Notes on National Product and Income Account - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Notes on National Product and Income Account
Description:
Check-out the website of the National Bureau of Economic Research http://www.nber.org. Check-out the book 'Frontier of Business Cycle Research,' ed. T. Cooley, 1995, ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:33
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Notes on National Product and Income Account
1
(No Transcript)
2
(No Transcript)
3
(No Transcript)
4
(No Transcript)
5
(No Transcript)
6
(No Transcript)
7
(No Transcript)
8
(No Transcript)
9
(No Transcript)
10
(No Transcript)
11
(No Transcript)
12
(No Transcript)
13
(No Transcript)
14
Table 2 Cyclical Behavior of the US Economy Deviations from Trend of Expenditure Components, 1954I-1991II Table 2 Cyclical Behavior of the US Economy Deviations from Trend of Expenditure Components, 1954I-1991II Table 2 Cyclical Behavior of the US Economy Deviations from Trend of Expenditure Components, 1954I-1991II Table 2 Cyclical Behavior of the US Economy Deviations from Trend of Expenditure Components, 1954I-1991II Table 2 Cyclical Behavior of the US Economy Deviations from Trend of Expenditure Components, 1954I-1991II Table 2 Cyclical Behavior of the US Economy Deviations from Trend of Expenditure Components, 1954I-1991II Table 2 Cyclical Behavior of the US Economy Deviations from Trend of Expenditure Components, 1954I-1991II Table 2 Cyclical Behavior of the US Economy Deviations from Trend of Expenditure Components, 1954I-1991II Table 2 Cyclical Behavior of the US Economy Deviations from Trend of Expenditure Components, 1954I-1991II
Cross-Correlation of Output with Cross-Correlation of Output with Cross-Correlation of Output with Cross-Correlation of Output with Cross-Correlation of Output with Cross-Correlation of Output with Cross-Correlation of Output with Cross-Correlation of Output with Cross-Correlation of Output with
Variable SD X(-3) X(-2) X(-1) X X(1) X(2) X(3)
GDP 1.72 .38 .63 .85 1 .85 .63 .38
C 1.27 .57 .72 .82 .83 .67 .46 .22
I 8.24 .38 .59 .79 .91 .76 .50 .22
G 2.04 -.03 -.01 -.01 .04 .08 .11 .16
Exp 5.53 -.29 -.10 .15 .37 .50 .54 .54
Imp 4.88 .31 .45 .62 .72 .71 .52 .28
Data Source NIPA. All data are deflated and HP filtered Data Source NIPA. All data are deflated and HP filtered Data Source NIPA. All data are deflated and HP filtered Data Source NIPA. All data are deflated and HP filtered Data Source NIPA. All data are deflated and HP filtered Data Source NIPA. All data are deflated and HP filtered Data Source NIPA. All data are deflated and HP filtered Data Source NIPA. All data are deflated and HP filtered Data Source NIPA. All data are deflated and HP filtered
15
Table 1 Cyclical Behavior of U.S. Labor Market Aggregates, 1954I-1991II Table 1 Cyclical Behavior of U.S. Labor Market Aggregates, 1954I-1991II Table 1 Cyclical Behavior of U.S. Labor Market Aggregates, 1954I-1991II Table 1 Cyclical Behavior of U.S. Labor Market Aggregates, 1954I-1991II Table 1 Cyclical Behavior of U.S. Labor Market Aggregates, 1954I-1991II Table 1 Cyclical Behavior of U.S. Labor Market Aggregates, 1954I-1991II Table 1 Cyclical Behavior of U.S. Labor Market Aggregates, 1954I-1991II Table 1 Cyclical Behavior of U.S. Labor Market Aggregates, 1954I-1991II Table 1 Cyclical Behavior of U.S. Labor Market Aggregates, 1954I-1991II Table 1 Cyclical Behavior of U.S. Labor Market Aggregates, 1954I-1991II Table 1 Cyclical Behavior of U.S. Labor Market Aggregates, 1954I-1991II Table 1 Cyclical Behavior of U.S. Labor Market Aggregates, 1954I-1991II Table 1 Cyclical Behavior of U.S. Labor Market Aggregates, 1954I-1991II
Cross-Correlation of Real GDP with Cross-Correlation of Real GDP with Cross-Correlation of Real GDP with Cross-Correlation of Real GDP with Cross-Correlation of Real GDP with Cross-Correlation of Real GDP with Cross-Correlation of Real GDP with Cross-Correlation of Real GDP with Cross-Correlation of Real GDP with Cross-Correlation of Real GDP with Cross-Correlation of Real GDP with Cross-Correlation of Real GDP with
Variable Volatility (SD) X(-5) X(-4) X(-3) X(-2) X(-1) X X(1) X(2) X(3) X(4) X(5)
Real Gross Domestic Product 1.72 -.02 .16 .38 .63 .85 .85 .63 .38 .16 -.02
