Lipid - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 57
Title: Lipid
1
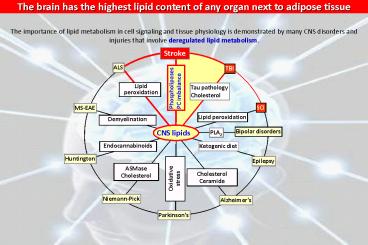
The brain has the highest lipid content of any
organ next to adipose tissue
The importance of lipid metabolism in cell
signaling and tissue physiology is demonstrated
by many CNS disorders and injuries that involve
deregulated lipid metabolism.
Stroke
ALS
TBI
Phospholipases PC imbalance
Tau pathology Cholesterol
Lipid peroxidation
SCI
MS-EAE
Lipid peroxidation
Demyelination
Bipolar disorders
CNS lipids
PLA2
Ketogenic diet
Endocannabinoids
Huntington
Epilepsy
ASMase Cholesterol
Cholesterol Ceramide
Oxidative stress
Niemann-Pick
Alzheimers
Parkinsons
2
Altered Lipid Metabolism in Stroke Therapeutic
strategies
Rao M Adibhatla, Ph. D. Dept. of Neurological
Surgery adibhatl_at_neurosurg.wisc.edu http//www.neu
rosurg.wisc.edu/labs/adibhatla
University of Wisconsin - Madison School of
Medicine and Public Health
3
Brain receives 15-20 of the body's blood supply
2 of the total body weight 3 lbs, size of
medium cauliflower
4
Atherosclerosis Plaque and stroke
LDL 500 PC, 200 SM, 400 cholesterol, TG, CE, and
apo B-100 EO6 anti-bodies against OxPC
5
Plaque Formation and Blood Clots
Ruptured plaque initiates blood clot formation
(red blood cells, fibrin clot)
6
Stroke or Brain attack
- 1st leading cause of disability, the 2nd leading
cause of death in elderly - An average of 740,000 strokes occur annually of
which 167,000 result in death - 4 million Americans are living with disabling
effects of stroke - Annual cost is gt 63 billion
7
Why does brain need blood supply?
- Blood carries oxygen and glucose
- Oxygen burns the glucose to generate energy (ATP)
- When a part of the brain doesnt get blood
supply, it doesnt get any energy - Outcome that part of the brain will be
incapacitated
What Is Stroke?
- Stroke is loss of blood supply to part of the
brain
Two types of strokes
- Ischemic (Greek, isch- is restriction, hema is
blood) - Hemorrhagic
8
Ischemic Stroke and blood brain barrier
dysfunction
Evans blue dye indicates blood-brain barrier
(BBB) breakdown
Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) will be
activated and break down the extracellular matrix
(ECM) and basement membrane leading to BBB
9
Tissue plasminogen activator (tPA, clot buster)
is the only FDA approved agent for stroke
treatment
LIMITATION tPA has hemorrhagic risk if given
after 3 hr
10
Desmoteplase
- Plasminogen activator derived from the saliva of
the vampire bat Desmodus rotundus living in South
America 9 hr treatment window
Ancrod (Viprinex)
- Derived from the venom of the Malayan pit viper.
6 hr treatment window
11
IRISH coffee (Caffeinol, Caffeine alcohol)
Transcranial doppler ultrasound tPA
MERCI retriever corkscrew type retriever
Penumbra stroke vacuum system. A new treatment
for stroke victims promises to suction out
clogged arteries in hopes of stopping the brain
attack before it does permanent harm.
12
The Cone of Brain Injury
Trauma Focal Global Anoxia Hypoxia Ischemia I
schemia Cerebral blood flow and energy
failure Disruption of ionic gradients Metabolic
responses Neuronal death
13
(No Transcript)
14
Drugs in phase III stroke clinical trials
ACTION AGENT Free radical scavenger (MCI
186) Edaravone (in use, Japan) NMDA receptor
antagonist/channel blocker Mg2 Nitrone, spin
trap agent (recently failed 12/2006)
NXY-059 Antioxidant Ebselen (Japan)
Cytidine-5-diphosphocholine (CDP-choline) non-xen
obiotic (not foreign to the body) Intermediate in
biosynthesis of phosphatidylcholine (PC, a major
membrane phospholipid)
15
Fluid Mosaic Model of the Biological Membrane
16
Why is phosphatidylcholine (PC) important ?
