Nutrition and Disease - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 41
Title:
Nutrition and Disease
Description:
Systemic: Itching, urticaria (hives), Vomiting, Abdominal cramps, diarrhea and ... Localized: hives and eczema or atopy (an umbrella term covering clinical ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:43
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Nutrition and Disease
1
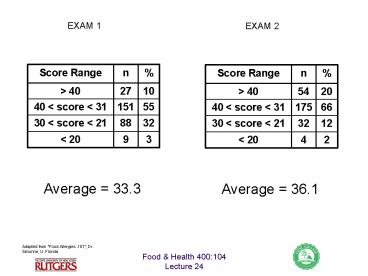
EXAM 1
EXAM 2
Average 33.3
Average 36.1
2
Food Allergies
Lecture 24April 21, 2008Dr. QuadroFood
Science Department
3
Prevalence of food allergy
- Experts agree that allergies in developed
countries are becoming more common. - In the U.S., food allergies afflict 2-2.5 adults
and 6-8 children. - 100-175 people in the U.S. die each year.
- Death generally result from anaphylactic shock,
often to peanuts or tree nuts. - More than 160 foods have been associated with
allergic reactions.
CEN/January 7, 2002 page 21.
4
What is food allergy?
- Food allergy is an inappropriate immune response
to an otherwise harmless food. - True food allergy involves several types of
immunological responses. - Food allergens are usually proteins.
- Some foods may contain haptens or haptens
carrier.
5
Understanding Immunological concepts
- Human body has many defense mechanisms to fight
off infectious diseases and other toxic foreign
substances. - Strong healthy adult human can fight off most of
infectious diseases. - Ability to fight off disease can be modulated by
genetics, age, race and lifestyles (diets,
exercise and amount of sleep etc.)
6
Basic Terminology
- Allergic reactions are Antigen-Antibody reactions
- Antigen a foreign substance
- Antibody a protein produced in response to an
antigen that is capable of binding specifically
to the antigen! - Haptens - a small molecule that has the ability
to combine with an Ab or a cell-surface receptor.
7
- Human body has two categories of defense system
- Non specific defenses
- Physical barriers (skin and mucous membrane)
- Chemical barriers (saliva, mucus, gastric juices,
etc) - Cellular defenses (certain cells can eat
invaders-phagocytes) - Inflammation (reddening, swelling and temperature
increase of the affected sites) - Fever (elevated body temperature)
- Molecular defenses (interferons or complementary
system etc.) - Specific defenses or specific immunity
- Antibodies (many kinds of antibodies for many
kinds of antigens)
8
- Food allergies are related to specific defenses
or specific immunity. - Immune literary means free of burden.
- Actions of the immune system are triggered by
antigens (foreign substances). - Most antigens are large protein molecules Some
antigens are polysaccharides and few are
glycoproteins (carbohydrate and protein) or
nucleo-proteins.
9
Specific Immunity
Immunity
Ab Antibodies
Acquired
Innate (inborn) Genetic factors
Passive (Ready-made-Ab)
Active (own Ab)
Natural Maternal Ab
Artificial (Ab from Other sources)
Natural (Exposure to Foreign Agents)
Artificial (immunization)
10
Antibodies (Immunoglobulins)
- Produces by B-linfocytes (bone marrow)
- Five classes of Immunoglobulins
- 1) IgG Main class of antibodies in blood-also
from mother-to-child (20) - 2) IgA Small amount in blood, but larger amount
in tears, milk, saliva, mucus and the lining
tissues - 3) IgM First Antibody secreted during the
primary response - 4) IgE Found mainly in body fluids and skin ---
Associated with allergy reactions! - 5) IgD Found in B-Cell membrane
11
Antibody structure
Binding site for the antigen
Binding site for the receptor
12
(No Transcript)
13
Primary and secondary responses to an antigen
Primary response first response when hosts
B-cell recognize the antigen
Secondary response upon second exposure to the
antigen, the Memory cells will divide, thus make
more of the total antibody
14
Nature of IgE Allergic Reactions
Antigen IgE Mast cells Mediator
release Mediators histamine and others
Picture credit from Dr. Gary E.
Kaiser http//www.cat.cc.md.us/courses/bio141/lecg
uide/index.html
15
What does histamine do?
- Vasodilation, increased capillary permeability,
bronchoconstriction etc.
16
Types of food allergies
- Immediate hypersensitivity with IgE which occurs
within minutes to a few hours after ingestion of
offending foods. - Systemic Itching, urticaria (hives), Vomiting,
Abdominal cramps, diarrhea and respiratory
distress, and in severe cases anaphylactic shock - Localized hives and eczema or atopy (an umbrella
term covering clinical presentations of food
allergy etc) - Delayed hypersensitivity reactions (gt8hours after
ingestion) cellular immunity involving
T-lymphocytes and macrophages
17
Lymphocytes
B lymphocytes mature in Bone marrow
and lymphatic tissue (spleen and lymph nodes) T
lymphocytes mature in the Thymus
18
T-lymphocytes
Mature in Thymus, which is most active just
before and after birth. The thymus starts to
shrink during puberty.
