Virtual Private Grid (VPG) : - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title: Virtual Private Grid (VPG) :
1
Virtual Private Grid (VPG) A Command Shell for
Utilizing Remote Machines Efficiently
- Kenji Kaneda, Kenjiro Taura, Akinori Yonezawa
Department of Computer Science, University of
Tokyo
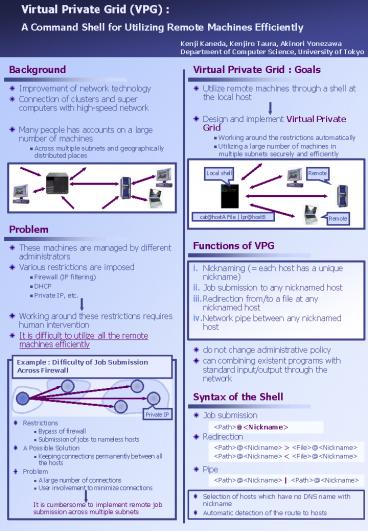
Background
Virtual Private Grid Goals
- Improvement of network technology
- Connection of clusters and super computers with
high-speed network - Many people has accounts on a large number of
machines - Across multiple subnets and geographically
distributed places
- Utilize remote machines through a shell at the
local host - Design and implement Virtual Private Grid
- Working around the restrictions automatically
- Utilizing a large number of machines in multiple
subnets securely and efficiently
Local shell
Remote
cat_at_hostA File lpr_at_hostB
Remote
Problem
Functions of VPG
- These machines are managed by different
administrators - Various restrictions are imposed
- Firewall (IP filtering)
- DHCP
- Private IP, etc.
- Working around these restrictions requires human
intervention - It is difficult to utilize all the remote
machines efficiently
- Nicknaming ( each host has a unique nickname)
- Job submission to any nicknamed host
- Redirection from/to a file at any nicknamed host
- Network pipe between any nicknamed host
- do not change administrative policy
- can combining existent programs with standard
input/output through the network
Example Difficulty of Job Submission Across
Firewall
Syntax of the Shell
- Job submission
- Redirection
- Pipe
Private IP
- Restrictions
- Bypass of firewall
- Submission of jobs to nameless hosts
- A Possible Solution
- Keeping connections permanently between all the
hosts - Problem
- A large number of connections
- User involvement to minimize connections
ltPathgt_at_ltNicknamegt
ltPathgt_at_ltNicknamegt gt ltFilegt_at_ltNicknamegt ltPathgt_at_ltNick
namegt lt ltFilegt_at_ltNicknamegt
ltPathgt_at_ltNicknamegt ltPathgt_at_ltNicknamegt
- Selection of hosts which have no DNS name with
nickname - Automatic detection of the route to hosts
It is cumbersome to implement remote job
submission across multiple subnets
2
Overview of Implementation
Related Work
- Daemons boot up at hosts
- Each daemon creates and keeps necessary
connections with SSH port forwarding - DHCP clients create a connection to the outside
- Multiple subnets are connected
- Finally, daemons finish creating connections
- Network becomes connected
- Using self stabilizing spanning tree algorithm
- GlobusI.Foster et al. http//www.globus.org
- Providing basic services for global computing
- RMFY.Tanaka et al. IWCC99
- Utilizing resources inside the firewall
- UfoAlbert D. Alexandrov et al. USENIX87
- Providing global file system
- Secure Shell
- Providing secure access to remote machines
- Virtual Private Network
- Constructing a private network on the Internet
Subnet Y
Host D (Private IP)
Host C (DHCP client)
Difference between VPG and SSH
Subnet Z
- Methods to utilize a large number of machines
with SSH - Giving a shell window to each host
- It requires a large number of windows
- Creating connections whenever submitting a job
- It entails high overhead
- Using SSH port forwarding
- It requires an user involvement
- Advantages of VPG
- Minimum connections for all the hosts to
communicate with each other - Easy and efficient network pipe and redirection
- Job submission to nameless hosts
Host B
Host A (Home host)
Subnet X
the host which the user initially logins
Difference between VPG and VPN
- VPG constructs a private network at the user
level - VPG places major emphasis on remote job submission
Summary and Future Work
Live Connection Dead Connection
- Developing Virtual Private Grid
- Working around the restrictions automatically
- Utilizing remote machines securely and
efficiently - Easier and more efficient utilization of remote
machines - Automatic and parallel resource selection
- Simple scheduler
- Control of dependency relation of files
- Automatic generation of executables
- File sharing/sync, etc.
Subnet Y
Host D (Private IP)
Host C (DHCP client)
Subnet Z
Host B
Host A (Home host)
Subnet X