OKAY - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 5
Title:
OKAY
Description:
If kchem krev or krev kchem, then will not have a current. for ... What if redox species (O) is adsorbed on electrode surface? Q. Qads. QDL (blank) only S.E. ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:72
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: OKAY
1
10-1
Potential Step Methods From Chronoamperometry
to Double-potential Step Chronocoulometry
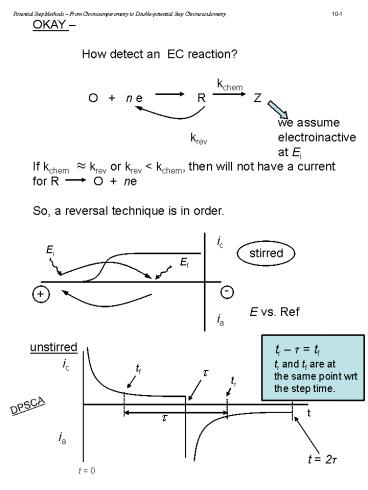
OKAY How detect an EC reaction?
kchem O n e R
Z we assume
krev electroinactive at Ei If kchem
krev or krev lt kchem, then will not have a
current for R O ne So, a reversal
technique is in order.
ic
Ei
stirred E vs. Ref
Ef
-
ia
unstirred
tr t tf
ic
tr and tf are at the same point wrt the step
time.
tf
tr
DPSCA
t
ia
t 2t
t 0
2
10-2
Potential Step Methods From Chronoamperometry
to Double-potential Step Chronocoulometry
recalling
we see
The maximum ratio, if R is stable. If
, R unstable at this value.
decreasing stability of R 1. larger kchem
2. larger
1.0
0.293
more stable
1
2
So, a chemically irreversible reaction can be
made reversible and DC if t is small enough.
But, if t too small, then tf is small enough
such that reaction looks ET limited.
3
10-3
Potential Step Methods From Chronoamperometry
to Double-potential Step Chronocoulometry
Measuring instantaneous currents is not always
easy.
Chronocoulometry (CC)
charge
Ef E Ei
i
Q
t
0 t
t
For O n e R, plot Q
vs. t1/2 If plot linear, then
reaction is D-Controlled
Q
QDL
QDL
t1/2
4
10-4
Potential Step Methods From Chronoamperometry
to Double-potential Step Chronocoulometry
What if redox species (O) is adsorbed on
electrode surface?
Q
Qads
QDL (blank) only S.E.
t1/2
is 2 D conc. in mol/cm2
We assume that Not so,
due to inherent Capacitance of adsorbed species
on surface.
How deal with this situation?
Double Potential Step Chronocoulometry
Q
t
5
10-5
Potential Step Methods From Chronoamperometry
to Double-potential Step Chronocoulometry
Qf vs. t
For adsorption
Qads QDL
sec1/2
QDL iff R not adsorbed!
Now get Qads by subtraction.
What about stability of R? (What else is DPSCC
good for?)
As kchem becomes faster
1.0
Completely irreversible
0 0
1.0
2.0