16.360 Lecture 13 - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
16.360 Lecture 13
Description:
In Cartesian coordinate, vector A is directed from origin to point ... 4. Scalar and vector triple product. a) scalar triple product. b) vector triple product ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:23
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: 16.360 Lecture 13
1
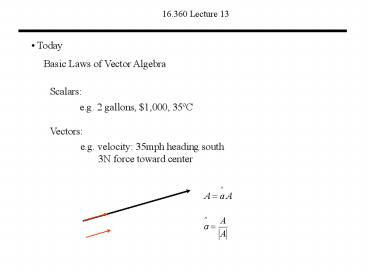
16.360 Lecture 13
- Today
Basic Laws of Vector Algebra
Scalars
e.g. 2 gallons, 1,000, 35ºC
Vectors
e.g. velocity 35mph heading south 3N
force toward center
2
16.360 Lecture 13
- Cartesian coordinate system
z
A
?
y
?
x
3
16.360 Lecture 13
- Vector addition and subtraction
C BA A B,
A
C
C
parallelogram rule
A
head-to-tail rule
C BA A B,
B
B
D A - B -(B A),
A
A
D
D (B-A)
B
B
4
16.360 Lecture 13
- position and distance
z
A
B
y
D A - B -(B A),
x
5
16.360 Lecture 13
- Vector multiplication
1. simple product
2. scalar product (dot product)
6
16.360 Lecture 13
Properties of scalar product (dot product)
a) commutative property
b) Distributitve property
7
16.360 Lecture 13
3. vector product (cross product)
a) anticommutative property
b) Distributitve property
c)
8
16.360 Lecture 13
3. vector product (cross product)
9
16.360 Lecture 13
Example vectors and angles
- In Cartesian coordinate, vector A is directed
from origin to point P1(2,3,3), and vector B is
directed from P1 to pint P2(1,-2,2). Find - (a) Vector A, its magnitude A, and unit vector
a - (b) the angle that A makes with the y-axis
- (c) Vector B
- (d) the angle between A and B
- (e) perpendicular distance from origin to vector
B
10
16.360 Lecture 13
4. Scalar and vector triple product
a) scalar triple product
b) vector triple product
11
16.360 Lecture 13
Example vector triple product
12
(No Transcript)