Design - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 28
Title:
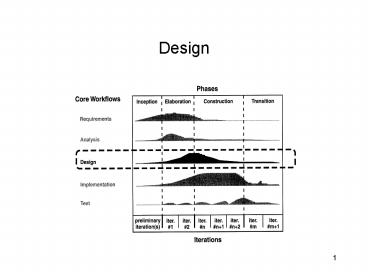
Design
Description:
Collaboration within design model describes how a use case is realized ... startup and termination, liveness, deadlock avoidance, starvation avoidance, ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:14
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Design
1
Design
2
Role of Design
- Develop blueprints for implementation
- Q What does this mean?
3
Design Model Hierarchy
4
Difference Between Analysis and Design Models
5
Example
6
Design as Use Case Realization
- Collaboration within design model describes how a
use case is realized - Should maintain traceability to use case
realization in analysis model - Provides physical realization of the use case and
handles non-functional requirements
7
Design Subsystems
- Subsystems organizes system into manageable
pieces - Subsystems can be very large and hierarchical
- But, a subsystem should be cohesive, and they
should be loosely coupled - Top level subsystems normally have direct trace
to analysis packages - Can represent reused software products or legacy
systems by wrapping them - means of integration
8
Architectural View of Design Model
- Decomposition of design model into subsystems,
their interfaces, and dependency between them -
subsystems and their interfaces make up
fundamental structure of software system - Key design classes - those trace to
architecturally significant analysis classes,
those general and central (e.g. abstract
classes), those having many relationships - Designs that realize key use cases
9
Deployment Model
- Object model describing physical distribution of
system in terms of how functionality distributed
among computational nodes - Each node a computational resource, e.g.
processor - Nodes have relationship representing means of
communication - Has major impact on design and implementation
- Q. Why?
10
Architectural Design
- Purpose is to outline the design and deployment
models and their architecture by identifying - Nodes and their network configurations
- Subsystems and their interfaces
- Architecturally significant classes
- Generic design mechanisms handling common
requirements, e.g. performance, persistency,
distribution - Many possibilities to consider, need to weight
whats more important
11
I/O of Architectural Design
12
Identifying Nodes and Network Configurations
- Network configuration often have major impact on
system architecture, including active classes
required and distribution of functionality among
network nodes - Which nodes involved and whats their processing
power and memory size? - What types of connections between the nodes, and
what protocols - Bandwidth, availability, quality?
- Need for redundant capacity, fault tolerance,
process migration, backup, etc.?
13
Example
14
Identifying Subsystems and Interfaces
15
Middleware Layer
16
Identifying Subsystem Interfaces
- From subsystem dependencies
- Inherit from analysis packages
- analysis class interfaces that are referenced
from another package
17
Identifying Active Classes
- Performance, throughput, availability factors
- System distribution onto nodes
- System startup and termination, liveness,
deadlock avoidance, starvation avoidance,
reconfiguration of nodes, and capacity of
connections - Q what kind of objects most likely to be active
objects?
18
Identifying Generic Design Mechanisms
- Persistency
- Transparent object distribution
- Security features
- Error detection and recovery
- Transaction management
- Concurrency control, etc.
19
Example Generic Collaboration Used in Several
Use Case Realizations
20
Mapping to Invoice Buyer Use Case
21
Design Use Case
- Purpose
- Identify design classes and/or subsystems whose
instances are needed to perform the use case flow
of events - Distributed the behavior of the use case to
interacting design objects and/or subsystems - Define requirements on the operations of design
classes and/or subsystems and their interfaces - Capture implementation requirements for the use
case
22
Identifying Participating Design Classes
- Identify design classes that trace to those
participating classes in the analysis model - Identify design classes that implement
non-functional requirements - From analysis model
- Discovered in the design process
- Identify missing classes
23
Pay Invoice Use Case Realization
24
Describe Object Interactions
- When use sequence diagrams
- If there are multiple flows, use one sequence
diagram for each flow - Should be based on object interaction defined in
analysis model (traceability) - Each design class identified in the realization
of the use case should have at least one object
in the sequence diagram - Focus on sequence of interaction or message
exchange - Should handle all relationships of the use case
25
Example
26
Identifying Participating Subsystems and
Interfaces
27
Design a Class
- Its operations
- Attributes
- Relationship it participates in
- Methods (that realize the operations)
- Its imposed states
- Its dependency to any generic design mechanisms
- Requirements relevant to its implementation
- Correct realization of any interface it is
required to provide
28
(No Transcript)