Dependent motion multiple cords - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 43
Title:
Dependent motion multiple cords
Description:
L1= yA (yA-yB) L2=2yB yC L3=yB (yB-yD) L4= yD yC. d(L1= yA (yA-yB))/dt d(L2=2yB yC)/dt d(L3=yB (yB-yD))/dt. 0=2vA - vB 0=2vB vC 0=2vB vD ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:26
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Dependent motion multiple cords
1
- Dependent motion multiple cords
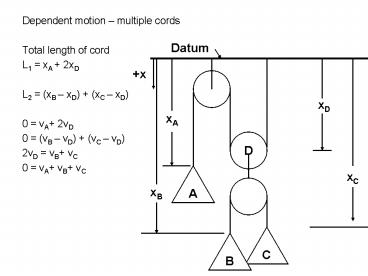
- Total length of cord
- L1 xA 2xD
- L2 (xB xD) (xC xD)
- 0 vA 2vD
- 0 (vB vD) (vC vD)
- 2vD vB vC
- 0 vA vB vC
Datum
x
xD
xA
D
A
xC
xB
C
B
2
Dependent motion
- Solution Procedure
- 1. Sketch with a datum line
3
Dependent motion
- Solution Procedure
- Sketch with a datum line
- Denote the positive direction
4
Dependent motion
- Solution Procedure
- Sketch with a datum line
- Denote the positive direction
- Denote the position of each object
5
Dependent motion
- Solution Procedure
- Sketch with a datum line
- Denote the positive direction
- Denote the position of each object
- Write an equation for the length of each cable
6
Dependent motion
- Solution Procedure
- Sketch with a datum line
- Denote the positive direction
- Denote the position of each object
- Write an equation for the length of each cable
- Apply the time derivatives
7
Dependent motion
- Solution Procedure
- Sketch with a datum line
- Denote the positive direction
- Denote the position of each object
- Write an equation for the length of each cable
- Apply the time derivatives
- Use the given data to solve for the unknowns
8
- 11-47 Block A moves down with a constant
- velocity of 2 ft/s. Determine (a) the velocity of
- block C, (b) the velocity of collar B relative to
block - A, (c) the relative velocity of portion D of the
cable - with respect to block A.
9
- 11-47 Block A moves down with a constant
- velocity of 2 ft/s. Determine (a) the velocity of
- block C, (b) the velocity of collar B relative to
block - A, (c) the relative velocity of portion D of the
cable - with respect to block A.
- Sketch with a datum line
- Denote the positive direction
- Denote the position of each object
- Write an equation for the length of each cable
- Apply the time derivatives
- Use the given data to solve for the unknowns
Datum Line
10
- 11-47 Block A moves down with a constant
- velocity of 2 ft/s. Determine (a) the velocity of
- block C, (b) the velocity of collar B relative to
block - A, (c) the relative velocity of portion D of the
cable - with respect to block A.
- Sketch with a datum line
- Denote the positive direction
- Denote the position of each object
- Write an equation for the length of each cable
- Apply the time derivatives
- Use the given data to solve for the unknowns
y
11
- 11-47 Block A moves down with a constant
- velocity of 2 ft/s. Determine (a) the velocity of
- block C, (b) the velocity of collar B relative to
block - A, (c) the relative velocity of portion D of the
cable - with respect to block A.
- Sketch with a datum line
- Denote the positive direction
- Denote the position of each object
- Write an equation for the length of each cable
- Apply the time derivatives
- Use the given data to solve for the unknowns
y
YD
YC
YB
YA
12
- 11-47 Block A moves down with a constant
- velocity of 2 ft/s. Determine (a) the velocity of
- block C, (b) the velocity of collar B relative to
block - A, (c) the relative velocity of portion D of the
cable - with respect to block A.
- Sketch with a datum line
- Denote the positive direction
- Denote the position of each object
- Write an equation for the length of each cable
- Apply the time derivatives
- Use the given data to solve for the unknowns
- L1 yA (yA-yB)
y
YD
YC
YB
YA
13
- 11-47 Block A moves down with a constant
- velocity of 2 ft/s. Determine (a) the velocity of
- block C, (b) the velocity of collar B relative to
block - A, (c) the relative velocity of portion D of the
cable - with respect to block A.
