New England
1 / 15
Title: New England
1
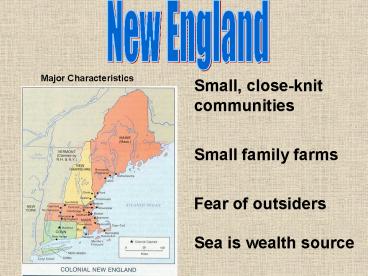
New England
Major Characteristics
Small, close-knit communities Small family
farms Fear of outsiders Sea is wealth source
2
Family Life
- Immigrants arrive as middle-class families
- Many children
- Live to see grandchildren
Elizabeth Freake and Baby Mary, 1670s, anonymous
artist
3
Economic Reliance on the Sea
- Fishing
- Whaling
- Shipbuilding
- Overseas trade
New England developed an elite class of merchants
4
Church in New England
Congregational (Puritan) Church Mandatory
attendance Pay taxes to Church (except RI) In
Mass., you must be a church member to vote.
5
Literacy
- High literacy rate
- Must be able to read the Bible
- All towns have schools
6
The New England Primer (Later edition)
The New England Primer (Colonial edition)
7
The Irony of Literacy
- Puritans encouraged independent study of the
Bible. - This brought independent minds like Anne
Hutchinson to criticize the of the authorities.
8
Democracy in New England
- Puritans believe social equality is dangerous
but. . . - Town Meetings are considered the paragon of
democracy.
Freedom of Speech by Norman Rockwell
9
The Decline of Puritan Theology
- WORK and WEALTH
- Puritans preached the Protestant Work Ethic
(that hard work was holy), believing wealth would
help the common good. .but - As people became more interested in trade and
work, and wealthy along the way, piety declined. - Tolerance of others was better for trade
- Half-Way Covenant (1662)
- Jeremiads by 1660s castigating the
selfishness - New England evolved from a holy experiment to a
merchant-dominated secular government.
10
John Freake, 1670s, Anonymous painter (The Freake
Limner)
11
Elizabeth Freake with Baby Mary, 1670s ,
Anonymous Painter (The Freake Limner)
12
The Gibbs Children, 1670
13
- Portrait of William Dudley, 1729 by John Smibert
14
Mr. Mrs. Francis Brinsley and son, 1729
15
Thomas Smith, Self Portrait, 1690s