Rational Drug Design : HIV Integrase - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 21
Title:
Rational Drug Design : HIV Integrase
Description:
The catalytic domainhas an RNaseH-type fold and belongs to the superfamily of ... I. Crystal reveals trimeric structure. II. Position of hydrogens undetermined ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:146
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Rational Drug Design : HIV Integrase
1
Rational Drug Design HIV Integrase
2
A process for drug design which bases the design
of the drug upon the structure of its protein
target.
- Structural mapping of the receptor (protein, P)
active site - Identification of ligands (L) of complementary
shape and appropriate functionality - Docking
- 4. Scoring
3
(No Transcript)
4
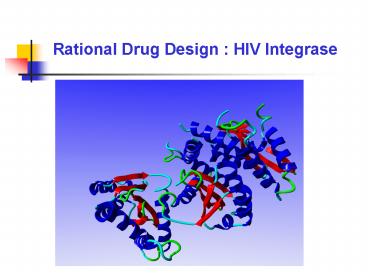
The catalytic domainhas an RNaseH-type fold and
belongs to the superfamily of polynucleotidyl
transferases. The active site is comprised of two
Asp residues and one Glu, in the typicalD,D(35)E
motif, each of which is required for catalysis.
5
de novo Ligand Design
6
de novo Ligand Design
7
de novo Ligand Design
8
de novo Ligand Design
9
de novo Ligand Design
10
de novo Ligand Design
11
four criteria to conclude that integrase is
theinhibitor target 1. found to be active
against recombinant integrase. 2. infected cells
treated with the drug must show an accumulation
of 2-LTR circles, resulting from the accumulation
of viral cDNA and decreased HIV integration into
host 3. integrase mutations must be found in
drug-resistant viruses 4, the drug should be
inactive in biochemical assays against
recombinantintegrases bearing the mutations
identified in the drug-resistant viruses
DKAs
DCQ acids DCT acids
PDP
SQL
Quinolone derived
12
Issues
- Crystal structure available for Integrase but
- I. Limitations of crystal structure
- only catalytic domain
- DNA binding not revealed
- cystal structure vs. physiologically active
structure - II. Position of hydrogens undetermined
- III. Residues missing or ill-defined
- IV. Protonation of His undetermined
- V. Solvation
13
Issues
- Crystal structure available for Integrase
Catalytic Domain but - I. Crystal reveals trimeric structure
- II. Position of hydrogens undetermined
- III. Residues missing or ill-defined
- IV. Protonation of His undetermined
- V. Solvation
14
Results
15
Results
16
Ligand Design
- Criterion for Ligand Selection
- I. Theoretical and experimental structures
- II. Fill active site
- III. Conformational structures
17
Ligand Design
- Criterion for Ligand Selection
- I. Theoretical and experimental structures
- II. Fill active site
- III. Conformational structures
18
Ligand Design
- Criterion for Ligand Selection
- I. Theoretical and experimental structures
- II. Fill active site
- III. Conformational structures
19
Site Mutations and Drug Resistance
- The prediction of the affects of mutations within
the - binding site on the effects of the ligands
involves - I. Identifying possible sights of mutations
- II. Determining effect of mutations
20
Site Mutations and Drug Resistance
21
Problem with Protein Flexibility
http//folding.stanford.edu/villin/S300x300.105.56
.95.mpg