Composition of Polybasic Acids vs' pH
1 / 10
Title:
Composition of Polybasic Acids vs' pH
Description:
Composition of Polybasic Acids vs. pH. Useful to know how the concentration of a ... Composition of Polybasic Acids vs. pH. ai represents the fraction of each ... –
Number of Views:34
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Composition of Polybasic Acids vs' pH
1
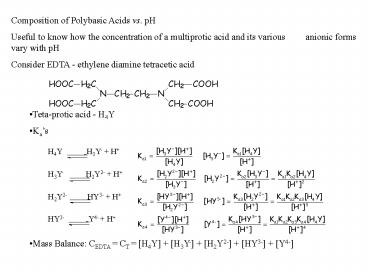
- Composition of Polybasic Acids vs. pH
- Useful to know how the concentration of a
multiprotic acid and its various anionic forms
vary with pH - Consider EDTA - ethylene diamine tetracetic acid
- Teta-protic acid - H4Y
- Kas
- H4Y H3Y- H
- H3Y- H2Y2- H
- H2Y2- HY3- H
- HY3- Y4- H
- Mass Balance CEDTA CT H4Y H3Y-
H2Y2- HY3- Y4-
2
- Composition of Polybasic Acids vs. pH
- ai represents the fraction of each species in
solution
- Examine Figure xxx, FAC7 p. xxx
3
- Complexometric Methods EDTA
- Some terms
- Lewis acid - base interactions involve the
donation of an electron pair by a Lewis base to
an electron pair acceptor, the Lewis acid - Lewis bases often contain electron rich donor
atoms such as amine nitrogens and oxygen atoms - Ligand molecules contain the electron donor atoms
- Ligand molecules having one donor atom are called
monodentate - Other ligand molecules have 2 donor atoms
(bidentate), 3 donor atoms (tridentate), 4
donor atoms (tetradentate), 5 donor atoms
(pentadentate) or 6 donor atoms (hexadentate) - Complexes formed from polydentate ligands are
called chelates - Chelate from the greek chele meaning claw
giving the English word chela meaning the
pincerlike organ or claw borne by certain of
the limbs of crustaceans and arachnids
4
- Complexometric Methods EDTA
- Some terms
- Lewis acids can metal ions, neutral metal atoms
and electron deficient atoms in molecules - The coordination number of the metal is the
number of ligand donor atoms connected to the
metal Lewis acid - Common coordination numbers are 2, 4 and 6
although 5 is not uncommon and 7 or 8 is known
for some large metal ions such as W - Consider several types of complexation reactions
for a metal with coordination number 4 - Formation of a 11 complex with a tetradentat
ligand - M D MD
- Formation of a 21 complex with 2 bidentate
ligands - M B MB
- MB B MB2
- M 2B MB2
5
- Complexometric Methods EDTA
- Consider several types of complexation reactions
for a metal with coordination number 4 - Formation of a 41 complex with 4 monodentate
ligands - M A MA
- MA A MA2
- MB2 A MA3
- MB3 A MA4
- M 4A MA4
- If its assumed Kf b2 b4 1020 and
- For the bidentate case, Kf1 1012 and Kf2 108
- For the tetradentate case, Kf1 108, Kf2 106,
Kf3 104 and Kf4 102 - Examine the titration curves of 60.00 mL of a
0.0200 M solution of a metal with - 0.0200 M D
- 0.0400 M B, and
- 0.0800 M A
See Figure 14-1, FAC7 p. 279
6
- Complexometric Methods EDTA
- Titration curves of a metal with various ligands
- Its obvious the tetradentate ligand gives a
superior titration curve - Its also the case that the formation constants
of metal complexes with polydentate ligands
having the same kind of donor atoms are larger - The entropy effect
7
- Complexometric Methods EDTA
- Titration curves for EDTA complex formation
- The reaction between a metal ion and EDTA depends
on the pH because the protonated EDTA species
present depends on pH - Remember
- At pH 8.00, the major species is HY3- and the
reaction between a metal ion is - Mn HY3- MY(n-4) H
- But we wish to calculate the titration curve from
Kf which involves the reaction Mn Y4-
MY(n-4) - and since Y4- a4CT,
8
- Complexometric Methods EDTA
- Titration curves for EDTA complex formation
- The text lists Kfs for 18 metal ion - EDTA
complexes in Table 14-1, FAC7 p. 282 - The strategy is to calculate Kf and pretend CT
behaves like Y4-, calculate Mn and CT then
calculate Y4- from a4CT - Example Calculate the titration curve for 50.00
mL 0.01000 M Ca2 with 0.01000 M EDTA at pH
10.00. - a4 as a function of pH is given in Table 14-2,
FAC7 p. 284 - at pH 10.00, a4 0.35
- Kf(CaY2-) 5.08 x 1010 Kf Kf a4 1.75
x 1010 - At 0.00 mL added EDTA, Ca2 0.01 pCa 2.00
- Y4- 0 pY ?
- At 10.00 mL added EDTA
9
- Complexometric Methods EDTA
- Example Calculate the titration curve for 50.00
mL 0.01000 M Ca2 with 0.01000 M EDTA at pH
10.00 - At the equivalence point
- At 55.00 mL
10
- Complexometric Methods EDTA
- Effect of pH on the shape of the titration curve
of Ca2 with EDTA - As pH decreases, a4 decreases rapidly, so a4Kf
Kf drops rapidly - Thus Ca2 at the equivalence point will be
higher and pCa lower - And Ca2 after the equivalence point will be
higher and pCa lower - See Figure 14-6, FAC7 p. 289
- Effect of Kf on shape of the titration curve
- As Kf decreases, pM at the equivalence point
decreases - As Kf decreases, pM after the equivalence point
decreases - See Figure 14-7, FAC7 p. 289
- There is a minimum pH at which any metal ion may
be titrated so as to give a satisfactory change
in pM with change in Volume of titrant at the
equivalence point - See Figure 14-8, FAC7 p. 290
- Consider the titration of Fe3 with EDTA
- If pH too high, Fe(OH)3 will precipitat, since
Ksp(Fe(OH)3) 4 x 10-38 - If Fe30.01, Fe(OH)3 precipitates at
OH-1.59 x 10-12, pH2.20 - Minimum pH for EDTA titration is 1.8, so the
solution must be buffered very carefully