- Sketch with a datum line
- Denote the positive direction
- Denote the position of each object
- Write an equation for the length of each cable
- Apply the time derivatives
- Use the given data to solve for the unknowns
- L1 yA (yA-yB) L22yByC
y
YD
YC
YB
YA
14
- 11-47 Block A moves down with a constant
- velocity of 2 ft/s. Determine (a) the velocity of
- block C, (b) the velocity of collar B relative to
block - A, (c) the relative velocity of portion D of the
cable - with respect to block A.
- Sketch with a datum line
- Denote the positive direction
- Denote the position of each object
- Write an equation for the length of each cable
- Apply the time derivatives
- Use the given data to solve for the unknowns
- L1 yA (yA-yB) L22yByC
L3yB(yB-yD)
y
YD
YC
YB
YA
15
- 11-47 Block A moves down with a constant
- velocity of 2 ft/s. Determine (a) the velocity of
- block C, (b) the velocity of collar B relative to
block - A, (c) the relative velocity of portion D of the
cable - with respect to block A.
- Sketch with a datum line
- Denote the positive direction
- Denote the position of each object
- Write an equation for the length of each cable
- Apply the time derivatives
- Use the given data to solve for the unknowns
- L1 yA (yA-yB) L22yByC
L3yB(yB-yD) - d(L1 yA (yA-yB))/dt
- 02vA-vB
y
YD
YC
YB
YA
16
- 11-47 Block A moves down with a constant
- velocity of 2 ft/s. Determine (a) the velocity of
- block C, (b) the velocity of collar B relative to
block - A, (c) the relative velocity of portion D of the
cable - with respect to block A.
- Sketch with a datum line
- Denote the positive direction
- Denote the position of each object
- Write an equation for the length of each cable
- Apply the time derivatives
- Use the given data to solve for the unknowns
- L1 yA (yA-yB) L22yByC
L3yB(yB-yD) - d(L1 yA (yA-yB))/dt d(L22yByC)/dt
- 02vA-vB 02vBvC
y
YD
YC
YB
YA
17
- 11-47 Block A moves down with a constant
- velocity of 2 ft/s. Determine (a) the velocity of
- block C, (b) the velocity of collar B relative to
block - A, (c) the relative velocity of portion D of the
cable - with respect to block A.
- Sketch with a datum line
- Denote the positive direction
- Denote the position of each object
- Write an equation for the length of each cable
- Apply the time derivatives
- Use the given data to solve for the unknowns
- L1 yA (yA-yB) L22yByC
L3yB(yB-yD) - d(L1 yA (yA-yB))/dt d(L22yByC)/dt
d(L3yB(yB-yD))/dt - 02vA - vB
02vBvC 02vB - vD
y
YD
YC
YB
YA
18
- 11-47 Block A moves down with a constant
- velocity of 2 ft/s. Determine (a) the velocity of
- block C, (b) the velocity of collar B relative to
block - A, (c) the relative velocity of portion D of the
cable - with respect to block A.
- Sketch with a datum line
- Denote the positive direction
- Denote the position of each object
- Write an equation for the length of each cable
- Apply the time derivatives
- Use the given data to solve for the unknowns
- L1 yA (yA-yB) L22yByC
L3yB(yB-yD) - d(L1 yA (yA-yB))/dt d(L22yByC)/dt
d(L3yB(yB-yD))/dt - 02vA - vB
02vBvC 02vB vD - Given vA2 ? vB2(2) 4
y
YD
YC
YB
YA
19
- 11-47 Block A moves down with a constant
- velocity of 2 ft/s. Determine (a) the velocity of
- block C, (b) the velocity of collar B relative to
block - A, (c) the relative velocity of portion D of the
cable - with respect to block A.
