Lymphocyte Differentiation - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 35
Title:
Lymphocyte Differentiation
Description:
pro-B cell:??heavy-chain genes(DH/ JH joining),?????????? ... To provide stimulatory modifying signals. Complex of CD19, CR2 (CD21) and TAPA-1 (CD18) ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:214
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Lymphocyte Differentiation
1
Lymphocyte Differentiation
2
Genetic Models
B cell development?activation and maturation
- Genetic models
- Germ-Line model
- The genome contributed by the grem cells contains
a large repertoire of immunoglobulin genes. - No special genetic mechanisms to account for
antibody diversity - Somatic-Variation model
- The genome contains a small number of
immunoglobulin genes, from which a large number
of antibody specificities are generated in
somatic cells by mutation or recombination. - Two-Gene model, 1965 by W. Dryer and J. Bennett
- Two separate genes encode a single immunoglobulin
heavy and light chain, one gene for the V region
and the other for the C region
3
B cell development?activation and maturation
Verification of the two-gene model
1967, by S. Tonegawa and N. Hozumi 1987, Tonegawa
got Nobel Prize
- Digested DNA fragemnts from embryonic and myeloma
cells hybridized with radiolabel-RNA - (b) V and C gene are brought closer together and
intervening DNA sequence is eliminated
4
Immunoglobulin Gene
B cell development?activation and maturation
- ???7????? (gene segments) ??????????????
- ??
- V?D?J?C?4??????
- ???14?????
- ???VH???DH?6?JH?9?CH(Cµ?Cd?C?3?C?1?Ca1?C?2?C?4?Ce?
Ca2)? - ??(???type light chains)
- V?J?C?3??????
- ?type(??V??5?J?????C???)???2?????
- ?type(??V? ???J????C???)???22?????
5
B cell development?activation and maturation
Immunoglobulin Germline Gene Segments in Human
6
B cell development?activation and maturation
Immunoglobulin Germline Gene Segments in Mouse
7
B cell development?activation and maturation
Heavy-Chain Gene Rearrangement in Human V-D-J
joining
8
B cell development?activation and maturation
?- Light-Chain Gene Rearrangement in Human V-J
joining
9
B cell development?activation and maturation
?- Light-Chain Gene Rearrangement in Human V-J
joining
10
B cell development?activation and maturation
Heavy-Chain Gene Rearrangement in the mouse
V-D-J joining
11
B cell development?activation and maturation
Kappa Light-Chain Gene Rearrangement in mouse
V-J joining
12
B cell development?activation and maturation
13
B cell development?activation and maturation
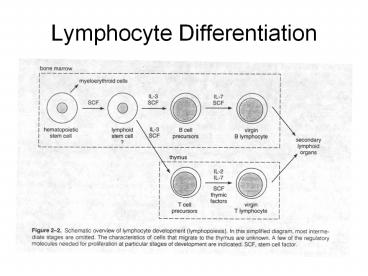
Overview
- Antigen-independent phase
- Immunocompetent B cells expressing membrane IgM
and IgD are generated in the bone marrow - Antigen-dependent phase
- B cells are activated and proliferated with
secondary lymphoid organs - To differentiate into memory B cell and plasma
cells
14
Differentiation of B cell
B cell development?activation and maturation
15
Differentiation of B cell
B cell development?activation and maturation
- pro-B cell??heavy-chain genes(DH/ JH
joining),?????????? - pre-B cell??heavy-chain genes(VH /DH/ JH
joining),?VDJ???Cµ??,??µpolypeptidelight-chain
genes????? - late pre-B cell?????????heavy chain?Ig-a?Ig-ß?sur
rogate light chain - immature B cell?????????surface IgM(s
IgM),??????????,????????????????,??????????
16
Differentiation of B cell
B cell development?activation and maturation
- mature B cell?????surface IgM?IgD(????????????)??
?????,? - 5 nucleotidase(CD73)??????????
- CD23????(oligosaccharide-bing portein)?
- adhesion proteinsLFA-1?ICAM-1?CD22?
- L-selectinsurface homing receptor,???????????????
