Shark Classification - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 44
Title:
Shark Classification
Description:
Like all sharks, the whale shark is cold-blooded. ... Whale sharks are often confused with whales because of their size and non-violent tendencies. ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
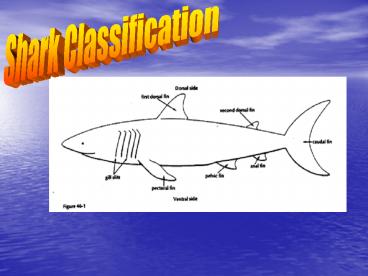
Number of Views:202
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Shark Classification
1
Shark Classification
2
Introduction To Classification
- Classification is the act of distributing things
into classes or categories of the same type.
3
About Classification
- Aristotle was the first to form a useful form of
classification in 300 B.C. - His was organized on the organisms blood color.
- Then he later organized by physical
characteristics.
4
- As science advanced, a more modern form of
classification developed - One founder of modern classification is Swedish
naturalist Carolus Linnaeus. - He developed a system that organized by special
features an organism had. - He also founded binomial nomenclature for naming.
5
- The modern classification system has become much
more advanced. - Classification makes everyday life easier by
putting organisms in a useful system. - Classification helps us to group the organisms we
live with every day. - Classification also lets us have a system for
reference and will continue to help as we study
the organisms around us.
6
The Shark
Cartilaginous- skeleton of cartilage Aquatic-
lives in water scales/denticles- small flat
plates that fit together to form skin covering
(tooth shaped) lateral line- sensory organs
along side of fish to help navigate and sense
other creatures gill filaments-threadlike part
of gills that are filled with blood vessels
where they basically breathe gill cover- bones
(cartilage) of fishs head that cover gills
7
Is the body kite-like if viewed from top ?
Yes
No
8
INCORRECT
- Try again..
9
Is there a small dorsal fin present at the tip of
the tail?
Yes
No
10
INCORRECT
- Try again..
11
Good Job!
- This organism belongs to the family Rajidae.
12
If body is kitelike (viewed from top) click this
button
If body is not kitelike (viewed from top) click
this button
13
Return to previous slide
14
WRONG!!
Go back to previous slide
15
If pelvic fin is absent, click this button If
pelvic fin is present, click this button
16
Return to previous slide
17
WRONG!!
Go back to previous slide
18
If six gill slits are present, click this
button If five gill slits are present, click
this button
19
Return to previous slide
20
WRONG!!
Go back to previous slide
21
If only one dorsal fin, click this button If
two dorsal fins, click this button
22
Return to previous slide
23
WRONG!!
Go back to previous slide
24
If mouth is at the front of the snout rather on
the underside of the head, click this button
If mouth is on the underside of the head, click
this button
25
Return to previous slide
26
WRONG!!
Go back to previous slide
27
Family Rhincodontidae
This is the whale shark. It belongs to family
rhincodontidae. Like all sharks, the whale shark
is cold-blooded. The whale shark can be 18 meters
in length and exceed 10 tons! The whale shark
mainly feeds on plankton, sardines, squid, and
anchovies. It resides mostly in Western
Australia. Whale sharks are often confused with
whales because of their size and non-violent
tendencies.
28
Does the body look kite-like if viewed from top?
No
Yes
29
INCORRECT
- Try again..
30
Pelvic fin absent or present?
Absent
Present
31
INCORRECT
- Try again..
32
You did it!
This organism is in family pristiophoridae.
33
If the body is kitelike, click this button
If the body is not kitelike, click this button
34
Return to previous slide
35
WRONG!!
Go back to previous slide
36
If pelvic fin is absent, click this button If
pelvic fin is present, click this button
37
Return to previous slide
38
WRONG!!
Go back to previous slide
39
If six gill slits are present, click this
button If five gill slits are present, click
this button
40
Return to previous slide
41
WRONG!!
Go back to previous slide
42
Family Hexanchidae
This is the cow shark. It is part of the family
Hexanchidae. Cow sharks can be about 3 to 4
meters long. They usually live deep down in warm,
temperate seas. Cow sharks can have anywhere
from 22 to 108 pups at a time!
43
Why we use Classification
Classification helps scientists characterize
traits and specifics on organisms. We use
classification to put all of earths known
organisms into group and families. Dichotomous
Keys help us to figure out what genus and species
an animal falls under. For example, if a new
organism was discovered, a scientist would go
through a Dichotomous Key to try to find out the
subjects kingdom, phylum, class, order, family,
genus, and species.
44
T
E
H
!
E
D
N