- Major membrane phospholipid
- Pathological breakdown causes growth arrest and
cell death. - 10 loss induces cell death.
- Source for lipid messengers, diacylglycerol, and
arachidonic acid
17
PC Synthesis in the Brain
Cytidine triphosphate
Cytidine
1,2-diacylglycerol
Phospho- choline
CDP-Choline
CCT
CPT
PC
Choline
CTPphosphocholine cytidylyltransferase (CCT) is
the rate-limiting enzyme in PC synthesis.
Absolute requirement for survival and knockout of
this gene is fatal.
CDP-choline (Cytidine diphosphocholine) is the
rate-limiting intermediate in PC synthesis
18
PC breakdown (hydrolysis) by phospholipases
PLD
Diacylglycerol Phosphocholine
PLC
PLC
PLA2
PC
PLA2
Arachidonic acid Lyso-PC
Phosphatidic acid choline
PLD
19
Animal model for stroke
Middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) for 1
hour using Intraluminal suture occlusion in
spontaneously hypertensive rat (develops
hypertension at 12 weeks).
Blood clot commonly blocks MCA in stroke
Stroke model transient middle cerebral artery
occlusion
20
CDP-choline reduced infarction and restored PC
after stroke
CDP-choline significantly reduced (by 50)
infarction after 1 hr MCAO/24 hr rep in rat model
of stroke.
Ipsi contra
Saline
Stroke resulted in significant loss of PC at 1
and 3 d. CDP-choline significantly restored PC.
Is CDP-choline only affecting the PC synthesis
? Has any effect on phospholipases ??
When the colorless chemical tetrazolium chloride
(TTC) diffuses into actively respiring tissues,
it accepts electrons from the mitochondrial
electron transport chain, reducing it to a pink
compound, known as formazan. The accumulation of
this pink compound stains the tissues red, and
the intensity of the red color is proportional to
the rate of respiration in those tissues. However
this staining do not differentiate between core
and penumbra regions.
21
Ca2 and PLA2 activity after stroke
- Data indicate that PLA2 activated after stroke
was mM-Ca2 dependent sPLA2
- PLA2 enzymes classified into 3 families.
PLA2 Ca2 MW sPLA2 mM 14 kD cPLA2 µM 85
kD iPLA2 none 84 kD
22
Secretory PLA2 (sPLA2) after stroke
- sPLA2 also know as inflammatory PLA2
- Messenger RNA (RT-PCR)
- Protein expression (Western blot)
- Enzyme activity
- Products
- after stroke were examined
23
sPLA2 mRNA and protein expression after tMCAO
Protein expression, Western blotting
mRNA (RT-PCR studies)
- sPLA2 IIA mRNA increased 4.7-fold and 6.2-fold in
the ipsi-cortex at 1 d and 3 d rep. CDP-choline
attenuated the increase in sPLA2 mRNA.
sPLA2 protein expression increased from 3 h to 7
d, maximum increase 4-fold at 1 d.
