Relating Electron Configuration to the Periodic Table - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 10
Title:
Relating Electron Configuration to the Periodic Table
Description:
Sn ( [Kr] 4d10 ) 5s2. 5p2. 1 valence e- 4 valence e- 2 valence e- Periodic Trends. Atomic Radius. Decreases from left to right across a period ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:68
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Relating Electron Configuration to the Periodic Table
1
Relating Electron Configuration to the Periodic
Table
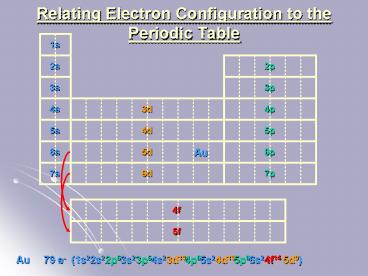
1s
2s
2p
3s
3p
4s
4p
3d
5s
5p
4d
6s
6p
5d
Au
7s
7p
6d
4f
5f
Au
(1s2
79 e-
2s2
2p6
3s2
3p6
4s2
3d10
4p6
5s2
4d10
5p6
6s2
4f14
5d9)
2
Predict the Electron Configurations of the
Following
- Example
P
P (1s22s22p63s23p3)
Co
Co (1s22s22p63s23p64s23d7)
Sr
Sr (1s22s22p63s23p64s23d104p65s2)
O
O ( He 2s22p4)
Fr
Fr ( Rn 7s1)
Am
Am ( Rn 7s25f7)
Core notation use noble gas to represent core
electrons
3
Electron Configurations of Negative Ions
- For negative ions add electrons to the last
unfilled shell.
P
P (1s22s22p63s23p3)
P3- (1s22s22p63s23p6)
P3-
O ( He 2s22p4)
O
O-
O- ( He 2s22p5)
O2-
O2- ( He 2s22p6)
4
Electron Configurations of Positive Ions
- For positive ions there are 2 rules
- e- in the outermost shell (largest n-value) are
removed first. - If there are e- in both the s- p- orbitals in
the outermost shell, remove the p-orbital e-
first.
K
K (1s22s22p63s23p64s1)
K
K (1s22s22p63s23p6 )
V (1s22s22p63s23p64s23d3)
V
V2
V2 (1s22s22p63s23p6 3d3)
Sn ( Kr 5s24d105p2)
Sn
Sn2
Sn2 ( Kr 4d10 )
5s2
Sn4
Sn4 ( Kr 4d10 )
5
What do the orbitals look like?
6
p - orbitals
d - orbitals
7
f - orbitals
8
Valence Electrons
- Valence electrons are the electrons in the
outermost s- p-orbitals
K
K (1s22s22p63s23p6 )
4s1
1 valence e-
V
V (1s22s22p63s23p6 3d3)
4s2
2 valence e-
Sn
Sn ( Kr 4d10 )
5s2
5p2
4 valence e-
9
Periodic Trends
- Atomic Radius
- Decreases from left to right across a period(due
to increased charge on the nucleus) - Increases from top to bottom in a group or
family(due to shielding effects larger
orbitals) - Electronegativity
- The attraction an atom has for a shared pair of
electrons in a covalent bond - Increases from left to right across a period
- Decreases from top to bottom in a group or
family
10
- Ionization Energy
- The energy needed to remove an electron.
- Increases from left to right across a period
- Decreases from top to bottom in a group or family