Parallel flow simulation - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 1
Title:
Parallel flow simulation
Description:
A vascular disorder can be detected by several imaging techniques such as X-ray ... Pre-operative surgical planning will allow evaluation of different procedures a ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:49
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Parallel flow simulation
1
- Simulated Vascular Reconstruction in a Virtual
Operating Theatre
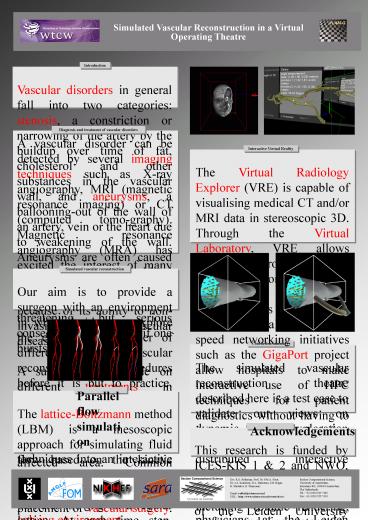
The Virtual Radiology Explorer (VRE) is capable
of visualising medical CT and/or MRI data in
stereoscopic 3D. Through the Virtual Laboratory,
VRE allows medical data from hospitals to be
processed on remote high performance computing
(HPC) systems for simulation and 3D
visualisation. High speed networking initiatives
such as the GigaPort project allow hospitals to
make interactive use of HPC techniques for
patient diagnostics without having to invest in
these (often expensive) machines. VRE provides
various methods for visualisation, including
volume rendering, surface rendering, interactive
clipping and surface mapping techniques. VRE can
be used in a CAVE Virtual Reality theatre but
also on low cost commodity PC hardware in
conjunction with a projection display and
tracking hardware, allowing VRE to be used in the
radiology department. Multi-modal interaction
methods such as speech recognition, hand
gestures, direct manipulation of virtual 3D
objects and measurement tools allow researchers
to explore simulation and visualization results
and to control their behaviour.
The simulated vascular reconstruction theatre
described here is a test case to validate our
views on dynamic exploration environments that
support distributed interactive simulation. A
prototype of VRE has already been evaluated by
radiologists and physicians at the Leiden
University Medical Center (LUMC). Based on their
feedback, we have extended VRE with multi-modal
interaction techniques and distributed simulation
support. The simulated vascular reconstruction
operating theatre will be validated through a
comparison of fluid flow simulation results and
the results of other simulation methods as well
as in vivo measurements of blood flow through
phantom structures and pre- and post-operative
MRA scans.
Parallel flow simulation
Acknowledgements
This research is funded by ICES-KIS 1 2 and
NWO, in cooperation with the medical imaging
department of the Leiden University Medical
Center (LUMC). We would like to thank Charles
Taylor, Stanford University, for the use of his
datasets.