- Sketch with a datum line
- Denote the positive direction
- Denote the position of each object
- Write an equation for the length of each cable
- Apply the time derivatives
- Use the given data to solve for the unknowns
- L1 yA (yA-yB) L22yByC
L3yB(yB-yD) - d(L1 yA (yA-yB))/dt d(L22yByC)/dt
d(L3yB(yB-yD))/dt - 02vA - vB
02vBvC 02vB vD - Given vA2 ? vB2(2) 4 ? vC - 2(4) - 8 ft/s
y
YD
YC
YB
YA
20
- 11-47 Block A moves down with a constant
- velocity of 2 ft/s. Determine (a) the velocity of
- block C, (b) the velocity of collar B relative to
block - A, (c) the relative velocity of portion D of the
cable - with respect to block A.
- Sketch with a datum line
- Denote the positive direction
- Denote the position of each object
- Write an equation for the length of each cable
- Apply the time derivatives
- Use the given data to solve for the unknowns
- L1 yA (yA-yB) L22yByC
L3yB(yB-yD) - d(L1 yA (yA-yB))/dt d(L22yByC)/dt
d(L3yB(yB-yD))/dt - 02vA - vB
02vBvC 02vB vD - Given vA2 ? vB2(2) 4 ? vC - 2(4) - 8 ft/s
- vB/A vB vA 4 2 2 ft/s
y
YD
YC
YB
YA
21
- 11-47 Block A moves down with a constant
- velocity of 2 ft/s. Determine (a) the velocity of
- block C, (b) the velocity of collar B relative to
block - A, (c) the relative velocity of portion D of the
cable - with respect to block A.
- Sketch with a datum line
- Denote the positive direction
- Denote the position of each object
- Write an equation for the length of each cable
- Apply the time derivatives
- Use the given data to solve for the unknowns
- L1 yA (yA-yB) L22yByC
L3yB(yB-yD) - d(L1 yA (yA-yB))/dt d(L22yByC)/dt
d(L3yB(yB-yD))/dt - 02vA - vB
02vBvC 02vB vD - Given vA2 ? vB2(2) 4 ? vC - 2(4) - 8 ft/s
- vB/A vB vA 4 2 2 ft/s
- vD/A vD vA 2(4) 2 6 ft/s
y
YD
YC
YB
YA
22
- 11-47 Block A moves down with a constant
- velocity of 2 ft/s. Determine (a) the velocity of
- block C, (b) the velocity of collar B relative to
block - A, (c) the relative velocity of portion D of the
cable - with respect to block A.
- Sketch with a datum line
- Denote the positive direction
- Denote the position of each object
- Write an equation for the length of each cable
- Apply the time derivatives
- Use the given data to solve for the unknowns
- L1 yA (yA-yB) L22yByC
L3yB(yB-yD) L4 yD yC - d(L1 yA (yA-yB))/dt d(L22yByC)/dt
d(L3yB(yB-yD))/dt - 02vA - vB
02vBvC 02vB vD - Given vA2 ? vB2(2) 4 ? vC - 2(4) - 8 ft/s
- vB/A vB vA 4 2 2 ft/s
- vD/A vD vA 2(4) 2 6 ft/s
y
YD
YC
YB
YA
23
- 11-47 Block A moves down with a constant
- velocity of 2 ft/s. Determine (a) the velocity of
- block C, (b) the velocity of collar B relative to
block - A, (c) the relative velocity of portion D of the
cable - with respect to block A.
- Sketch with a datum line
- Denote the positive direction
- Denote the position of each object
- Write an equation for the length of each cable
- Apply the time derivatives
- Use the given data to solve for the unknowns
- L1 yA (yA-yB) L22yByC
L3yB(yB-yD) L4 yD yC - d(L1 yA (yA-yB))/dt d(L22yByC)/dt
d(L3yB(yB-yD))/dt d(L4 yD yC)/dt - 02vA - vB
02vBvC 02vB vD - Given vA2 ? vB2(2) 4 ? vC - 2(4) - 8 ft/s
- vB/A vB vA 4 2 2 ft/s
- vD/A vD vA 2(4) 2 6 ft/s
y
YD
YC
YB
YA
24
- 11-47 Block A moves down with a constant
- velocity of 2 ft/s. Determine (a) the velocity of
- block C, (b) the velocity of collar B relative to
block - A, (c) the relative velocity of portion D of the
cable - with respect to block A.