24
CDP-choline attenuated sPLA2 protein expression
and activity after stroke
sPLA2 protein expression, Western blotting
sPLA2 enzyme activity
25
CDP choline restored CCTa protein expression and
activity after tMCAO
CCT protein expression, Western blotting
CCT enzyme activity
26
CDP-choline attenuated the arachidonic acid (AA)
release after stroke
AA 204 (20 carbon atoms with 4 double
bonds) 204 D5,8,11,14 CH3(CH2)3(CH2CC)4(CH2)3CO
OH Precursor for eicosonoids
27
Reactive Oxygen Species and lipid peroxidation
Arachidonic Acid Metabolism
GSH
Mitochondria
Lipid Peroxidation
ROS (?OH, O2-, H2O2)
MDA, HNE, Acrolein Cholesterol aldehydes (atherona
ls)
COX
EICOSONOIDS (eicoso- 20 carbon derived from
AA) (Prostaglandins, leukotrienes thromboxanes)
Arachidonic Acid
LOX
28
GLOBAL ischemia (cardiac arrest) in gerbil
4-hydroxynonenal (HNE) is one of the toxic
aldehydes generated during lipid peroxidation
that affects protein function
29
Inflammatory Cytokines
- Proinflammatory cytokines,
- TNF-a and IL-1ß are
- Pleiotropic
- (one cytokine affects different cells)
- Redundant
- (different cytokines do the same function)
- Multifunctional
- (same cytokine regulates different functions)
Heat Redness Swelling Pain
Loss of function
Quintet
Rubor Calor Tumor
Dolor Functio laesa
30
Restoring PC synthesis provides benefit after
stroke CDP-choline by differentially affecting
PLA2 (?) and CCT (?) restores PC
TNF-a and IL-1ß disrupt phospholipid homeostasis
by up-regulating phospholipases,
sphingomyelinases and down-regulating CCT and SMS
after stroke.
Front. Biosci. 2008
31
Phospholipase A2 and CDP-choline
Sphingomyelin preserved
SMase ?
PC preserved
Cardiolipin preserved
PLA2 activation ?
AA ?
Lyso-PC ?
OH ?
CDP-choline
CCT ?
Toxic aldehydes ?
GSH ?
32
TNF-a ab and IL-1ra reduced infarct after stroke
TNF-a antibody (TNF-a ab) and IL-1 receptor
antagonist (IL-1ra) treatment neutralizes the
actions of TNF-a and IL-1.
Cytokines and CDP-choline in stroke
- CDP-choline
- Attenuated TNF-a and IL-1ß levels
- Effect on Lipids
- restored PC
- decreased arachidonic acid and lyso-PC release
33
Integration of cytokine biology to lipid
metabolism
TNF-a and IL-1ß disrupt PC homeostasis in the cell
PC loss can occur due to hydrolysis, or
inhibition of its synthesis, or both
Ischemia/reperfusion
Hydrolysis
TNF-a ? IL-1 ?
Synthesis
PLA2 ?
CCT ?
PC ?
Cell death
- Effects of CDP-choline are opposite to those of
TNF-a and IL-1ß. - CDP-choline partly counteracting pro-inflammatory
cytokine effects
Ischemia CDP-choline
TNF-a ? IL-1 ?
PLA2 ?
CCT ?
PC ?
34
Stages of Development for a Neuroprotective Drug
Preclinical Laboratory (animal) Studies
Phase I Trial for Toxicity (in normal volunteers)
Phase IIa Trial for Dosimetry and Safety
Phase IIb Trial to Estimate Chance of Efficacy
Phase III Trial to Confirm Efficacy
In patients
FDA Approval
Phase IV Surveillance of Approved Drug (follow-up
for possible side effects)
35
1,026 Treatments
Of the 1,026 agents tested in animal stroke
models, only 114 have undergone clinical trials.
None worked. WHY ?
36
Neuroprotection Stroke Time for a compromise
(Yes/No taken into account/not taken into
account No. of indicates relevant importance).
The figure highlights clear discrepancies between
the experimental and clinical situation that
should be taken into consideration for improving
stroke treatment. Note in experimental stroke
animals, the process of inflammation and
apoptosis may occur more quickly.
37
CDP-choline Brain uptake
- Route of administration Oral (USA) vs i.v.
(non-USA). - Brain uptake of CDP-choline, 0.5 (oral) vs 2
i.v.
- CDP-choline liposomes
- Effective at low doses
- lt100 nm can cross BBB
- Will be in circulation for up to 24 hrs.
- Intact drug will be delivered by circumventing
CCT step. - Brain uptake increased to 23.
Stroke
Control
42 kDa CCT
ß-actin
Cytidine
CTP
1,2-diacylglycerol
Phospho- choline
CDP-Choline
CCT
CPT
Choline
PC
38
drug
Polar head group
Non-polar fatty acid chain
39
Conclusions
- Stroke injury is complex and multi-dimensional. A
multi-pronged approach using drug cocktails are
necessary. - Combining CDP-choline with other agents provided
synergistic benefits in experimental models - Effective treatments for stroke requires not only
the discovery of protective agents, but also
effectively deliver them to stroke stricken
brain.
