E-Tables
- Tend to be displayed in HTML
- May provide a pull-down list to view other
categories in the table - Some e-tables will provide an alternate format
for the table that can be downloaded (e.g., the
Canadian Census tables are available in
comma-separated ASCII, IVT, and print-friendly
formats)
14
(No Transcript)
15
(No Transcript)
16
Databases
- Often use HTML forms to define the statistics to
be retrieved - May offer a variety of output formats for the
retrieved statistics (e.g., E-STAT provides IVT
format for Beyond 20/20, graphs, charts, maps,
and ASCII formats for spreadsheets and databases)
17
(No Transcript)
18
(No Transcript)
19
(No Transcript)
20
Framework of Statistical Information
Aggregate Data
21
Aggregate Data
- Aggregate data consist of statistics that are
organized into a data structure and stored in a
database or in a data file. - The data structure is based on tabulations
organized by time, geography, or social content.
22
Aggregate Data
- Data Structure
- Time
- Geography
- Social Content
- Example
- CANSIM II
23
Aggregate Data
- Time series data have long fueled econometric
models based on macro-economic indicators. - Comma-separate values (CSV) have become an
important format for time series data, which is
often manipulated in Excel if not analyzed in a
spreadsheet.
24
Aggregate Data
- Data Structure
- Time
- Geography
- Social Content
- Example
- CENSUS
25
(No Transcript)
26
Aggregate Data
- Increased availability of GIS software has
created greater demand for Census statistics
organized as aggregate data. - Beyond 20/20 has become a popular tool for
reshaping census statistics from 1996 and 2001
for use with GIS software. - DBF is the most commonly used format to share
census statistics with GIS software.
27
Aggregate Data
A map from E-STAT of Montreal Census Tracts
28
Aggregate Data
- Small area statistics are a special category of
aggregate data. These data files consist of
statistics for small geographic areas usually
calculated from a population or manufacturing
census or an administrative database with enough
cases to create accurate summaries for small
areas.
29
Aggregate Data
- Data Structure
- Time
- Geography
- Social Content
- Example
- Cause of Death (HID)
30
Aggregate Data
- Also known as cross-classified tables, these
files tend to be made of statistics constructed
from social-content variables. Examples of
cross-classified tables in DLI are found in
education and justice.
31
Framework of Statistical Information
Microdata
32
Microdata
- This is raw data organized in a file where the
lines in the file represent a specific unit of
observation and the information on the lines are
the values of variables. - There are different types of microdata files,
which will now be discussed.
33
Confidential Microdata
- Master files these files contain the fullness of
detail captured about each case of the unit of
observation. This detail is specific enough that
the identify of a case can often be disclosed
easily. Therefore, these files are treated as
confidential.
34
Confidential Microdata
- Share files these are confidential files in
which the participants in the survey have signed
a consent form permitting Statistics Canada to
allow access to their information for approved
research. - These files consist of a subset of the cases in
the master file.
35
Confidential Microdata
- In summary, confidential microdata get grouped
into two types - master files and share files.
36
Public Use Microdata
- These microdata are specially prepared to
minimize the possibility of disclosing or
identifying any of the cases in a file, i.e,
participants in a survey. - The original data from the master file are edited
to create a public use microdata file.
37
Public Use Microdata
- Steps in Anonymizing Microdata
- Remove of all personal identification information
(names, addresses, etc) - Include only gross levels of geography
- Collapse detailed information into a smaller
number of general categories - Cap the upper range of values of variables with
rare cases - Suppress the values of a variable or
- Suppress entire cases.
38
Public Use Microdata
- Statistics Canada PUMFs
- Only available for select social surveys that
undergo a review of the Data Release Committee,
an internal Statistics Canada committee. - No enterprise public use microdata.
39
Public Use Microdata
- Statistics Canada PUMFs
- Almost all PUMFs consist of cross-sectional
samples, that is, samples where the data have
been collected from respondents at one point in
time. - Longitudinal samples, where data are collected
from the same individuals two or more times, are
difficult to anonymize and maintain any useful
information.
40
Synthetic Microdata
- These data files have been created to assist with
the analysis of confidential data files. - The files provide the full variable structure of
the confidential microdata but do not contain any
real cases. - They are intended to be used by researchers
wanting to submit a file of commands in a
statistical packages language for remote job
submission.
41
Synthetic Microdata
- They are also being used by those with approved
projects in Research Data Centres to help prepare
their analysis strategies prior to working in an
RDC. - Synthetic files are also commonly referred to as
dummy files, although a more technical use of
this term does exist for this specific type of
synthetic file.
42
Synthetic Microdata
- A variety of synthetic file types are being
created and tested by author divisions. - One type has no real data but does contain a
complete set of real variables. This type is the
more technical reference to a dummy file. - Another type has a mix of real data but no real
cases. The purpose of this type is to provide --
in the aggregate -- results that should be close
to an analysis of the real microdata file.
43
Synthetic Microdata
- Users of these files must be advised that none of
the analytic results from these files should ever
be reported. Their only purpose is to help
researchers construct their statistical analysis
programs to guard against syntax errors that
might exist in their setup.
44
Framework of Statistical Information
45
Framework Summary
- This framework provides a way of thinking about
the types of statistical information that exist. - Is the information Statistics or Data?
- If Statistics, is the information in print or
online? - If online, is it in an e-pub, e-table, or
database? - If Data, is the information aggregate data or
microdata?