- Sketch with a datum line
- Denote the positive direction
- Denote the position of each object
- Write an equation for the length of each cable
- Apply the time derivatives
- Use the given data to solve for the unknowns
- L1 yA (yA-yB) L22yByC
L3yB(yB-yD) L4 yD yC - d(L1 yA (yA-yB))/dt d(L22yByC)/dt
d(L3yB(yB-yD))/dt d(L4 yD yC)/dt - 02vA - vB
02vBvC 02vB vD
0 vD vC - Given vA2 ? vB2(2) 4 ? vC - 2(4) - 8 ft/s
- vB/A vB vA 4 2 2 ft/s
- vD/A vD vA 2(4) 2 6 ft/s
y
YD
YC
YB
YA
25
- 11-47 Block A moves down with a constant
- velocity of 2 ft/s. Determine (a) the velocity of
- block C, (b) the velocity of collar B relative to
block - A, (c) the relative velocity of portion D of the
cable - with respect to block A.
- Sketch with a datum line
- Denote the positive direction
- Denote the position of each object
- Write an equation for the length of each cable
- Apply the time derivatives
- Use the given data to solve for the unknowns
- L1 yA (yA-yB) L22yByC
L3yB(yB-yD) L4 yD yC - d(L1 yA (yA-yB))/dt d(L22yByC)/dt
d(L3yB(yB-yD))/dt d(L4 yD yC)/dt - 02vA - vB
02vBvC 02vB vD
0 vD vC - Given vA2 ? vB2(2) 4 ? vC - 2(4) - 8 ft/s
vD -(-8) 8 ft/s - vB/A vB vA 4 2 2 ft/s
- vD/A vD vA 2(4) 2 6 ft/s
y
YD
YC
YB
YA
26
- 11-47 Block A moves down with a constant
- velocity of 2 ft/s. Determine (a) the velocity of
- block C, (b) the velocity of collar B relative to
block - A, (c) the relative velocity of portion D of the
cable - with respect to block A.
- Sketch with a datum line
- Denote the positive direction
- Denote the position of each object
- Write an equation for the length of each cable
- Apply the time derivatives
- Use the given data to solve for the unknowns
- L1 yA (yA-yB) L22yByC
L3yB(yB-yD) L4 yD yC - d(L1 yA (yA-yB))/dt d(L22yByC)/dt
d(L3yB(yB-yD))/dt d(L4 yD yC)/dt - 02vA - vB
02vBvC 02vB vD
0 vD vC - Given vA2 ? vB2(2) 4 ? vC - 2(4) - 8 ft/s
vD -(-8) 8 ft/s - vB/A vB vA 4 2 2 ft/s
- vD/A vD vA 2(4) 2 6 ft/s
vD/A 8 2 6
ft/s
y
YD
YC
YB
YA
27
- 11-57 Slider block B moves to the left
- with a constant velocity of 2 in/s. At t0,
- slider block A is moving to the right with
- a constant acceleration and a velocity
- of 4 in/s. Knowing that at t2s slider
- block C has moved 1.5 in. to the right,
- determine (a) the velocity of slider
- block C at t0, (b) the accelerations of
- A and C.
28
- 11-57 Slider block B moves to the left with a
- constant velocity of 2 in/s. At t0, slider
- block A is moving to the right with a
- constant acceleration and a velocity of 4
- in/s. Knowing that at t2s slider block C has
- moved 1.5 in. to the right, determine (a) the
- velocity of slider block C at t0, (b) the
- accelerations of A and C.
- Sketch with a datum line
- Denote the positive direction
- Denote the position of each object
- Write an equation for the length of each cable
- Apply the time derivatives
- Use the given data to solve for the unknowns
29
X
- 11-57 Slider block B moves to the left with a
- constant velocity of 2 in/s. At t0, slider
- block A is moving to the right with a
- constant acceleration and a velocity of 4
- in/s. Knowing that at t2s slider block C has
- moved 1.5 in. to the right, determine (a) the
- velocity of slider block C at t0, (b) the
- accelerations of A and C.