Our ultimate goal for brain protection in stroke
patients appears evanescent but should not be
considered as elusive Minds are like parachutes.
They only function when they are open
40
Thank you
Eric Larsen, PhD
Jim Hatcher, BS
Francis Tsao, PhD Kudret Tureyen, MD Richard
Chen, MS Collaborators Robert Dempsey,
MD Timothy Heath, PhD Dandan Sun, MD PhD
NIH/NINDS American Heart Association UW Medical
School Res. Committee UW Graduate
School UW-Neurological Surgery Ferrer Grupo,
Barcelona, Spain Elder Pharmaceuticals, India
41
References
- del Zoppo GJ (2006) Stroke and neurovascular
protection. N Engl J Med 354 553-555. - http//www.sfn.org/skins/main/pdf/brainfacts/brain
facts.pdf a publication by Society for
Neuroscience A primer on the Brain and Nervous
system - http//www.ninds.nih.gov/disorders/stroke/preventi
ng_stroke.htm - http//www.nytimes.com/packages/html/health/200705
27_STROKEB_FEATURE/blocker.html - http//health.nytimes.com/health/guides/disease/st
roke/medications.html
42
CDP-choline Stroke clinical trials
- Total 13 clinical trials including four in USA
(500-2000 mg) - European and Japanese studies showed beneficial
effects - US Initial CDP-choline studies showed benefit,
but later trials were inconclusive.
- Factors to consider
- Brain uptake
- Metabolism
- Time-to-treatment
- Primary outcome measure
43
CDP-choline Metabolism, Time-to-treatment and
Primary Outcome
- Metabolism
- In rodents, CDP-choline increases plasma levels
of cytidine and choline. - In humans, uridine but not cytidine is increased
in plasma due to cytidine deaminase in GI tract
and liver. - Time-to-treatment
- Treatment was initiated up to 24 hrs after the
onset of symptoms (Average time-to-treatment was
13.5 hrs). - Most of the neuroprotective drugs are effective
only if administered lt 2 to 4 hrs after onset of
symptoms. - Primary outcome
- Improvement gt 7 points in NIHSS (3 point scale,
11 items). CDP-choline for 6-weeks showed benefit
at 6-weeks but not at 12-week follow-up.
CDP-choline is effective in Stroke (December
2002).
44
- Presentation is available at
- http//www.neurosurg.wisc.edu/labs/adibhatla
- Neuroscience 500 Undergraduate Stroke talk
- Questions or comments
- Dr. Rao M Adibhatla
- Phone 608.263.1791
- adibhatl_at_neurosurg.wisc.edu
45
TNF-a and IL-1ß relationship to PC and SM
metabolism
TNF-a and IL-1ß are up-regulated after stroke and
activate hydrolyzing enzymes (phospholipases,
sphingomyelinases (SMase)) and down-regulate CCT
(critical enzyme in PC synthesis), sphingomyelin
synthase (SMS)
Stroke
Hydrolysis ?
Synthesis ?
Phospholipase, SMase ?
TNF-a ? IL-1 ?
CCT, SMS ?
Loss of membrane phospholipids (PC SM), ?
generation of AA and Ceramide ?
46
The Neurovascular Unit and Intact Blood-Brain
Barrier (BBB)
Neurovascular unit comprised of endothelium,
astrocytes and neurons. Communication occurs
between neurons and microvessels (endothelial
cells that forms BBB and basal lamina) through
astrocytes.
47
1,026 experimental treatments in stroke
114 (clinically tested) 912 (tested only in
animal models) Thrombolytic Excitotoxicity
Anti-inflammatory Anti-oxidant Calcium
blockers Nootropic
Drugs in phase III stroke clinical trials
ACTION AGENT tPA (in clinical use, FDA
approved) thrombolytic NMDA receptor
antagonist/channel blocker Mg2 Nitrone spin trap
agent (failed 12/2006) NXY-059/cerovive
Why drugs that work in animal stroke models do
not work in humans ?
