Lung Volume Reduction Surgery - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 15
Title:
Lung Volume Reduction Surgery
Description:
Paradoxically can improve FEV1 and exercise function by ... Approx 1-3% % of malignant tumors of lung. Central- smooth cherry red tumor. Peripheral nodule ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:420
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Lung Volume Reduction Surgery
1
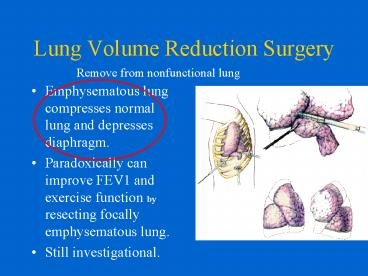
Lung Volume Reduction Surgery
Remove from nonfunctional lung
- Emphysematous lung compresses normal lung and
depresses diaphragm. - Paradoxically can improve FEV1 and exercise
function by resecting focally emphysematous lung. - Still investigational.
2
Lung Transplantation
Better prognosis, better candidate
Next in line
Not for CA
- Last resort for lung disease otherwise
untreatable with death immanent. - Selection
- disease, age, co-morbidity
- Surgical techniques
- lobe, one or both lungs
- Immunosuppression
- BOOP
3
Carcinoid Tumor
Submucosal tumor different from GI carcinoids
(causes carcinoid syndrome)
- Approx 1-3 of malignant tumors of lung.
- Central- smooth cherry red tumor.
- Peripheral nodule
- Airway obstruction and atelectasis
- Typical vs. atypical
4
Olser-Weber-RenduHemorrhagic Telangiectasia
Syndrome
In lung, skin, brain
- Familial
- Nosebleeds
- Lip and tongue telangiectasia on exam
- Cyanosis
- Cerebral abscess
- Peripheral pulmonary nodules
- Rx occlude feeding vessels by angio or surgery
- Rare type of A-V malformation arising from a
central PA
5
Invasive Aspergillosis
Necrosis of lung
- Immunosuppressed pt. With prolonged neutropenia
- Fever
- Chest pain
- Hemoptysis
- Pathognomonic radiographic features
- Amphotericin /- pulmonary resection may be
curative
Big cavity in lungs was thought to be TB
6
Esophageal Perforation
Know this for test
- Cervical or thoracic
- Spontaneous- Boorhave syndrome
- Iatrogenic- esophageal dilatation, intubation
- Chest pain, fever
- LgtR pleural effusion with low pH
- Dx by esophagram
- Survival will depend upon surgical repair or
drainage within 6-24 hours. - Very limited role for non-surgical management.
7
Clubbing and Osteoarthropathy
Pulmonary clubbing also seen in cyanotic heart Dz
- Clubbing may occur with chronic cyanosis ,
inflammatory disease or tumor. - Hypertrophic pulmonary osteoarthropathy (HPO)
occurs only with tumor. - Lung CA, fibrous tumor of pleural
Clubbing with arthralgias
8
Clubbing and HPO
- Pain in knees ankles and tibia gt wrists and
elbows. - Pain disappears almost immediately following
resection of tumor. - Clubbing resolves more slowly
- Recurrence of either clubbing or HPO means that
there is recurrence of tumor.
9
Pneumothorax
Increased percussion note
- Very common.
- Spontaneous- young tall people.
- Apical blebs
- Chest tube drainage.
- Bleb resection and pleurodesis if recurrent.
- Secondary- older patients with COPD
- Much higher MM
- Tension- lethal
May cause recurrence
More difficult w/ underlying lung Dz.
10
Pneumothorax
Lung mets that is cystic
- Rarely pneumothorax is caused by necrotic or
cystic tumors, typically sarcomas. - In this case the pneumothorax was caused by lung
metastasis from an angiosarcoma of the scalp.
11
Tracheal Neoplasms
Types that block the airway in bronchi, add
carcinoid
- Mucoepidermoid tumor
- Adenocystic carcinoma
- Squamous carcinoma
In anterior wall of trachea
May present with wheezing DDX for asthma
12
Laser Ablation
- YAG laser ablation of endobronchial tumor offers
effective palliation in Lung CA patients with
dyspnea. - Mean 3 mo.
- EndobrachyRT increases palliation to mean 6 mo.
13
Cardiac Herniation
- If a defect is left in the pericardium more than
approximately 3-4 cm in diameter, herniation of
the heart may occur. - Larger defects should be repaired with 2mm PFTE
- Sudden profound shock following right
pneumonectomy
14
Continuing Medical Education
- The questions that will be asked on your exam
will be the same questions that will be asked
twenty years from now. - BUT
- The answers will change.
- The bad news is that you will have to form a
life-long practice of continuous self-education. - The good news is that you will still be learning
new and exciting information twenty years from
now.
15
Thoracic Surgery An evolving practice
- Technological change occurs with blinding
rapidity. - The information and technical skills that allow
one to successfully practice medicine WILL change.
- Success in practice will depend upon careful
evaluation of new technology with retraining as
indicated.