Non linear elasticity - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 53
Title: Non linear elasticity
1
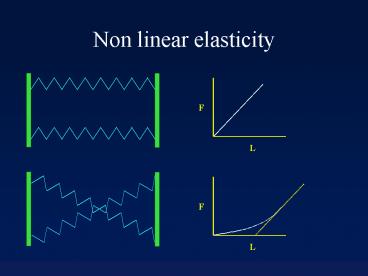
Non linear elasticity
F
L
F
L
2
Balloon in a string bag model of arterial
elasticity
3
Effect of protein digestion on elasticity
Einc Nm-2 x 105
Elastase
Intact vessel
Collagenase
2.6
2.2
1.8
1.4
1.0
R/Ro
4
Problem
5
Plink!
Plink!
6
Possible Solutions
F
L
From Brown R.E. et al., (1994) Conn Tiss Res 30
295-308
7
Possible Solutions
8
Possible Solutions
- Stiffness is a combination of
- Force/length relation of elastin fibres
- Resistance of ground substance to shear
- Force/length relation of collagen fibres
Adapted from Brown R.E. et al., (1994) Conn Tiss
Res 30 295-308
9
Gradual recruitment of collagen fibres
With thanks to Dr. Martin Zulliger, Laboratoire
de Genie Médicale, Ecole Polytechnique Fédéral de
Lausanne
10
Connection between VSMC and collagen
Muscle cell
Collagen fibres
11
Connection between elastic lamellae and VSMC
12
(No Transcript)
13
At low strains f is zero
Therefore a plot of Eobs against we should give a
straight line of gradient Ee and zero intercept
y m x c
14
At high strains f is 1
Dividing by wc gives
Therefore a plot of Eobs/wc against we/wc
should Give a straight line of gradient Ee and
intercept Ec
y m x c
15
Relationship between caudal artery systolic
pressure and age
104
16
(No Transcript)
17
Aortic elastin content and age
Normal
Hypertensive
Ex hypertensive
Thoracic
Abdominal
18
Aortic collagen content and age
Normal
Hypertensive
Ex hypertensive
Thoracic
Abdominal
19
Relationship between Einc measured at low strain
and the weight fraction of elastin
y 5.944x 0.567 r 0.779
Einc Nm-2 x 105
We (elastin/wet weight)
20
Relationship between Einc measured at high strain
and the ratio of elastin to collagen
y 0.441x 0.247 r 0.805
2.0
1.5
1.0
Einc/Wc Nm-2 x 108
0.5
0.0
0.0
1.0
2.0
3.0
We/Wc
21
Two linear components in parallel
At low stretch
At high stretch
At intermediate stretches
22
Elastic face
Ehlers Danlos syndrome
23
Limitations
- No account of VSMC
- Fibre angle
- Nature of connection between various components
- Residual strains
24
Models which take into account a range of
collagen fibre lengths and consider fibre angle
- G. A. Holzapfel and T. C. Gasser, Journal of
Elasticity 61, 1 (2000). - Characteristic fibre angle.
- M. A. Zulliger et al., J Biomech 37, 989 (2004).
- Characteristic fibre angle
- Elastin and collagen ratio
- Assumes no radial gradient in composition and
structure - N. J. Driessen et al., J Theor Biol 226, 53
(2004). - Assumes collagen fibre alignment between
principal stretch directions - Two layer structure with differing characteristic
angles - No account of other components
- T.C. Gasser, R.W. and G.A. Holzapfel. Journal of
the Royal Society, Interface. 3,15-35 (2006). - 4 families of fibre angles (adventitial, 2 and
medial, 2) - No account yet of RS OR VSMC activity
25
Need for quantitative data on fibre orientation
26
Non linear microscopy
- Two photon excited fluorescence
- Autofluorescence of elastin collagen
- Second harmonic generation
- Autofluorescence of collagen
Both techniques are confocal
27
Combining SHG and TPF images
SHG (Collagen)
TPEF (Elastin ?)