- Sketch with a datum line
- Denote the positive direction
- Denote the position of each object
- Write an equation for the length of each cable
- Apply the time derivatives
- Use the given data to solve for the unknowns
30
X
- 11-57 Slider block B moves to the left with a
- constant velocity of 2 in/s. At t0, slider
- block A is moving to the right with a
- constant acceleration and a velocity of 4
- in/s. Knowing that at t2s slider block C has
- moved 1.5 in. to the right, determine (a) the
- velocity of slider block C at t0, (b) the
- accelerations of A and C.
- Sketch with a datum line
- Denote the positive direction
- Denote the position of each object
- Write an equation for the length of each cable
- Apply the time derivatives
- Use the given data to solve for the unknowns
XC
XB
XA
31
X
- 11-57 Slider block B moves to the left with a
- constant velocity of 2 in/s. At t0, slider
- block A is moving to the right with a
- constant acceleration and a velocity of 4
- in/s. Knowing that at t2s slider block C has
- moved 1.5 in. to the right, determine (a) the
- velocity of slider block C at t0, (b) the
- accelerations of A and C.
- Sketch with a datum line
- Denote the positive direction
- Denote the position of each object
- Write an equation for the length of each cable
- Apply the time derivatives
- Use the given data to solve for the unknowns
- L -3xA 4xC 2xB
XC
XB
XA
32
X
- 11-57 Slider block B moves to the left with a
- constant velocity of 2 in/s. At t0, slider
- block A is moving to the right with a
- constant acceleration and a velocity of 4
- in/s. Knowing that at t2s slider block C has
- moved 1.5 in. to the right, determine (a) the
- velocity of slider block C at t0, (b) the
- accelerations of A and C.
- Sketch with a datum line
- Denote the positive direction
- Denote the position of each object
- Write an equation for the length of each cable
- Apply the time derivatives
- Use the given data to solve for the unknowns
- L -3xA 4xC 2xB
- d(L -3xA 4xC 2xB)/dt
- 0 -3vA 4vC 2vB
XC
XB
XA
33
X
- 11-57 Slider block B moves to the left with a
- constant velocity of 2 in/s. At t0, slider
- block A is moving to the right with a
- constant acceleration and a velocity of 4
- in/s. Knowing that at t2s slider block C has
- moved 1.5 in. to the right, determine (a) the
- velocity of slider block C at t0, (b) the
- accelerations of A and C.
- Sketch with a datum line
- Denote the positive direction
- Denote the position of each object
- Write an equation for the length of each cable
- Apply the time derivatives
- Use the given data to solve for the unknowns
- L -3xA 4xC 2xB
- d(L -3xA 4xC 2xB)/dt
- 0 -3vA 4vC 2vB 0 -3aA 4aC
2aB
XC
XB
XA
34
X
- 11-57 Slider block B moves to the left with a
- constant velocity of 2 in/s. At t0, slider
- block A is moving to the right with a
- constant acceleration and a velocity of 4
- in/s. Knowing that at t2s slider block C has
- moved 1.5 in. to the right, determine (a) the
- velocity of slider block C at t0, (b) the
- accelerations of A and C.
- Sketch with a datum line
Given vB - 2, aB 0 - Denote the positive direction
- Denote the position of each object
- Write an equation for the length of each cable
- Apply the time derivatives
- Use the given data to solve for the unknowns
- L -3xA 4xC 2xB
- d(L -3xA 4xC 2xB)/dt
- 0 -3vA 4vC 2vB 0 -3aA 4aC
2aB
XC
XB
XA
35
X
- 11-57 Slider block B moves to the left with a
- constant velocity of 2 in/s. At t0, slider
- block A is moving to the right with a
- constant acceleration and a velocity of 4
- in/s. Knowing that at t2s slider block C has
- moved 1.5 in. to the right, determine (a) the
- velocity of slider block C at t0, (b) the
- accelerations of A and C.