Hours (Household Survey) 1.49 -.10 .05 .25 .46 .70 .86 .85 .74 .58 .38 .17
Employment 1.09 -.17 -.03 .16 .38 .63 .83 .88 .80 .65 .46 .25
Hours per Worker 0.54 .07 .20 .36 .49 .64 .70 .58 .42 .28 .12 -.02
GDP/Hours 0.87 .12 .23 .33 .47 .50 .51 .22 -.01 -.24 -.32 -.34
Average Hourly Real Compensation (Business Sector) 0.93 .35 .39 .41 .43 .41 .35 .25 .16 .05 -0.7 -.18
Real Employee Compensation (NIPA)/Hours (Household Survey) 0.65 -.11 -.11 -.13 .06 .02 .10 .13 .14 .10 .08 .04
Cross-Correlation of Cross-Correlation of Cross-Correlation of Cross-Correlation of Cross-Correlation of Cross-Correlation of Cross-Correlation of Cross-Correlation of Cross-Correlation of Cross-Correlation of Cross-Correlation of Cross-Correlation of
Employment and Average Labor Productivity (X) 1.09 .73 .68 .57 .35 .09 -.15 -.32
Vacancies and Unemployment (X) 12.54 -.36 -.61 -.82 -.95 -.93 -.77 -.54
GNP and Labor Share (X) 1.07 -.61 -.73 -.78 -.74 -.48 -.22 -.00
Source Finn E. Kydland (1995), () Source M. Merz (1995) using CITIBASE data for the period 1959I-1988II, () Average Labor Productivity is defined as Real GNP over Employment Source Finn E. Kydland (1995), () Source M. Merz (1995) using CITIBASE data for the period 1959I-1988II, () Average Labor Productivity is defined as Real GNP over Employment Source Finn E. Kydland (1995), () Source M. Merz (1995) using CITIBASE data for the period 1959I-1988II, () Average Labor Productivity is defined as Real GNP over Employment Source Finn E. Kydland (1995), () Source M. Merz (1995) using CITIBASE data for the period 1959I-1988II, () Average Labor Productivity is defined as Real GNP over Employment Source Finn E. Kydland (1995), () Source M. Merz (1995) using CITIBASE data for the period 1959I-1988II, () Average Labor Productivity is defined as Real GNP over Employment Source Finn E. Kydland (1995), () Source M. Merz (1995) using CITIBASE data for the period 1959I-1988II, () Average Labor Productivity is defined as Real GNP over Employment Source Finn E. Kydland (1995), () Source M. Merz (1995) using CITIBASE data for the period 1959I-1988II, () Average Labor Productivity is defined as Real GNP over Employment Source Finn E. Kydland (1995), () Source M. Merz (1995) using CITIBASE data for the period 1959I-1988II, () Average Labor Productivity is defined as Real GNP over Employment Source Finn E. Kydland (1995), () Source M. Merz (1995) using CITIBASE data for the period 1959I-1988II, () Average Labor Productivity is defined as Real GNP over Employment Source Finn E. Kydland (1995), () Source M. Merz (1995) using CITIBASE data for the period 1959I-1988II, () Average Labor Productivity is defined as Real GNP over Employment Source Finn E. Kydland (1995), () Source M. Merz (1995) using CITIBASE data for the period 1959I-1988II, () Average Labor Productivity is defined as Real GNP over Employment Source Finn E. Kydland (1995), () Source M. Merz (1995) using CITIBASE data for the period 1959I-1988II, () Average Labor Productivity is defined as Real GNP over Employment Source Finn E. Kydland (1995), () Source M. Merz (1995) using CITIBASE data for the period 1959I-1988II, () Average Labor Productivity is defined as Real GNP over Employment
16
The Stylized Facts about the Business Cycle
- Output
- fluctuations in GDP are persistent
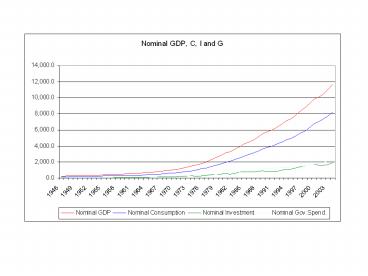
- Expenditure
- consumption is procyclical and less volatile than
GDP - investment is procyclical and 5 times as volatile
as GDP - government expenditures are acyclical
- Productivity
- the average output per hour of work is somewhat
procyclical and leads the cycle
17
The Stylized Facts about the Business Cycle
- Labor Markets
- employment volatility accounts for 2/3 of the
volatility of total hours - hours-per-worker volatility accounts for 1/3 of
the volatility of total hours - employment is procyclical lags the cycle
- hors-per-worker are procyclical and lead the
cycle - total hours are procyclical and almost as
volatile as GDP
18
References
- Chapters 2 and 3 in Williamson
- Check-out the website of the National Bureau of
Economic Research http//www.nber.org - Check-out the book "Frontier of Business Cycle
Research," ed. T. Cooley, 1995, Princeton
University Press