28
Rat aorta adventitia inwards
Rat aorta
29
Assessment of changes in fibre angleThe mandrel
stretching experiment
1mm
0.55 mm
Fresh rat carotid artery
30
Rat carotidcircumferential stretch
60
40
20
0
31
Quantification in progressBut, in the carotid
artery and aorta of the cow and pig (at least),
there is a sudden transition in fibre orientation
at about 30µm from the IEL
32
Bovine aorta
Transverse
Axial
VSMC
Elastin
Collagen
33
Mapping fibre angle
34
Mapping fibre angle
35
Mapping fibre angle
? circumferential direction ?
36
The case of the three layered media
37
The media of the pig carotid artery appears to
consist of two distinct layers.
three
- Histology
- Comparison of vessels with 1 and 2 layer
media - Quasi static stress strain behavior
- Opening angle as a measure of residual strain
- Inflation tests at various axial loads
- Entire media
- Inner layer
- Outer layer
38
Rat aorta (a typical elastic artery)
39
Pig carotid (an atypical elastic artery)
Transverse section (elastic stain)
40
Longitudinal section
Elastin
41
Tangential section
42
Pig carotid tangential sections
43
TEM
44
Pig carotid
45
Pig aorta
46
Pig carotid
47
Sheep
Cow
Horse
48
Transverse section of rabbit aorta
With thanks to T. Matsumoto
49
- Initially we found the two layered media only in
animals weighing more that 75 kg - But not all animals gt 75kg
- We believed that 2nd layer depended on size
- There is currently one exception so far
(excluding young animals) - Pigmy goat (25kg)
- Question
- Is there anything that links the animals that
have the second layer?
50
Kangaroos, possums, wombats (Marsupials)
Armadillos, sloths, anteaters
Shrews, moles, hedgehogs
Bats
Tree shrews
51
(No Transcript)
52
Thickness of the two medial layers
53
The outer layer is relatively thicker in thinner
vessels
40
2
R
0.91
35
P lt 0.01
Data from 6 animals
30
outer/total
25
20
15
200
400
600
800
Total medial thickness micron
54
Outer layer has constant thickness in the pig
55
Phenotype of the VSMC
Inner layer Contractile
Outer layer not fibroblast
Pig left Iliac
Pig left Carotid
With thanks to Sheena Bhadye
56
Smooth Muscle Actin
Desmin
With thanks to Chris Evagora Luke Timmins
57
2 Layer summary
- Carotid artery in rat, pig and cow has an inner
axially orientated layer ? 30µm thick - Carotid artery in large mammals has 2 more medial
layers. - Size alone or animal order?
- Ungulates
- Cetartiodactyla (even toed ungulates)
- Pigs, sheep, cows, camels, whales
- Perissodactyla (odd toed ungulates)
- Horses, rhinos, tapirs
- Small ungulates peccary?
- Other mammalian orders
- Primates, Afrotheria, Carnivora, Bats, etc. etc.?
- In the pig, the thickness of the outer layer is
independent of the total medial thickness - Static elastic properties of two layers differ
- Inner more compliant than entire media more than
outer - Preliminary results only
58
Human common carotid
Newborn
Dragendorff, O., Gefaesse des Stammes und der
Gliedmassen, in Handbuch der Anatomie des
Kindes, K. Peter, G. Wetzel and F. Heiderich,
Eds. 1931, Verlag von JF Bergmann Munich. p.
361-363.
28 years
59
Future work
- Detailed measurement of elastic properties in the
circumferential and axial direction. - Extended models of multilayer elasticity.
- Separate elastic properties for each layer.
- Characterisation of VSMC phenotype
- Synthetic organelles
- Ca, K channels
- Further animal studies
- Small ungulates
- Big carnivores
60
Overall summary
- Carotid artery in rat, pig and cow has an inner
axially orientated layer ? 30µm thick - Carotid artery in large mammals has 2 more medial
layers. - Size alone or animal order?
- Ungulates
- Artodactyla (even toed ungulates)
- Pigs, sheep, cows, camels, whales??
- Perissodactyla (odd toed ungulates)
- Horses, rhinos, tapirs
- Big carnivora?
- Small ungulates peccary?
- Primates?
- In the pig, the thickness of the outer layer is
independent of the total medial thickness - Static elastic properties of two layers differ
- Inner more compliant than entire media more than
outer - Preliminary results only