Comparative Annotation of Viral Genomes with Non-Conserved Gene Structure - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 1
Title:
Comparative Annotation of Viral Genomes with Non-Conserved Gene Structure
Description:
Saskia de Groot and Jotun Hein. Department of Statistics, University of Oxford. Motivation. Viral genome annotation is a complex task: Overlapping and nested ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:35
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Comparative Annotation of Viral Genomes with Non-Conserved Gene Structure
1
Comparative Annotation of Viral Genomes with
Non-Conserved Gene Structure
Saskia de Groot and Jotun Hein Department of
Statistics, University of Oxford
- Motivation
- Viral genome annotation is a complex task
- Overlapping and nested reading frames
- Atypical sequence evolution
- Non-conserved gene structure
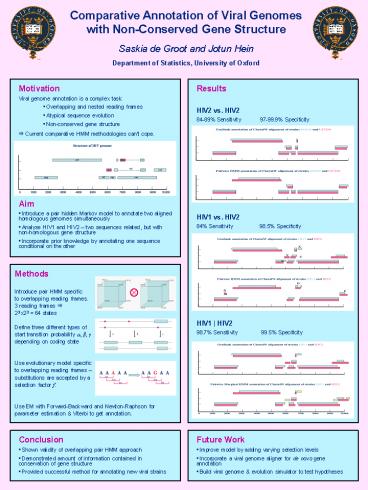
Results HIV2 vs. HIV2 84-89 Sensitivity
97-99.9 Specificity HIV1 vs.
HIV2 84 Sensitivity 98.5
Specificity HIV1 HIV2 98.7
Sensitivity 99.5 Specificity
? Current comparative HMM methodologies cant
cope.
- Aim
- Introduce a pair hidden Markov model to annotate
two aligned homologous genomes simultaneously - Analyse HIV1 and HIV2 two sequences related,
but with non-homologous gene structure - Incorporate prior knowledge by annotating one
sequence conditional on the other
Methods Introduce pair HMM specific to
overlapping reading frames. 3 reading frames
? 23 x23 64 states Define three different
types of start transition probability a, ß,
? depending on coding state Use evolutionary
model specific to overlapping reading frames
substitutions are accepted by a selection
factor f. Use EM with Forward-Backward and
Newton-Raphson for parameter estimation
Viterbi to get annotation.
- Conclusion
- Shown validity of overlapping pair HMM approach
- Demonstrated amount of information contained in
conservation of gene structure - Provided successful method for annotating new
viral strains
- Future Work
- Improve model by adding varying selection levels
- Incorporate a viral genome aligner for de novo
gene annotation - Build viral genome evolution simulator to test
hypotheses