SECONDARY STORAGE - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 9
Title:
SECONDARY STORAGE
Description:
Cartridge tape. CD-ROM. Magnetic-Optical drive. PC Cards. Smart Cards. SECONDARY STORAGE ... Cheap per MB (compared to RAM/ROM) Convenient (compared to filing ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:22
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: SECONDARY STORAGE
1
SECONDARY STORAGE
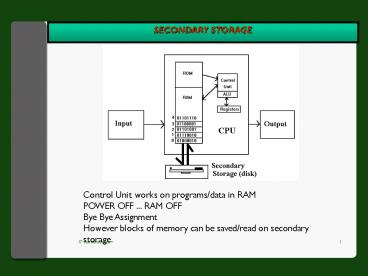
Control Unit works on programs/data in RAM POWER
OFF ... RAM OFF Bye Bye Assignment However blocks
of memory can be saved/read on secondary storage.
2
SECONDARY STORAGE
- Non-volatile (compared to RAM)
- Cheap per MB (compared to RAM/ROM)
- Convenient (compared to filing cabinet)
- Relatively fast (compared to filing cabinet)
Secondary Storage Media and Devices Floppy
Disks Hard Disks Tape and Tape drive Cartridge
tape CD-ROM Magnetic-Optical drive PC Cards Smart
Cards
3
FLOPPY DISKS
- 3 1/2-inch diskette
- Circular piece of plastic
- Made up of tracks sectors
- 512 bytes in each sector
Size Type Tracks Sectors Capacity IBM 3½
DD 80 9 720KB 3½ HD 80 18
1.44MB
eg. for a 3½ disk (double density)
4
HARD DISKS
- Made up of platters, cylinders and sectors
- Rotation speed 7200 rpm
- head 'floats' on surface
- bad sectors head crash
- capacities range from 10 to 100 GB
- Maintaining data stored on a disk
- Backup
- Fragmentation
5
Formatting a Disk
- Defines the tracks and sectors on the surface of
the disk. - Generally erases all data ('cleans' the disk)
- creates FAT (File Allocation Table) and root
directory structure - FAT contains information on sectors for each
file plus free sectors
Time to retrieve data from disk Access
Time Seek Time Time for the read/write
head to find the right track Rotational Delay
Time for the right sector to rotate under the
read/write head Data Transfer Time Time for the
data to transfer from disk to RAM
6
Hard Disk Vs Floppy Disk
Hard Floppy rotates constantly stops/starts
high speed . low speed High storage
capacity . Low storage capacity .. Access
time approx. . Access time approx. ..
- OPTICAL STORAGE TECHNOLOGY
- CD-ROM (compact disk read-only memory)- 650 MB
of information - DVD (digital video disk) - 4.7 gigabytes
- CD-R (compact disk-recordable)
- CD-RW (compact disk-rewritable)
- Magneto-optical (MO) combines magnetic/optical
technology by changing polarity of spot (1 to 0
etc.)
7
CDROM
- Compact Disk Read Only Memory
- high capacity, 600 - 700 MB
- read only (WORM)
- Speed rated as ?X. 16X speed 150 kbps x
16 2,400 kbps. - high capacity is ideal for storage of the very
large sound, graphics and video files - when recording data, laser light burns pits on
CD - when reading data, pits will not reflect light
(binary bit 0) but lands will reflect light
(binary bit 1)
8
TAPE
- Thin ribbon of plastic
- Sequential storage mainly for backup
- Types of tape organisation
- QIC records data in narrow tracks along the
length of the tape. When the end is reached, the
tape reverses direction and data is recorded on
the next track in the opposite direction. This is
called longitudinal or serpentine recording. - DAT drives use helical scan technology to record
data across the width of the tape at a 6 degree
angle.
9
OTHER TYPES OF STORAGE DEVICES
- PC cards
- Small, credit card-sized cards that fit into PC
Card expansion slots - Used for storage, communications and additional
memory. - Most often used with portable computers
- Can store more than 300 MB of data
RAID storage systems
- Smart Cards
- Credit card-sized devices that contain a
microprocessor - Microprocessor can store up to 8,000 bytes of
information. - Examples of uses - prepaid telephone card,
employee time card