- Sketch with a datum line
Given vB - 2, aB 0 - Denote the positive direction
t 0, aA k, vA 4 - Denote the position of each object
- Write an equation for the length of each cable
- Apply the time derivatives
- Use the given data to solve for the unknowns
- L -3xA 4xC 2xB
- d(L -3xA 4xC 2xB)/dt
- 0 -3vA 4vC 2vB 0 -3aA 4aC
2aB
XC
XB
XA
36
X
- 11-57 Slider block B moves to the left with a
- constant velocity of 2 in/s. At t0, slider
- block A is moving to the right with a
- constant acceleration and a velocity of 4
- in/s. Knowing that at t2s slider block C has
- moved 1.5 in. to the right, determine (a) the
- velocity of slider block C at t0, (b) the
- accelerations of A and C.
- Sketch with a datum line
Given vB - 2, aB 0 - Denote the positive direction
t 0, aA k, vA 4 - Denote the position of each object
t 2, delta xC 1.5 - Write an equation for the length of each cable
- Apply the time derivatives
- Use the given data to solve for the unknowns
- L -3xA 4xC 2xB
- d(L -3xA 4xC 2xB)/dt
- 0 -3vA 4vC 2vB 0 -3aA 4aC
2aB
XC
XB
XA
37
X
- 11-57 Slider block B moves to the left with a
- constant velocity of 2 in/s. At t0, slider
- block A is moving to the right with a
- constant acceleration and a velocity of 4
- in/s. Knowing that at t2s slider block C has
- moved 1.5 in. to the right, determine (a) the
- velocity of slider block C at t0, (b) the
- accelerations of A and C.
- Sketch with a datum line
Given vB - 2, aB 0 - Denote the positive direction
t 0, aA k, vA 4 - Denote the position of each object
t 2, delta xC 1.5 - Write an equation for the length of each cable
- Apply the time derivatives
- Use the given data to solve for the unknowns
- L -3xA 4xC 2xB
- d(L -3xA 4xC 2xB)/dt
- 0 -3vA 4vC 2vB 0 -3aA 4aC
2aB - aC (2aB 3aA)/4
XC
XB
XA
38
X
- 11-57 Slider block B moves to the left with a
- constant velocity of 2 in/s. At t0, slider
- block A is moving to the right with a
- constant acceleration and a velocity of 4
- in/s. Knowing that at t2s slider block C has
- moved 1.5 in. to the right, determine (a) the
- velocity of slider block C at t0, (b) the
- accelerations of A and C.
- Sketch with a datum line
Given vB - 2, aB 0 - Denote the positive direction
t 0, aA k, vA 4 - Denote the position of each object
t 2, delta xC 1.5 - Write an equation for the length of each cable
- Apply the time derivatives
- Use the given data to solve for the unknowns
- L -3xA 4xC 2xB
- d(L -3xA 4xC 2xB)/dt
- 0 -3vA 4vC 2vB 0 -3aA 4aC
2aB - aC (2aB 3aA)/4 (2(0) 3k)/4 3k/4
XC
XB
XA
39
X
- 11-57 Slider block B moves to the left with a
- constant velocity of 2 in/s. At t0, slider
- block A is moving to the right with a
- constant acceleration and a velocity of 4
- in/s. Knowing that at t2s slider block C has
- moved 1.5 in. to the right, determine (a) the
- velocity of slider block C at t0, (b) the
- accelerations of A and C.
- Sketch with a datum line
Given vB - 2, aB 0 - Denote the positive direction
t 0, aA k, vA 4 - Denote the position of each object
t 2, delta xC 1.5 - Write an equation for the length of each cable
- Apply the time derivatives
- Use the given data to solve for the unknowns
- L -3xA 4xC 2xB
- d(L -3xA 4xC 2xB)/dt
- 0 -3vA 4vC 2vB 0 -3aA 4aC
2aB - aC (2aB 3aA)/4 (2(0) 3k)/4 3k/4
- at t 0, vC0 (2vB0 3vA0)/4
XC
XB
XA
40
X
- 11-57 Slider block B moves to the left with a
- constant velocity of 2 in/s. At t0, slider
- block A is moving to the right with a
- constant acceleration and a velocity of 4
- in/s. Knowing that at t2s slider block C has
- moved 1.5 in. to the right, determine (a) the
- velocity of slider block C at t0, (b) the
- accelerations of A and C.