- Helper T-Cells
- Recognise antigens on surface of leukocytes,
especially macrophages - Enlagre and form a clone of T-helper cells
- Secrete interferon and cytokines which stimulate
B-cells and stimulate killer -cells - Can be infected by HIV
- Killer T-Cells
- Also called cytotoxic
- Destroy abnormal body cells, e.g. virus infected
or cancer cells - Stimulated by cytokines (THcells)
- Release perforin, which forms pores in target
cells. This allows water and ions in lysis
- Suppressor T-Cells
- Control the immune system when the antigen
/pathogen has - been destroyed
- Only recently discovered so
- little is known about them
- Memory T-Cells
- Can survive a long time and give lifelong
immunity from infection - Can stimulate memory B-cells to produce
antibodies - Can trigger production of killer T cells
19
How T-cells work
20
Stages of food allergy or hypersensitivity
- A. Sensitization initial meeting of an allergen
and the immune system that results in IgE
production! - B. Activation of mast cells
- IgE
- Non-IgE substances (eg. Drugs)
21
Most common sites for allergic reactions
22
Symptoms-Food Allergy
- Nausea
- Diarrhea
- Abdominal cramps
- Pruritic rashes
- Angioedema
- Asthma/rhinitis
- Vomiting
- Hives
- Laryngeal edema
- Anaphylaxis
Exercise exacerbates symptoms
23
Anaphylaxis
- Potential fatal reaction to a food allergen
causing reduced oxygen supply to the heart and
other body tissues. - Symptoms include difficult breathing, low blood
pressure, pale skin, a weak rapid pulse, loss of
consciousness, death.
24
Most common allergenic foods
- Legumes (Peanuts and Soybeans)
- Mollusks and shellfish (snails, mussels, oysters,
scallops, clams, squid) - Milk
- Eggs
- Fish (cod, salmon, haddock etc)
- Crustacea (shrimp, crawfish, lobster etc.)
- Wheat
- Tree nuts (almonds, walnuts, Brazil nuts etc)
- Selected food additives
25
Children and Good Allergy
- High prevalence in the first few years of life
- Immature immune system and immature digestive
system - Cows milk and soy, most common allergens
- Breast feeding is recommended
- Delay introduction of common allergenic foods
- Sensitivity to most of the allergenic foods is
usually lost by young children as they grow up
26
Cross-Reaction the reaction of one antigen with
antibodies developed against another antigen.
27
Cross-Reaction
28
Hidden food ingredients in ready made food
products
- Milk and milk product derivatives
- Egg and egg derivatives
- Peanuts, tree nuts and derivatives
- Fish derivatives (surimi, fish sauce, fish paste
etc) - Soy and its derivatives
29
Eating out is a nightmare?
- African, Chinese, Indonesian, Mexican, Thai, and
Vietnamese dishes often contain peanuts. It is
recommended that peanut-allergic individuals
avoid these types of foods and restaurants. - For traditional food restaurants,
cross-contamination of allergens to other foods
can also a problem.
30
Solutions
- People who have food allergy need a total
avoidance of the offending foods. - Read food ingredient list.
- Eliminate cross-contamination during cooking and
preparation!!!!
31
Common prescribed medications
- epinephrine (relaxes smooth muscle, constricts
blood vessels, and stimulates the heart used for
severe systemic reactions-anaphylaxis) - antihistamines (block the binding of histamine
to histamine receptors on target cells) - sodium cromolyn (prevents mast cells from
releasing histamines).
32
Other types of food allergy, Non-IgE Mediated
- Immune Complex-mediated
- Symptoms usually gastrointestinal
- Delayed type hypersensitivity
- Symptoms usually gastrointestinal
33
Food Aversion
- A strong desire to avoid a particular food
Food Intolerance
Adverse reaction to food that does not involve
the immune system
34
Food Intolerance
- Direct effect of food
- Enzyme deficiency (e.g., lactase, sucrase etc)
- Symptoms of food intolerance bloating, cramping,
gas and diarrhea - Main cause of food intolerance carbohydrates
(lactose, fructose, sorbitol)
35
Allergy VS Intolerance
- True Allergy-Total avoidance necessary!
- Intolerance- Small amount may be tolerated
36
Diagnosis
- Determine if the symptoms are mediated by the
immune system
37
Other causes of allergy-like food problems
- Microbial products- e.g. histamine Some food
products have high levels of histamine (eg
fermented foods) - Pharmacological reaction-tyramine,
phenylethylamine, cafiene dose dependent - Idiosyncratic reactions (adverse reactions of
drugs etc dose dependent) - Psychological disorders
38
Diagnosis
- Determine if the symptoms are mediated by the
immune system - Complete physical
- Detailed case history
- Food diary
- Positive identification of the allergen
39
Prick skin Test (PST)
- Drop of the substance under test on the forearm
- Allow a tiny amount to enter the skin (doctor
pricks it with a needle) - After 15min, verify presence of bump
40
Radioallergosorbent Test (RAST)
- Requires blood samples
- Laboratory test are performed to look if the
patients has IgE against specific types of food
41
Resources for food allergies
- Food Allergy and Anaphylaxis network (FAAN)
- American Academy of Allergy, Asthma and
Immunology - American Dietetic Association
- Asthma and Allergy Foundation