??? - MHC class II?????T?????
- CD40??T?????
- ??B????????????????virgin B cell(naïve B cell)?
- ???B??????????,??????????antigen-independent??matu
re B cell??secondary lymphoid organs?,????????????
?plasma cell????????(IgM)?
17
B cell development?activation and maturation
?
?
18
B cell development?activation and maturation
- Pro B-cells contact with stromal cells in the
bone marrow - c-kit on pro B-cell interacts with stem-cell
factor on surface of stromal cells - Pro B-cells begin to divide and differentiate
into pre B-Cell - To express the receptor of IL-7 on the surface of
pre B-Cell
Back
19
B-1 B cell
Back
20
B cell development?activation and maturation
The Cell Cycle of B lymphocytes
21
B cell activation and maturation
B cell development?activation and maturation
- B????????
- Ig-a?Ig-ß
- ??B????????????protein tyrosine
kinases(PTKs,CD45??????domain?????)? - ??
- Thymus-dependentB?????(????????)???,???T?????????
??B??????CD40??TH??????CD40L(CD40 ligand)??????
22
B cell activation and maturation
B cell development?activation and maturation
- Thymus-independenB????????,?????????,????T???????
????B????????IgM?IgD????????B????? - T????
- B???????????TH?????,T??????helper factors??B???
- ????B?????B7 proteins(T cell costimulators)???????
?(IL-6?TNFa)??TH??????????? - B????T??????????T???????,???????????,?????????????
isotype (class)switching?????,???IgG?IgA?IgE?
23
B cell development?activation and maturation
- Ig-a?Ig-ß
- Immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif
(ITAM) - The cytoplasmic tail of both Ig-a(61 amino acids
) and Ig-ßlong (48 amino acids), 18-residue motif - To transduce the antigen-mIg binding stimulus
into cell to become an effective intracellular
signal - Binding stimulus is mediated by tyrosine kinases
(PTKs) - The BCR itself has no PTK activity
- Modification of coreceptors
- B-cell coreceptor
- To provide stimulatory modifying signals
- Complex of CD19, CR2 (CD21) and TAPA-1 (CD18)
- CD22
- Associated with the B-cell receptor in resting B
cells - A negative signal to make B-cell more difficult
to activate
24
B cell development?activation and maturation
The initial stage of signal transduction by an
activated BCR
25
B cell development?activation and maturation
- CD19 immunoglobulin superfamily protein, long
cytoplasma tail, and three extracellular Ig-fold
domain - CR2 receptor of complement (C3d)
- TATP-1 transmembrane protein
26
B cell development?activation and maturation
- Thymus-dependent antigens (TD antigens)
- Require to interact with TH cell
- Thymus-independent antigens (TI antigens)
- Not to require to interact with TH cell
- Typ1, such as lipopolysaccharide of bacterial
cell wall - Polyclonal B-cell activators
- Activate immature and mature B cells
- Fully T-cell independence
- Type2, highly repetitious molecules, such as
polymeric proteins - Not polyclonal B-cell activators
- Activate mature B cells
- need T-cell cytokines
27
B cell development?activation and maturation
Signals from TI and TD Antigens for B-cell
Activation
28
B-cell Activation by TD antigens
29
The Humoral Responses- Primary and Secondary
Response
30
Class Switching
- isotype (class)switching(?????)
- ?B????(?????????)???????
- ??heavy chain gene rearrangment???????????(???????
??VDJ joining???????,?????????V????,??????????????
????????)? - T????????????????????????T???????IgA???,IL-4??B??
??IgG??
31
(No Transcript)
32
(No Transcript)
33
(No Transcript)
34
Plasma cell and Memory B cell
- Plasma cell
- Plasma cells???bone marrow?,??marrow???plasma
cell????????????????????? - Plasma cells ??????,????????????
- ????????
- Memory B cell(????)
- ?????????,?????????isotype?????????,??????,???????
??????homing(????)???????? - ?????????????,??B???????????????,??????(??????????
???)? - ?????B?????????????,???????,????????B????B?????,??
????????
35
(No Transcript)