- Sketch with a datum line
Given vB - 2, aB 0 - Denote the positive direction
t 0, aA k, vA 4 - Denote the position of each object
t 2, delta xC 1.5 - Write an equation for the length of each cable
- Apply the time derivatives
- Use the given data to solve for the unknowns
- L -3xA 4xC 2xB
- d(L -3xA 4xC 2xB)/dt
- 0 -3vA 4vC 2vB 0 -3aA 4aC
2aB - aC (2aB 3aA)/4 (2(0) 3k)/4 3k/4
- at t 0, vC0 (2vB0 3vA0)/4 (2(-2)
3(4))/4 2 in/s
XC
XB
XA
41
X
- 11-57 Slider block B moves to the left with a
- constant velocity of 2 in/s. At t0, slider
- block A is moving to the right with a
- constant acceleration and a velocity of 4
- in/s. Knowing that at t2s slider block C has
- moved 1.5 in. to the right, determine (a) the
- velocity of slider block C at t0, (b) the
- accelerations of A and C.
- Sketch with a datum line
Given vB - 2, aB 0 - Denote the positive direction
t 0, aA k, vA 4 - Denote the position of each object
t 2, delta xC 1.5 - Write an equation for the length of each cable
- Apply the time derivatives
- Use the given data to solve for the unknowns
- L -3xA 4xC 2xB
- d(L -3xA 4xC 2xB)/dt
- 0 -3vA 4vC 2vB 0 -3aA 4aC
2aB - aC (2aB 3aA)/4 (2(0) 3k)/4 3k/4
- at t 0, vC0 (2vB0 3vA0)/4 (2(-2)
3(4))/4 2 in/s
XC
XB
XA
42
X
- 11-57 Slider block B moves to the left with a
- constant velocity of 2 in/s. At t0, slider
- block A is moving to the right with a
- constant acceleration and a velocity of 4
- in/s. Knowing that at t2s slider block C has
- moved 1.5 in. to the right, determine (a) the
- velocity of slider block C at t0, (b) the
- accelerations of A and C.
- Sketch with a datum line
Given vB - 2, aB 0 - Denote the positive direction
t 0, aA k, vA 4 - Denote the position of each object
t 2, delta xC 1.5 - Write an equation for the length of each cable
- Apply the time derivatives
- Use the given data to solve for the unknowns
- L -3xA 4xC 2xB
- d(L -3xA 4xC 2xB)/dt
- 0 -3vA 4vC 2vB 0 -3aA 4aC
2aB - aC (2aB 3aA)/4 (2(0) 3k)/4 3k/4
- at t 0, vC0 (2vB0 3vA0)/4 (2(-2)
3(4))/4 2 in/s
XC
XB
XA
43
X
- 11-57 Slider block B moves to the left with a
- constant velocity of 2 in/s. At t0, slider
- block A is moving to the right with a
- constant acceleration and a velocity of 4
- in/s. Knowing that at t2s slider block C has
- moved 1.5 in. to the right, determine (a) the
- velocity of slider block C at t0, (b) the
- accelerations of A and C.
- Sketch with a datum line
Given vB - 2, aB 0 - Denote the positive direction
t 0, aA k, vA 4 - Denote the position of each object
t 2, delta xC 1.5 - Write an equation for the length of each cable
- Apply the time derivatives
- Use the given data to solve for the unknowns
- L -3xA 4xC 2xB
- d(L -3xA 4xC 2xB)/dt
- 0 -3vA 4vC 2vB 0 -3aA 4aC
2aB - aC (2aB 3aA)/4 (2(0) 3k)/4 3k/4
- at t 0, vC0 (2vB0 3vA0)/4 (2(-2)
3(4))/4 2 in/s
XC
XB
XA