Astronomical Seeing - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 16
Title:
Astronomical Seeing
Description:
... each cell will have a slightly different refractive index. ... If the cells of varying refractive index are far above the telescope, scintillation occurs. ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:27
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Astronomical Seeing
1
Astronomical Seeing
2
The Project
- Students will be introduced to the concept of
astronomical seeing and how it affects the
quality of astronomical images. - The causes of seeing are discussed.
- Students are presented with a selection of images
taken under different conditions and are asked to
chose which images have been taken under the best
seeing conditions. - A discussion is then initiated on how best to
identify the effects of seeing in an image and
how scientists take seeing into account.
National Schools Observatory
3
Setting Up the Experiment 1
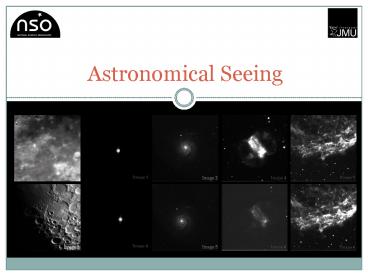
- Students are presented the data twice.
- Distribute copies of the image sets (.jpg format)
for each object. - Images can then be analysed on computers by
loading the images in your default image viewer
or viewed collectively via projection. - Distribute a copy of the worksheet to each of the
students. - Allow the students to quickly rank the quality of
the astronomical image. - If the students cannot distinguish between an
image, note this on the worksheet.
National Schools Observatory
4
Setting Up the Experiment 2
- Deliver the lecture on seeing (concept
introduction folder) , and allow the students to
have a more detailed look at the images. - Using what they have learnt from the lecture. See
if they can now distinguish between some of the
better images. - Prompt the students to look for areas where two
stars are close together the better the seeing
the more resolvable (distinguishable) the two
stars will be. - Look out for stars which are much dimmer in some
images due diffusion through seeing effects. - Look for small features e.g. Craters on the Moon,
the rings on Saturn or dust in galaxy and nebulae
images. The sharper and better resolved the
detail on these features, the better the seeing.
National Schools Observatory
5
Measuring and recording 1
- Rank the images in order of their quality on the
work sheet. - 1 Best and 6 Worst.
- If you are unsure, place a joint ranking with the
image you think is the closest.
National Schools Observatory
6
Astronomical Seeing
- Even the best ground based optical telescopes are
restricted by the presence of the Earths
atmosphere. - Light from distant objects must pass through the
Earths atmosphere before we can observe it. - The atmosphere contains a layer of turbulent air.
- As the light passes through this turbulent layer
the light waves are perturbed, altering how they
are detected on the ground. - This effect is called seeing.
Image created by NSO
National Schools Observatory
7
Seeing and Meteorology
- Variation in temperature, humidity and wind speed
make the atmosphere very turbulent. - Turbulent air contains pockets or cells which
have differing density to the region of air
surrounding it. - It is cells such as these which cause clear-air
turbulence, which is often experienced when
flying in aircraft. - These cells will vary in size and shape and tend
to drift around in the atmosphere. - Due to their differing density, each cell will
have a slightly different refractive index.
National Schools Observatory
8
Refractive Index
- Light in a vacuum travels at a constant velocity,
c. (3x108 ms-1) - When light travels in a medium, the velocity
changes by a factor of 1/n , where n is the
refractive index of the medium. - The refractive index depends on the
characteristics of the medium. - Changing from one medium to another will cause
the angle of the incident light to change. - This occurs as the light travels from cell to
cell.
Image created by NSO
National Schools Observatory
9
Seeing and Meteorology (2)
- Large temperature gradients cause turbulence.
These arise if air masses of different
temperatures mix. - This will occur when hot air rises from the
ground and meets the colder air at higher
altitudes or when the wind drives in weather
fronts from surrounding areas. - This means that seeing is better when
- Observations are recorded at high altitude. i.e.
The light passes through less of the turbulent
air. - Observations are recorded during a period of high
pressure, when wind speeds are low at all
altitudes. - Observations are taken close to the zenith, where
there is less atmosphere for the light to pass
through.
National Schools Observatory
10
Scintillation
- If the cells of varying refractive index are far
above the telescope, scintillation occurs. - Scintillation is observed as irregular changes in
the brightness of the observed objects. - This is what makes stars twinkle at night.
- This will make dim objects and stars invisible on
images taken during bad seeing.
National Schools Observatory
11
Oscillation
- Light travelling through areas of differing
refractive index will also change position in the
focal plane. - This causes distortions in the recorded image.
- This effect is called oscillation.
- The distortion rate is very high, typically more
than a 100 times a second. - Since exposure times are normally much longer
than the distortion rate. Distortion is averaged
over the time of exposure resulting in a blurry
image.
National Schools Observatory
12
Seeing and Stars
- The resolution limit of a telescope , or how well
a telescope can see objects, is determined by the
size of its main mirror. - However, telescope resolution is also limited by
the diffraction of light. - The result of this is that distant point source
objects, such as stars, spread out to a small
spot known as the Airy disk. - Astronomical seeing causes this disk pattern to
be disrupted into a speckle pattern. - This will cause stars next to each other to merge
into a single object. - On larger telescopes the diffraction effects are
very small due to the large size of the mirror.
National Schools Observatory
13
Pickering Scale
- Due to oscillation, a point source such as a star
will spread out and become speckled. - The Pickering scale is a method of quantifying
how good or bad seeing is. - 1 Perfect seeing 10 Very bad seeing.
1 2 3 4
5
6 7 8 9
10
National Schools Observatory
14
Measuring and recording 2
- Rank the images in order of the quality of seeing
on the work sheet. - 1 Best Seeing to 6 Worst Seeing.
- Record the reasons for choosing the rank of each
image. - Record which part of the image has been used to
identify bad seeing. - Compare the best and worst image. What are the
differences?
National Schools Observatory
15
Discussion After the Experiment
- Is bad seeing easier to identify on some objects
more than others? - What are the best methods for identifying bad
seeing on an astronomical image? - Pick the image with the worst seeing, what kind
of weather might you have expected on that day? - Are there any images which have artifacts that
cannot be attributed to seeing?
National Schools Observatory
16
Questions, Exercises and Tasks
- What methods are there for overcoming
astronomical seeing? - Are some parts of the world affected more than
others? Where is the best place to locate a
telescope? - Are small telescopes affected more than large
telescopes? - Will observations of more distance objects such
as galaxies be more prone to seeing effects?
National Schools Observatory