48
CDP-choline Stroke clinical trials
- Total 13 clinical trials including four in USA
(500-2000 mg) - European and Japanese studies showed beneficial
effects - US Initial CDP-choline studies showed benefit,
but later trials were inconclusive. - Factors to consider
- Brain uptake, Metabolism, Time-to-treatment,
Primary outcome
Note One difference between the animal studies
vs clinical trials is that animal studies
typically use much higher doses of CDP-choline
(500-1000 mg/kg i.p. or i.v. immediately after
stroke) Whereas clinical trials administer 2000
mg/patient within 24 hr of stroke symptoms, and
daily for 6 weeks and outcome was measured at 12
weeks. for ex a 70 kg patient receiving 2000 mg
citicoline, the dose amounts to 28 mg/kg).
500-2000 mg/kg for 70 kg patient requires 35-140
gm (35-70 gms of NXY-059 was given/36 hrs to
stroke patients) Although a dose used in animal
studies cannot extrapolate to humans, these
represent vastly different dosing. On a similar
note, CDP-choline encapsulated in liposomes (18
mg/kg i.v.) significantly reduced infarction
compared to free CDP-choline (500 mg/kg) in a rat
stroke model.
Neurology 2002 J Neurosci. Res. 2002, 2003
49
CDP-choline Brain uptake
- Route of administration Oral (USA) vs i.v.
(non-USA). - Brain uptake of CDP-choline, 0.5 (oral) vs 2
i.v.
50
Conclusions
- Increasing PC synthesis or inhibiting hydrolysis
provided benefit after tMCAO - OxPC formation
- Western blot indicated presence of OxPC- bound
protein adduct after tMCAO - tMCAO SM synthases (?) and SMases (?)
- Anti-cytokine treatment (TNF-a antibody or IL-1
receptor antagonist) - prevented sPLA2 up-regulation
- restored PC, SM levels and prevented ceramide
accumulation - D609, a PC-PLC inhibitor
- significantly decreased OxPC formation and
infarction after tMCAO - May be affecting the cell cycle (at the G1
phase). Prevented bFGF-induced proliferation of
astrocytes - May prevent macrophage/microglia proliferation
and protect mature neurons entering into cell
cycle and commit suicide - CDP-choline clinical trails needs to be
revisited. Route of administration needs to be
modified. - Combination of thrombolytics neuroprotectants
- Our ultimate goal for brain protection in stroke
patients appears evanescent but should not be
considered as elusive - Vivien - Vivien
51
Integration of cytokine biology to lipid
metabolism
TNF-a and IL-1ß disrupt PC homeostasis in the cell
52
HNE in Rat middle cerebral artery occlusion
(MCAO) model
3h
12h
48h
- Confocal images of the rat brain after 3hr
MCAO/reperfusion. HNE-modified proteins indicated
in red and Bcl-2 in green. A yellow color
indicates co-localization. - At 12 h reperfusion, both HNE and Bcl-2
colocalize in some neurons (arrows) - At 48 h reperfusion, most of the neurons show HNE
(red)
53
The brain has the highest lipid content of any
organ next to adipose tissue
The importance of lipid metabolism in cell
signaling and tissue physiology is demonstrated
by many CNS disorders and injuries that involve
deregulated lipid metabolism.
Stroke
ALS
TBI
Phospholipases PC imbalance
Tau pathology Cholesterol
Lipid peroxidation
SCI
MS-EAE
Lipid peroxidation
Demyelination
Bipolar disorders
CNS lipids
PLA2
Ketogenic diet
Endocannabinoids
Huntington
Epilepsy
ASMase Cholesterol
Cholesterol Ceramide
Oxidative stress
Niemann-Pick
Alzheimers
Parkinsons
54
(No Transcript)
55
Coleman ML, Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology
5, 355-366 (May 2004)
56
(No Transcript)
57
Forebrain ischemia in gerbil
- Bilateral carotid artery occlusion in gerbil
for10 min/ reperfusion for up to 6 days. - HNE is one of the toxic aldehydes generated
during lipid peroxidation that affects protein
function by binding to thiol (SH) groups.
Free Rad Biol Med 2006